Heat-killed Lactobacillus plantarum L-137 attenuates obesity and associated metabolic abnormalities in C57BL/6 J mice on a high-fat diet
- PMID: 33996364
- PMCID: PMC8099634
- DOI: 10.12938/bmfh.2020-040
Heat-killed Lactobacillus plantarum L-137 attenuates obesity and associated metabolic abnormalities in C57BL/6 J mice on a high-fat diet
Abstract
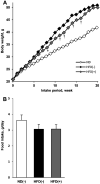
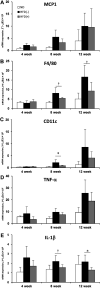
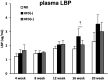
Heat-killed Lactobacillus plantarum L-137 (HK L-137) has anti-allergic, antitumor, and antiviral effects in mice, as well as an anti-inflammatory effect in rats with metabolic syndrome through regulation of immunity. To evaluate the influence of HK L-137 on chronic inflammation in mice with diet-induced obesity, C57BL/6 J mice were fed a normal diet (16% of energy as fat) or a high-fat diet (62% of energy as fat) with or without 0.002% HK L-137 for 4 to 20 weeks. It was found that HK L-137 supplementation alleviated weight gain and elevation of plasma glucose, cholesterol, alanine aminotransferase, and aspartate transaminase levels in mice with diet-induced obesity. Expression of several inflammation-related genes, including F4/80, CD11c, and IL-1β, in the epididymal adipose tissue of these mice was significantly downregulated by HK L-137. In addition, plasma levels of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein, a marker of endotoxemia, tended to be decreased by administration of HK L-137. These findings suggest that HK L-137 supplementation ameliorates obesity-induced metabolic abnormalities and adipose tissue inflammation, possibly through improvement of intestinal permeability.
Keywords: Lactobacillus; adipose tissue; cholesterol; inflammation; macrophage; obesity.
©2021 BMFH Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of heat-killed Lactobacillus plantarum L-137 on cardiac and adipose tissue in rats with metabolic syndrome.Sci Rep. 2018 May 25;8(1):8156. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26588-x. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29802339 Free PMC article.
-
Lactobacillus plantarum LC27 and Bifidobacterium longum LC67 simultaneously alleviate high-fat diet-induced colitis, endotoxemia, liver steatosis, and obesity in mice.Nutr Res. 2019 Jul;67:78-89. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2019.03.008. Epub 2019 Mar 20. Nutr Res. 2019. PMID: 30982555
-
Administration of Lactobacillus gasseri SBT2055 suppresses macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue in diet-induced obese mice.Br J Nutr. 2015 Oct 28;114(8):1180-7. doi: 10.1017/S0007114515002627. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Br J Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26299683
-
Lactobacillus plantarum OLL2712 regulates glucose metabolism in C57BL/6 mice fed a high-fat diet.J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2013;59(2):144-7. doi: 10.3177/jnsv.59.144. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2013. PMID: 23727645
-
Gallotannins and Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1 Mitigate High-Fat Diet-Induced Inflammation and Induce Biomarkers for Thermogenesis in Adipose Tissue in Gnotobiotic Mice.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2019 May;63(9):e1800937. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201800937. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2019. PMID: 30908878
Cited by
-
Changes in Digestive Health, Satiety and Overall Well-Being after 14 Days of a Multi-Functional GI Primer Supplement.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 19;16(18):3173. doi: 10.3390/nu16183173. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39339773 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Heat-killed Bifidobacterium longum BBMN68 and inulin protect against high-fat diet-induced obesity by modulating gut microbiota.Front Nutr. 2024 Aug 14;11:1406070. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1406070. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39206310 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Menopausal Effect of Heat-Killed Bifidobacterium breve HDB7040 via Estrogen Receptor-Selective Modulation in MCF-7 Cells and Ovariectomized Rats.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 28;34(8):1580-1591. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2402.02035. Epub 2024 Jun 17. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39081245 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial effect of heat-killed Lactiplantibacillus plantarum L-137 on intestinal barrier function of rat small intestinal epithelial cells.Sci Rep. 2024 May 29;14(1):12319. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62657-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38811623 Free PMC article.
-
Postbiotics as Metabolites and Their Biotherapeutic Potential.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 16;25(10):5441. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105441. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791478 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kanneganti TD, Dixit VD. 2012. Immunological complications of obesity. Nat Immunol 13: 707–712. - PubMed
-
- Kitade H, Sawamoto K, Nagashimada M, Inoue H, Yamamoto Y, Sai Y, Takamura T, Yamamoto H, Miyamoto K, Ginsberg HN, Mukaida N, Kaneko S, Ota T. 2012. CCR5 plays a critical role in obesity-induced adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance by regulating both macrophage recruitment and M1/M2 status. Diabetes 61: 1680–1690. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

