Recession indicators worldwide - statistics & facts
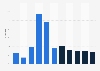
A prime example occurred in 2022, when recession concerns peaked as the global economy had not fully recovered from the COVID-19 pandemic when the Russia-Ukraine conflict began to impact economic growth. During this period, rising global inflation and widespread market uncertainty led to recession fears that exceeded those seen at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic. The level of uncertainty about global economic activity is often reflected in such widespread concerns about recession risks among businesses, consumers, and financial markets.
Key indicators of recession
It has become commonly accepted that a recession occurs in times of continuous negative real GDP growth. However, there are a variety of criteria that should be observed along with the GDP. Recessions are usually accompanied by higher unemployment rates: In the United States (U.S.), for instance, the unemployment rate almost doubled between 2008 and 2010 as the global financial crisis hit the economy. The pandemic brought another rise in the unemployment rates in most developed countries, despite employment figures starting to stabilize towards the end of 2020. Another commonly used indicator is the decline in industrial production, which could be seen globally between June 2021 and May 2022. Lastly, trends on the financial markets provide a more trackable indicator of a recession.Signals on the financial markets
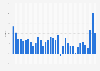
Recession warning lights often appear in the financial markets first, as they reflect investors’ confidence in the development of the economy. One of the most reliable indicators of an impending recession is the inverted U.S. Treasury yield curve, which means that bonds of longer maturities provide a lower yield than bonds with short maturities. This indicates a high level of uncertainty and mistrust around the condition of financial markets in the future. Trends in major stock indices, such as the Dow Jones Industrial Average and the S&P 500, can also signal economic concerns. Significant stock market declines often indicate that investors are uncertain about the health of the economy, and when combined with other indicators, may suggest increased recession risks.While no single indicator can definitively predict a recession, monitoring multiple economic signals provides valuable insights into potential economic downturns. Understanding these warning signs enables stakeholders to better prepare for and navigate through periods of economic uncertainty.