Identification of novel functional inhibitors of acid sphingomyelinase
- PMID: 21909365
- PMCID: PMC3166082
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023852
Identification of novel functional inhibitors of acid sphingomyelinase
Abstract
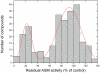
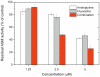
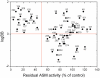
We describe a hitherto unknown feature for 27 small drug-like molecules, namely functional inhibition of acid sphingomyelinase (ASM). These entities named FIASMAs (Functional Inhibitors of Acid SphingoMyelinAse), therefore, can be potentially used to treat diseases associated with enhanced activity of ASM, such as Alzheimer's disease, major depression, radiation- and chemotherapy-induced apoptosis and endotoxic shock syndrome. Residual activity of ASM measured in the presence of 10 µM drug concentration shows a bimodal distribution; thus the tested drugs can be classified into two groups with lower and higher inhibitory activity. All FIASMAs share distinct physicochemical properties in showing lipophilic and weakly basic properties. Hierarchical clustering of Tanimoto coefficients revealed that FIASMAs occur among drugs of various chemical scaffolds. Moreover, FIASMAs more frequently violate Lipinski's Rule-of-Five than compounds without effect on ASM. Inhibition of ASM appears to be associated with good permeability across the blood-brain barrier. In the present investigation, we developed a novel structure-property-activity relationship by using a random forest-based binary classification learner. Virtual screening revealed that only six out of 768 (0.78%) compounds of natural products functionally inhibit ASM, whereas this inhibitory activity occurs in 135 out of 2028 (6.66%) drugs licensed for medical use in humans.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional Inhibitors of Acid Sphingomyelinase (FIASMAs): a novel pharmacological group of drugs with broad clinical applications.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2010;26(1):9-20. doi: 10.1159/000315101. Epub 2010 May 18. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20502000 Review.
-
Acid sphingomyelinase (ASM) and COVID-19: A review of the potential use of ASM inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2.Cell Biochem Funct. 2023 Apr;41(3):284-295. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3789. Epub 2023 Mar 17. Cell Biochem Funct. 2023. PMID: 36929117 Review.
-
Derivatization of common antidepressant drugs increases inhibition of acid sphingomyelinase and reduces induction of phospholipidosis.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2018 Dec;125(12):1837-1845. doi: 10.1007/s00702-018-1923-z. Epub 2018 Sep 6. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2018. PMID: 30191367
-
Functional inhibitors of acid sphingomyelinase (FIASMAs).Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2013;(215):169-86. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-1368-4_9. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23579455 Review.
-
Identification of new functional inhibitors of acid sphingomyelinase using a structure-property-activity relation model.J Med Chem. 2008 Jan 24;51(2):219-37. doi: 10.1021/jm070524a. Epub 2007 Nov 21. J Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18027916
Cited by
-
Elongation of Very Long-Chain Fatty Acids (ELOVL) in Atopic Dermatitis and the Cutaneous Adverse Effect AGEP of Drugs.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 28;25(17):9344. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179344. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence that keratinocyte microvesicle particles carrying platelet-activating factor mediate the widespread multiorgan damage associated with intoxicated thermal burn injury.J Leukoc Biol. 2024 Oct 1;116(4):766-778. doi: 10.1093/jleuko/qiae078. J Leukoc Biol. 2024. PMID: 38531065 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular docking as a tool for the discovery of novel insight about the role of acid sphingomyelinase inhibitors in SARS- CoV-2 infectivity.BMC Public Health. 2024 Feb 6;24(1):395. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-17747-z. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38321448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel insight into the lipid network of plasma extracellular vesicles reveal sex-based differences in the lipidomic profile of alcohol use disorder patients.Biol Sex Differ. 2024 Jan 25;15(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13293-024-00584-5. Biol Sex Differ. 2024. PMID: 38273378 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypical Screening of an MMV Open Box Library and Identification of Compounds with Antiviral Activity against St. Louis Encephalitis Virus.Viruses. 2023 Dec 13;15(12):2416. doi: 10.3390/v15122416. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 38140657 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hannun YA, Luberto C. Ceramide in the eukaryotic stress response. Trends Cell Biol. 2000;10:73–80. - PubMed
-
- Castillo SS, Levy M, Thaikoottathil JV, Goldkorn T. Reactive nitrogen and oxygen species activate different sphingomyelinases to induce apoptosis in airway epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 2007;313:2680–2686. - PubMed
-
- Grassmé H, Jekle A, Riehle A, Schwarz H, Berger J, et al. CD95 signaling via ceramide-rich membrane rafts. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:20589–20596. - PubMed
-
- Grassmé H, Jendrossek V, Riehle A, von Kürthy G, Berger J, et al. Host defense against Pseudomonas aeruginosa requires ceramide-rich membrane rafts. Nat Med. 2003;9:322–330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources


