Article
Acid Rain
Acid rain is the wet or dry deposition of acidic substances and their precursors on the Earth's surface. The ongoing industrialization of society has resulted in the increased release of acidic chemicals into the atmosphere.


Enter your search term
Signing up enhances your TCE experience with the ability to save items to your personal reading list, and access the interactive map.
Create AccountArticle
Acid rain is the wet or dry deposition of acidic substances and their precursors on the Earth's surface. The ongoing industrialization of society has resulted in the increased release of acidic chemicals into the atmosphere.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/e65c5497-0412-4440-b734-58a2c72d429e.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/e65c5497-0412-4440-b734-58a2c72d429e.jpg

Article
For example, in British Columbia, the Coastal Western Hemlock Zone is one of 14 biogeoclimatic zones. It occupies high precipitation areas up to 1000 m elevation west of the coastal mountains from the Washington to Alaska borders and beyond.
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Article
In Canada the official national meteorological service definition of a blizzard is a period of 6 or more hours with winds above 40 km/h, with visibility reduced to below 1 km by blowing or drifting snow, and with windchills over 1600 W/ m2 (watts per square metre).
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/5495ea9b-3457-434f-85cd-cec24b373bd3.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/5495ea9b-3457-434f-85cd-cec24b373bd3.jpg

Macleans
This article was originally published in Maclean’s magazine on March 18, 2002. Partner content is not updated.
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Article
Chinooks are warm, dry, gusty, westerly winds that blow down from the Rocky Mountains into the mountains' eastern slopes and the western prairies. The Chinook belongs to a family of winds experienced in many parts of the world where long mountain chains lie more or less at right angles to the prevailing wind. Examples include the Foehn in Europe, the Zonda in Argentina and the Berg in South Africa. In Canada, the Chinook belt lies almost exclusively within southern and central Alberta.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/ecf3dcdb-d1d5-49d1-a385-264f348ad3b2.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/ecf3dcdb-d1d5-49d1-a385-264f348ad3b2.jpg

Article
Climate is often defined as average weather, when weather means the current state of the atmosphere. For scientists, climates are the result of exchanges of heat and moisture at the Earth's surface. Because of its size, Canada has many different climates.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/564ff157-335a-409a-81af-13f050b3079a.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/564ff157-335a-409a-81af-13f050b3079a.jpg

Article
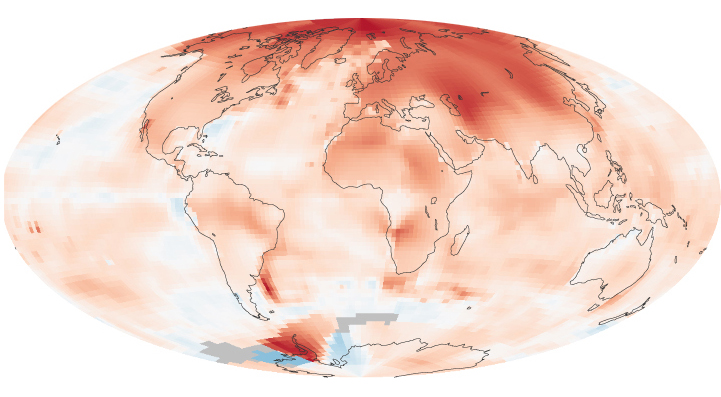
Climate change occurs when long-term weather patterns begin to shift. These periods of change have occurred throughout the Earth’s history over extended periods of time. However, since the Industrial Revolution the world has been warming at an unprecedented rate. Because of this, the current period of climate change is often referred to as “global warming.” Human activities that release heat-trapping greenhouse gases, such as the burning of fossil fuels, are largely responsible for this increased rate of change. The implications of this global increase in temperature are potentially disastrous and include extreme weather events, rising sea levels and loss of habitat for plants, animals and humans. In Canada, efforts to mitigate climate change include phasing-out coal-fired power plants in Ontario and instituting a carbon tax in British Columbia. (This is the full-length entry about climate change. For a plain-language summary, please see Climate Change (Plain-Language Summary).)
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/5ff84049-689a-43d8-8625-462b97b5a67f.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/5ff84049-689a-43d8-8625-462b97b5a67f.jpg
Macleans
To the uninitiated, it looks no more exciting than a long, thin log of grey plasticene. But to scientists like Jeffrey Fox, a Texas geologist who oversaw its extraction last week from the bottom of a deep bay 16 km north of Victoria, the 9.This article was originally published in Maclean's Magazine on September 2, 1996
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Article
Environment Canada devised the climate severity index to rate a locality's climate according to human comfort and well being. The index has a range from 1 to 100, with a score of 1 representing the least severe climate and 100 the most.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/ccf0af1a-002e-4354-a12c-75c5dd40fc2e.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/ccf0af1a-002e-4354-a12c-75c5dd40fc2e.jpg

Article
Cloud, visible suspension in the atmosphere composed of tiny water droplets or ICE crystals from about one to a few hundred micrometres in diameter.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/Twitter_Cards/cloud.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/Twitter_Cards/cloud.jpg

Article
During the prolonged darkness of winter, the air over the huge snow- and ice-covered surfaces of Canada may stagnate for weeks, radiating heat to outer space.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/4746fd27-236c-4c5b-a1e2-a5d87eba78b2.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/4746fd27-236c-4c5b-a1e2-a5d87eba78b2.jpg

Article
Drought is the condition of critically low water supply caused by persistently below-normal precipitation.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/ea2328a1-2ce9-4f2e-be69-d92cbfb2ae7a.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/ea2328a1-2ce9-4f2e-be69-d92cbfb2ae7a.jpg

Editorial
The following article is an editorial written by The Canadian Encyclopedia staff. Editorials are not usually updated.
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Article
El Niño is a pronounced warming of the Pacific Ocean current off the coast of South America.
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Editorial
The following article is an editorial written by The Canadian Encyclopedia staff. Editorials are not usually updated.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/d81f3a59-7d06-4216-b784-966dbba49c9a.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/d81f3a59-7d06-4216-b784-966dbba49c9a.jpg
