Effect of nonergot dopamine agonists on symptoms of restless legs syndrome
- PMID: 18474889
- PMCID: PMC2384985
- DOI: 10.1370/afm.845
Effect of nonergot dopamine agonists on symptoms of restless legs syndrome
Abstract
Purpose: We performed a meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials of nonergot dopamine agonists (NEDAs) for the treatment of restless legs syndrome.
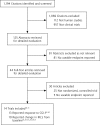
Methods: A systematic literature search was conducted through July 2007. The primary outcome measures assessed were the percentage of responders to medication as determined by the Clinical Global Impression-Improvement (CGI-I) scale and the adjusted mean change in the International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group Scale (IRLS) score from baseline compared with placebo. Meta-regression analysis was performed to evaluate the impact of study duration on the primary outcomes. Safety endpoints were also evaluated.
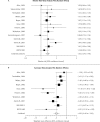
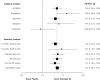
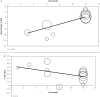
Results: A total of 14 trials (n = 3,197 subjects) were included in the meta-analysis. NEDA use resulted in greater response as measured by the CGI-I scale (relative risk [RR] 1.36; 95% CI, 1.24 to 1.49; P <.001), and greater reductions in IRLS scores (weighted mean difference [WMD] -4.93; 95% CI, -6.42 to -3.43; P <.001) from baseline vs placebo. Meta-regression analysis showed an inverse relationship between study duration and reduction in IRLS score. NEDAs were associated with a significant risk of adverse events (including nausea, dizziness, somnolence, and fatigue.)
Conclusions: Use of NEDAs in patients with moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome results in significant reductions in symptom severity, but a significant portion of patients will discontinue their use as a result of adverse events.
Figures

Comment in
-
Review: nonergot dopamine agonists reduce symptoms in the restless legs syndrome but may be discontinued due to adverse events.ACP J Club. 2008 Nov-Dec;149(4):10. ACP J Club. 2008. PMID: 18937388 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Effect of non-ergot dopamine agonists on health-related quality of life of patients with restless legs syndrome.Ann Pharmacother. 2009 May;43(5):813-21. doi: 10.1345/aph.1L673. Epub 2009 Apr 28. Ann Pharmacother. 2009. PMID: 19401472
-
Efficacy of Pramipexole for the Treatment of Primary Restless Leg Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials.Clin Ther. 2016 Jan 1;38(1):162-179.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.10.010. Epub 2015 Nov 11. Clin Ther. 2016. PMID: 26572941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relation of the International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group rating scale with the Clinical Global Impression severity scale, the restless legs syndrome 6-item questionnaire, and the restless legs syndrome-quality of life questionnaire.Sleep Med. 2013 Dec;14(12):1375-80. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2013.09.008. Epub 2013 Oct 18. Sleep Med. 2013. PMID: 24246378 Clinical Trial.
-
Dose response of Gabapentin Enacarbil versus placebo in subjects with moderate-to-severe primary restless legs syndrome: an integrated analysis of three 12-week studies.CNS Drugs. 2012 Sep 1;26(9):773-80. doi: 10.2165/11634870-000000000-00000. CNS Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22849331
-
Pharmacologic therapy for primary restless legs syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis.JAMA Intern Med. 2013 Apr 8;173(7):496-505. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.3733. JAMA Intern Med. 2013. PMID: 23460396 Review.
Cited by
-
Withania somnifera as an Adjunctive Treatment for Refractory Restless Legs Syndrome in Parkinson's Disease: A Case Report.Cureus. 2021 Dec 28;13(12):e20775. doi: 10.7759/cureus.20775. eCollection 2021 Dec. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 35111460 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine receptor D1- and D2-agonists do not spark brown adipose tissue thermogenesis in mice.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 19;10(1):20203. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-77143-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33214601 Free PMC article.
-
Acceptability and feasibility of a 12-week yoga vs. educational film program for the management of restless legs syndrome (RLS): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2019 Feb 15;20(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s13063-019-3217-7. Trials. 2019. PMID: 30770767 Free PMC article.
-
A double-blind, randomized, controlled trial to compare the efficacy and tolerability of fixed doses of ropinirole, bupropion, and iron in treatment of restless legs syndrome (Willis-Ekbom disease).Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2016 Oct-Dec;19(4):472-477. doi: 10.4103/0972-2327.194424. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27994356 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine agonists for restless legs syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Mar 16;2011(3):CD006009. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006009.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 21412893 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allen RP, Walters AS, Montplaisir J, et al. Restless legs syndrome prevalence and impact: REST general population study. Arch Intern Med. 2005; 165(11):1286–1292. - PubMed
-
- Berger K, Kurth T. RLS epidemiology—frequencies, risk factors and methods in population studies. Mov Disord 2007. Jun 7; [Epub ahead of print] DOI:10.1002/mds.21589. - PubMed
-
- Lee HB, Hening WA, Allen RP, et al. Race and restless legs syndrome symptoms in an adult community sample in east Baltimore. Sleep Med. 2006; 7(8):642–645. - PubMed
-
- Dinwiddie LC. Restless legs syndrome: not just a problem for dialysis patients. ANNA J. 1997; 24(6):655–662. - PubMed
-
- Berger K, Luedemann J, Trenkwalder C, et al. Sex and the risk of restless legs syndrome in the general population. Arch Intern Med. 2004; 164(2):196–202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

