When Do Seasons Start and End?
When does spring start or fall end? It depends on which definition you use. We explain the two most common ones: astronomical and meteorological.

Fiery fall colors in Vermont, United States.
©iStock.com/DenisTangneyJr
Seasons in Your City
Use our Seasons Calculator to see exact times and dates for spring, summer, fall, and winter in your city.
Thanksgiving: Harvest celebrations around the world
The Four Seasons
The year is commonly divided into four seasons: spring, summer, fall (or autumn), and winter. Because we divide a year into 12 months, each season lasts about three months.
However, the dates when the seasons begin and end vary depending on whom you ask. Two methods are most commonly used to define the dates of the seasons: the astronomical definition and the meteorological definition.
1. Astronomical Seasons
The astronomical definition uses the dates of equinoxes and solstices to mark the beginning and end of the seasons:
- Spring begins on the spring equinox;
- summer begins on the summer solstice;
- fall (autumn) begins on the fall equinox; and
- winter begins on the winter solstice.
The beginning of each season marks the end of the last.
Because the timings of the equinoxes and solstices change each year, the length of astronomical seasons within a year and between years also vary.
What are equinoxes and solstices?
2. Meteorological Seasons
According to the meteorological definition, the seasons begin on the first day of the months that include the equinoxes and solstices. In the Northern Hemisphere, for example,
- spring runs from March 1 to May 31;
- summer runs from June 1 to August 31;
- fall (autumn) runs from September 1 to November 30; and
- winter runs from December 1 to February 28 (February 29 in a leap year).
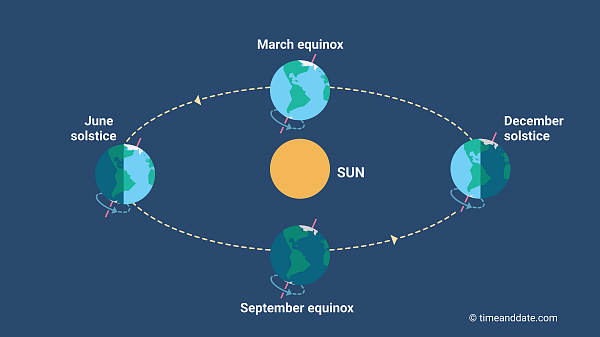
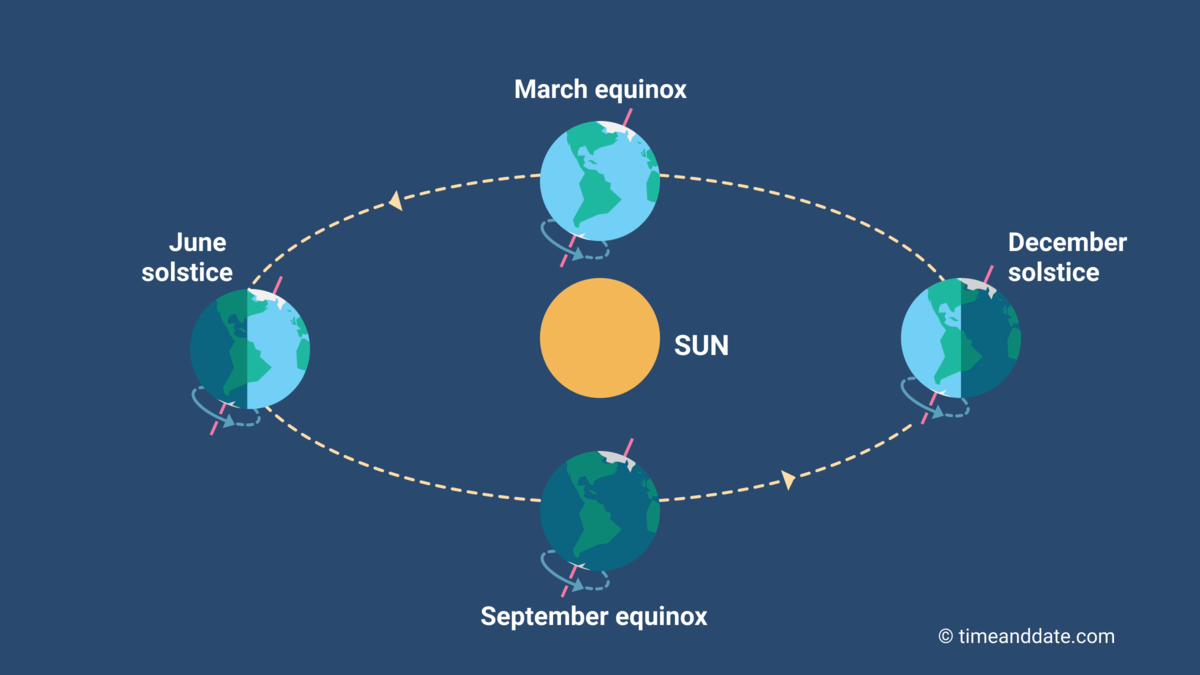
In June, the Northern Hemisphere gets more sunlight, kicking off the summer season. The Southern Hemisphere tilts away from the Sun, and winter starts. The opposite happens in December.
©timeanddate.com
Opposite Hemispheres, Opposite Seasons
Seasons in the Southern Hemisphere are opposite to those in the Northern Hemisphere. For example, under the definition of astronomical seasons, the June solstice marks the start of summer in the Northern Hemisphere, but it is the start of winter in the Southern Hemisphere.
The same rule applies for the other seasons. South of the equator, spring starts with the September equinox, summer with the December solstice, and autumn with the March equinox.
The meteorological seasons in the Southern Hemisphere are also opposite to those in the Northern Hemisphere:
- Spring starts September 1 and ends November 30;
- summer starts December 1 and ends February 28 (February 29 in a Leap Year);
- fall (autumn) starts March 1 and ends May 31; and
- winter starts June 1 and ends August 31.
Some Countries Follow Their Own Traditions
The question of which definition to use divides countries and regions around the world. Many countries use both definitions, depending on the context.
However, there are also countries that use their own unique system to determine the beginning of the seasons:
- In Ireland, St Brigid’s Day on February 1 is often thought to mark the beginning of spring in the ancient Celtic calendar system.
- Some cultures, especially those in South Asia, have calendars that divide the year into six seasons, instead of the four that most people in the western part of the world are familiar with.
- In Finland and Sweden, the dates of the seasons are not based on the calendar at all, but on temperatures. This means the seasons within each county start and end on different dates, depending on the regions and their climate.
- In Iceland, the first day of summer, a national holiday, falls on the first Thursday after April 18.
Areas closer to the equator don’t experience the same seasonal patterns as higher latitudes. Here, seasons are often defined by recurring weather patterns. For example, in the north of Australia, the year is divided into the wet season (November–April) and the dry season (May–October).
