Virion
| Morphology: | Spherical |
| Envelope: | Yes |
| Diameter (nm): | 120–160 |
| Length (nm): | |
| Structural components: | Core, capsid, envelope |
| Buoyant density (g/mL): | 1.23–1.24 |
| Buoyant density method: | CsCl |
| Lipid composition: | Envelope lipids are derived from cytoplasma membrane of host cell |
| Additional information: | Surface projections made by the spike (S) protein; some strains contain a second layer of surface projections made of HE protein |
Genome
| Nucleic acid: | RNA | |
| Strandedness: | ||
| Polarity: | ||
| Configuration: | ||
| Segment organization: | Segment no. 1 (kb): | 29.0–31.4 |
| One segment(s): | 29–31.4 (kb) total (calculated) | |
| G + C content (%): | 37.6–41.8 | |
| mRNA transcripts: | 7–10 | |
| Open reading frames: | 7–10 | |
| Additional information: | The genome contains a leader at the 5′ end and a poly(A) tail; genes are arranged in the order 5′-replicase-(HE)-S-E-M-N-3′, with a variable number of other genes that are believed to be non-structural | |
Replication
| Entry mechanism: | Receptor-mediated endocytosis |
| Site of transcription: | Cytoplasm |
| Transcriptase: | Virus-encoded RNA-dependent RNA polymerase |
| Site of genome replication: | Cytoplasm |
| Replicase: | Virus-encoded RNA-dependent RNA polymerase |
| Replication intermediate: | Negative-strand RNA intermediate |
| Site of virion assembly: | Cytoplasm, the intermediate compartment |
| Egress mechanism: | Budding through the pre-Golgi and Golgi to the basolateral (MHV) surface |
| Additional information: | Only the membrane (M) and envelope (E) proteins are required for the production of virus-like particles (VLPs) |
History
| Year of event | Event | References |
|---|---|---|
| 1949 | Murine hepatitis coronavirus (MHV) associated with encephalomyelitis in mice | Cheever et al (1949) |
| 1967 | HCoV-OC43 isolated from patients with common cold | McIntosh et al (1967) |
| 1968 | Electron microscopy reveals that BCoV has a second, short surface protein (HE) | Bridger et al (1978) |
| 1975 | ICTV approves Coronaviridae family with one genus, Coronavirus | Tyrrell et al (1975) |
| 1981 | Spike protein shown to be responsible for membrane fusion | Holmes et al (1981) |
| 1982 | Leader sequence at 5′ of mRNAs is from 5′ of genome (MHV) | Lai et al (1982) |
| 1982 | First coronavirus gene (N) sequenced (MHV) | Skinner and Siddell (1982) |
| 1983 | Leader-primed transcription model proposed (MHV); discontinuous transcription during positive strand synthesis | Lai et al (1983) |
| 1984 | M protein (MHV) is located in Golgi membranes | Tooze et al (1984) |
| 1985 | Near start of genes is a sequence similar to 3′ end of the leader RNA at 5′ end of the genome (MHV) | Budzilowicz et al (1985) |
| 1985 | Coronavirus defective RNAs discovered (MHV) | Makino et al (1985) |
| 1985 | Homologous recombination achieved with MHV | Lai et al (1985) |
| 1991 | Cell susceptibility to MHV conferred by a receptor of the carcinoembryonic antigen family | Dveksler et al (1991) |
| 1996 | ICTV recognises Coronaviridae as containing 2 genera: Coronavirus and Torovirus | Cavanagh et al (1997) |
| 1996 | ICTV recognises the order Nidovirales containing families Coronaviridae and Arteriviridae | Cavanagh et al (1997) |
| 1996 | M and E proteins sufficient for the formation of virus-like particles | Bos et al (1996); Vennema et al (1996) |
| 1997 | Insertion of gene for green fluorescent protein into genome of MHV by recombination | Fischer et al (1997) |
| 2000 | In-vitro construction of chimeric coronaviruses that cross the species barrier | Kuo et al (2000) |
| 1999 | Insertion of a transcription control sequence into MHV by recombination | Hsue and Masters (1999) |
| 2002 | A novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV) recognised as aetiological agent of severe acute respiratory disease (SARS) in humans in Guandong Province, China | Drosten et al (2003); Ksiazek et al (2003); Peiris et al (2003) |
| 2003 | Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 recognised as functional receptor for SARS-CoV | Li et al (2003) |
| 2003 | SARS-like CoVs identified in wild carnivores sold at live markets in Guandong Province, China | Guan et al (2004); Tu et al (2004) |
| 2005 | Bats recognised as natural reservoirs of SARS-like CoVs | Lau et al (2005); Li et al (2005) |
| 2005 | Specific changes detected in the spike protein and accessory proteins 3a and 8 of SARS-CoV | Song et al (2005) |
| 2005 | Human coronavirus HKU1 identified in the nasopharyngeal aspirates of patients with pneumonia in Hong Kong | Woo et al (2005) |
| 2005 | Design of wide-spectrum inhibitors of coronavirus main protease | Yang et al (2005) |
| 2005 | Transcriptomics and proteomics approaches proposed for coronaviral infections | Jiang et al (2005) |
| 2006 | A common ancestor is recognised for BCoV, HCoV-OC43 and PHEV | Vijgen et al (2006) |
| 2007 | Identification of coronavirus interferon antagonist proteins | Ye et al (2007) |
| 2009 | ICTV recognises the family Coronaviridae as containing two subfamilies, Coronavirinae and Torovirinae, with the former including three genera | Carstens (2010) |
| 2009 | According to the new taxonomy, genus Coronavirus is replaced by genera Alpha-, Beta- and Gammacoronavirus, corresponding to the old antigenic groups | Carstens (2010) |
| 2009 | BCoV, HCoV-OC43, PHEV, CRCoV and related viruses are recognised as host variants of a unique species, Betacoronavirus-1, of the genus Betacoronavirus | Carstens (2010) |
| 2009 | SARS-CoV and bat SARS-CoVs are recognised as host variants of a unique species, SARSr-CoV, of the genus Betacoronavirus | Carstens (2010) |
| 2010 | An important role in the coronavirus lyfe cycle is assigned to the ubiquitin-proteasome system | Raaben et al (2010) |
Genus Members
| Species name | Synonyms | Wild-type strains/isolates | Natural host range | Experimental host range | Membership status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Murine coronavirus | Murine hepatitis virus (MHV); Rat coronavirus (Rat sialodacryoadenitis coronavirus) (RtCoV [SDAV]); Puffinosis coronavirus (PCoV) | MHV: A59, JHM; RtCoV: Parker, SDAV-681 | Mice (MHV), rats (RtCoV); Manx shearwater (PCoV) | Mice (PCoV) | Type species |
| Betacoronavirus 1 | Bovine coronavirus (BCoV); Human coronavirus OC43 (HCoV-OC43); Human enteric coronavirus (HECoV); Porcine hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus (PHEV); Canine respiratory coronavirus (CRCoV); Equine coronavirus (ECoV); Bubaline coronavirus (BuCoV); Giraffe coronavirus (GiCoV); Sable antelope coronavirus (SACoV); Sambaar deer coronavirus (SDCoV); Waterbuck coronavirus (WbCoV); White-tailed deer coronavirus (WtDCoV); Elk coronavirus (EkCoV) | BCoV:Mebus; DB2; HCoV-OC43:VR759;VA; PHEV:Minnesota; CRCoV:4182; BuCoV:179/07-11; GiCoV:US/OH3/2003 | Cattle, humans, swine, dogs, horses, ruminants | Turkeys,dogs (BCoV); mice(HCoV-OC43);cattle(HECoV) | Approved member |
| Human coronavirus HKU-1 (HCoV-HKU1) | N5P8; Caen; LZ20 | Humans | Approved member | ||
| Pipistrellus bat coronavirus HKU5 (Pi-BatCoV-HKU5) | HKU5-1 LMH03f | Bats (Pipistrellus spp.) | Approved member | ||
| Rousettus bat coronavirus HKU9 (Ro-BatCoV-HKU9) | HKU9-1 BF_005I | Bats (Rousettus spp.) | Approved member | ||
| SARS-related coronavirus (SARSr-CoV) | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV); Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related Rhinolopus bat coronavirus (SARSr-Rh-BatCoV); Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related Rhinolopus bat coronavirus 273 (SARSr-Rh-BatCoV-273); Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related Rhinolopus bat coronavirus HKU3 (SARSr-Rh-BatCoV-HKU3) | SARS-CoV: Urbani; Toronto; GDO3 | Humans, wild carnivores (SARS-CoV); bats | Mice, hamsters, cats, ferrets, non-human primates | Approved member |
| Tylonycteris bat coronavirus HKU4 (Ty-BatCoV-HKU4) | HKU4-1 B04f | Bats (Tylonycteris spp.) | Approved member |
Nucleotide Sequences
| Genomic region | Species | Strain | Nucleotides | Access number | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complete genome | Murine coronavirus (MHV) | A59-C12 | 31,357 | AF029248 | Leparc-Goffart et al (1997) |
| Complete genome | Murine coronavirus (Rt-CoV) | Parker | 31,250 | NC_012936 | Spiro et al (2009) direct submission |
| Complete genome | Ty-BatCoV-HKU4 | HKU4-1 B04f | 30,286 | NC_009019 | Woo et al (2007) |
| Complete genome | Pi-BatCoV-HKU5 | HKU5-1 LMH03f | 30,482 | NC_009020 | Woo et al (2007) |
| Complete genome | Ro-BatCoV-HKU9 | HKU9-1 BF_005I | 29,114 | NC_009021 | Woo et al (2007) |
| Complete genome | HCoV-HKU1 | N5P8 genotype A/B | 29,755 | DQ339101 | Woo et al (2006) |
| Complete genome | Betacoronavirus-1 (BCoV) | DB2 | 31,023 | DQ811784 | Spiro, et al (2006) direct submission |
| Complete genome | Betacoronavirus-1 (PHEV) | VW572 | 30,480 | DQ011855 | Vijgen et al. (2006) |
| Complete genome | Betacoronavirus-1 (SACoV) | US/OH1/2003 | 30,995 | EF424621 | Zhang et al (2007) direct submission |
| Complete genome | Betacoronavirus-1 (GiCoV) | US/OH3/2003 | 31,002 | EF424623 | Hasoksuz et al (2007) |
| Complete genome | Betacoronavirus-1 (ECoV) | NC99 | 30,992 | EF446615 | Zhang et al (2007) |
| Complete genome | Betacoronavirus-1 (HECoV) | 4408 | 31,029 | FJ415324 | Zhu et al (2008) direct submission |
| Complete genome | Betacoronavirus-1 (HCoV-OC43) | 87309 Belgium 2003 | 30,723 | AY903459 | Vijgen et al (2005) |
| Complete genome | Betacoronavirus-1 (SDCoV) | US/OH-WD388/1994 | 30,997 | FJ425189 | Alekseev et al (2008) |
| Complete genome | Betacoronavirus-1 (WbCoV) | US/OH-WD358/1994 | 30,962 | FJ425186 | Alekseev et al (2008) |
| Complete genome | Betacoronavirus-1 (WtDCoV) | US/OH-WD470/1994 | 31,020 | FJ425187 | Alekseev et al (2008) |
| Complete genome | SARSr-CoV (SARS-CoV) | HKU-39849 | 29,742 | AY278491 | Zeng et al (2003) |
| Complete genome | SARSr-CoV (SARSr-Rh-BatCoV HKU3) | HKU3-2 | 29,687 | DQ084199 | Lau et al (2005) |
| Complete genome | SARSr-CoV (SARSr-Rh-BatCoV 273) | BtCoV/273/2005 | 29,704 | DQ648856 | Tang et al (2006) |
| Genomic 3′ end | Betacoronavirus-1 (BuCoV) | Italy/179/07-11 | 9,679 | EU019216 | Decaro et al (2008) |
| Genomic 3′ end | Betacoronavirus-1 (CRCoV) | 240/05 | 9,686 | EU999954 | Lorusso et al (2009) |
| N protein gene | Murine coronavirus (PCoV) | 1,728 | AJ544718 | Wu et al (2003) direct submission |
Proteins
| Protein name | Protein name abbreviation | Number of amino acids | Molecular weight (kDa) | Time of expression | Accession numbers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyprotein 1ab (replicase complex) | pp1ab | 6793–7241 | 740–800 | Throughout | AAR91584; AAP13442; ADE34721; ADE34822; ABG47068; YP_001039961; ADM33557; YP_001039952; BAF75628; YP_459949; YP_003038518; AAT84359; YP_001671996; ADI59786; YP_003029844; ABD75543 | Encoded by two ORFs, 1a and 1b; pseudoknot involved in frameshifting; cleaved to several products, including an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase |
| Hemagglutinin esterase | HE | 386–439 | 65 | Throughout | D00764; AAT98579; AAY68296; YP_209232; ABP38257; NP_937949 | Present in all members of the genus except SARSr-CoV, Ro-BatCoV-HKU9, Ty-BatCoV-HKU4, Pi-BatCoV-HKU5; non-essential |
| Spike glycoprotein | S | 1241–1376 | 150–220 | Throughout | AAM77000; ACJ66971; ACJ67012; AAF25499; YP_003038522; ACJ66977; CAA83661; AAQ67205; AAF69334; AAF97738; ABD75545; ABN10857; ABG47052; ADM33574; ABN10911; YP_001039962; ADE34733; ACU31051; AAV97986 | Highly glycosylated; forms homotrimers; cleaved to S1 and S2 subunits |
| Membrane protein | M | 219–230 | 23–25 | Throughout | AF220295; ABP38308; ABG78752; AAY68301; AAT84357; AAF36439; AAD33106; ABD75508; ABN10854; YP_729208; ABN10890; ADM33569; ABD75325; ADE34793; AAP41041; AAU04653 | N-linked or O-linked glycans; triple-spanning |
| Envelope protein | E | 75–88 | 9–12 | Throughout | AAR01017; AAM77003; NP_150081; ABG78751; YP_003029850; ACN89766; ABD75515; ABN10889; ABN10862; YP_729207; ABD75324; ACZ72168; AAP41040 | Essential for virion assembly; E plus M forms virus-like particles |
| Nucleocapsid protein | N | 417–470 | 50–60 | Throughout | AAA66397; ACL13001; ABP38321; AAR01019; ACH72650; ABP87995; ACN89747; AAD33104; ABD75581; ABN10900; ABN10939; ABG47067; AAZ41337; ADK66848; ABN10855; AAP50495; ACZ72030 | Highly basic phosphoprotein; forms a helical nucleocapsid |
| Non-structural protein 2a (32 kDa) | ns2a (ns2 or ns32kDA) | 194–278 | 30–32 | Throughout | AAF25507; ABV74052; ABG78746; ABP87988; AAA74377; ACN89750; AAU06354; AAF97736; YP_459950 | Unique to Betacoronavirus-1 and Murine coronavirus; ns2a in murine coronavirus; ns2 or ns32kDa in Betacoronavirus-1; gene between pp1ab and HE genes |
| Non-structural protein 4 | ns4 | 106–139 | 15 | Throughout | AAF97739; YP_003029849; YP_209234; ACN89764 | Unique to Murine coronavirus; two distinct ORFs (4a, 4b) in Betacoronavirus-1; not essential; may be truncated in some strains |
| Non-structural protein 4a (4.9 kDa) | ns4a (ns4.9 kDa) | 29–44 | 4.9 | Throughout | AAF25500; AAF25510; AAG40624; ABV74055; ACL12997; ACJ35490 | Unique to Betacoronavirus-1; not essential for replication; may be truncated in some strains |
| Non-structural protein 4b (4.8 kDa) | ns4b (ns4.8 kDa) | 43–45 | 4.7–4.8 | Throughout | AAF25501; AAG60546; AAL40402; ACJ35491 | Unique to Betacoronavirus-1; not essential for replication; may be truncated in some strains |
| Non-structural protein 5 (12.7 kDa) | ns5 (ns5a or ns12.7 kDa) | 107–112 | 12.6–13.1 | Throughout | AAF19390; NP_068672; AAF97740; YP_173239; YP_003038502; AAF25502; ACX46843 | Unique to Murine coronavirus/Betcoronavirus-1/HCoV-HKU1; ns5 in MHV;ns12.7 kDa in BCoV; ns4 in HCoV-HKU1; not essential; may be truncated in some strains |
| Internal protein | I (N2) | 136–220 | 23 | Throughout | ACN89765; ACN89684; ACT11047; AAF25516; ABG78754; AAY68303; ABP87996; NP_937955; ACT11037; ABC70724 | Unique to Murine coronavirus/Betacoronavirus-1/HCoV-HKU1; ORF is within the N gene; not essential; may be truncated in some strains |
| SARS-CoV 3a protein | Sars3a | 274 | 30.9 | Throughout | ACZ72036; ACZ72226; ACQ82726; ADE34813; ADE34734; ABD75316; AAU04635 | Unique to SARSr-CoV; O-glycosylated, triple membrane spanning; forms homotetramers; not essential for replication |
| SARS-CoV 3b protein | Sars3b | 114–154 | 12.8–17.7 | Throughout | ACZ71978; ACB69862; ACB69907; AAU04636; YP_001382387; ABD75317 | Unique to SARSr-CoV; not essential for replication |
| SARS-CoV 6 protein | Sars6 | 63 | 7.5 | Throughout | ABA02272; ACZ72098; ACZ71861; AAP13448; AAU04639; ABD75318; ADE34737; ADE34805 | Unique to SARSr-CoV; not essential for replication |
| SARS-CoV 7a protein | Sars7a | 122 | 13.9 | Throughout | ACQ82731; ACZ72041; ACZ72128; ACZ72216; ACZ72260; NP_828857 | Unique to SARSr-CoV; type I transmembrane protein; not essential for replication |
| SARS-CoV 7b protein | Sars7b | 44 | 5.3 | Throughout | CAJ15124; ABA02274; ABA02274; ACZ71953; BAC81397; AAS44625; ACQ82732; AAU04656; YP_001382367; ABD75329; ADE34728 | Unique to SARSr-CoV; not essential for replication |
| SARS-CoV 8 protein | Sars8 | 122–123 | 13.8 | Throughout | AAZ67036; ABG47066; AAU04657; AAZ67036; AAV91639 | Unique to some SARSr-CoVs (early human and animal SARS-CoVs); present as two distinct ORFs (8a and 8b) in human SARS-CoV due to a 29-nt deletion |
| SARS-CoV 8a protein | Sars8a | 39 | 4.3 | Throughout | NP_849176; ACZ72058; ACZ72277; ACZ71804; ACZ71969 | Unique to most human SARSr-CoVs; originating from a 29-nt deletion in ORF8; not essential for replication |
| SARS-CoV 8b protein | Sars8b | 84 | 9.5 | Throughout | CAJ15126; NP_849177; ACZ72059; BAC81413; AAP41046; ACZ71805 | Unique to most human SARSr-CoVs; originating from a 29-nt deletion in ORF8; not essential for replication |
| SARS-CoV 9b protein | Sars9b | 97–98 | 10.8 | Throughout | ACB69891; AAR87585; BAC81401; AAP69659; ACB69857; AAU04659; ADE34821; ADE34810; AAZ67037 | Unique to SARSr-CoV; gene located within N gene; not essential for replication |
| SARS-CoV 14 protein | Sars14 | 70 | 7.8 | Throughout | ACZ72047; ADC35508; ACZ72207; ACZ72032; AAU04674; YP_001382371; AAZ67042; AAZ67045 | Unique to SARSr-CoV; also known as ORF10 protein; not essential for replication |
Biology
| Species | Permissive cell lines | Tissue tropism | Cytopathic effects | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Murine coronavirus (MHV) | Sac(−), L2, DBT, RK13, 17Cl-1 | Intestine, liver, CNS | Syncytia with several cell types | Tropism is virus strain dependent |
| Murine coronavirus (RtCoV) | L2, LBC, RBL-02 | Respiratory tract, parotid gland | Syncytia formation | Infects laboratory rats at high prevalence |
| Murine coronavirus (PCoV) | NCTC-1469 | Skin, lung, blood | Cell rounding and detachment, syncitya formation | |
| Betacoronavirus-1 (BCoV) | HRT-18, PK15, PK3, MDBK, BEK-1 | Intestine, respiratory tract | Cell lysis; syncytia if trypsin present | No genetic differences between enteric and respiratory strains |
| Betacoronavirus-1 (HCoV-OC43) | HRT-18, MA-321, DRG-N | Upper respiratory tract | Cytoplasm vacuolisation, degeneration of monolayer | Infects astrocytes and microglial cells; some strains replicate in the enteric tract |
| Betacoronavirus-1 (HECoV) | HRT-18; HFI; J774; C6/36 | Intestinal epithelium | Formation of giant cells and small syncytia | |
| Betacoronavirus-1 (PHEV) | Pk-15, IBRS2, SK, SK-K | Intestine and CNS | Syncytia formation | Also replicates in respiratory tract |
| Betacoronavirus-1 (CRCoV) | HRT-18 | Respiratory tract | No evident cytopathic effect | Also replicates in the intestine |
| Betacoronavirus-1 (ACoV) | HRT-18 | Intestinal epithelium | Cell rounding and detachment | |
| Betacoronavirus-1 (ECoV) | HRT-18 | Intestinal epithelium | Round refractile cells, syncytia formation | |
| Betacoronavirus-1 (BuCoV) | HRT-18 | Respiratory tract | Syncytia formation and subsequent cell lysis | Poor growth in MDBK cells |
| Betacoronavirus-1 (GiCoV, SACoV, SDCoV, WbCoV, WtDCoV, EkCoV) | HRT-18 | Intestinal epithelium | Rounded cells and syncytia formation | |
| HCoV-HKU1 | None | Upper and lower respiratory tract | Not applicable | A certain replication has been obtained using human ciliated airway epithelial cell cultures |
| SARSr-CoV (SARS-CoV) | Vero-E6; FRhK-4; Caco-2; LLC-Mk2; HuH7; RK-13; MA-104; CV-1 | Lower respiratory tract (pneumocytes/macrophages) | Cell rounding, refractivity and cell detachment | Also grows on lymphoid cell cultures causing a non-lytic infection |
Diseases
| Disease | Causative agent | Affected organisms | Disease characteristics | Transmission route/vector | Treatment | Geographic distribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse hepatitis and encephalitis | Murine coronavirus (MHV) | Mice | Hepatitis, diarrhoea, acute or chronic demyelinating encephalomyelitis | Faecal-oral | None | Worldwide |
| Rat pneumonia and sialodacryoadenitis | Murine coronavirus (RtCoV, SDAV) | Rats | Pneumonia, rhinitis, sialodacryoadenitis | Aerosol | None | Worldwide |
| Puffinosis | Murine coronavirus (PCoV) | Manx shearwater (Puffinus puffinus) | Blisters on the webs of the feet, conjunctivitis and locking of the ankle joint of the legs | Likely aerosol | None | South-west coast of Wales |
| Bovine enteritis and respiratory disease | Betacoronavirus-1 (BCoV) | Cattle | Acute enteritis in newborns, wynter dysentery in adults, respiratory disease in all ages | Faecal-oral, aerosol | Only symptomatic | Worldwide |
| Human common cold | Betacoronavirus-1 (HCoV-OC43) | Humans | Common cold (sneezing, coughing, nasal discharge) | Aerosol | Only symptomatic | Worldwide |
| Human enteritis | Betacoronavirus-1 (HECoV) | Humans | Diarrhoea | Faecal-oral | Only symptomatic | A single case reported in the USA |
| swine encephalomyelitis, vomiting and wasting disease | Betacoronavirus-1 (PHEV) | Swine | vomiting, weight loss, encephalomyelitis | Faecal-oral | Only symptomatic | Worldwide |
| Canine respiratory disease | Betacoronavirus-1 (CRCoV) | Dogs | Cough, nasal discharge, tracheobronchitis | Aerosol | Only symptomatic | Worldwide |
| Equine enteritis | Betacoronavirus-1 (ECoV) | Horses | Enteritis | Faecal-oral | Only symptomatic | USA, Japan |
| Buffalo enteritis | Betacoronavirus-1 (BuCoV) | Water buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis) | Enteritis | Faecal-oral | Only symptomatic | Italy, Bulgaria |
| Alpaca enteritis | Betacoronavirus-1 (ACoV) | Alpacas (Vicugna pacos) | Enteritis, fever | Faecal-oral | Only symptomatic | USA |
| Wild-ruminant enteritis | Betacoronavirus-1 (GiCoV, SACoV, SDCoV, WbCoV, WtDCoV, EkCoV) | Wild ruminants (giraffes, sable antelopes, sambaar deer, waterbuck, white-tailed deer, elks) | Enteritis | Faecal-oral | Only symptomatic | USA |
| Human respiratory disease | HCoV-HKU1 | Humans | Fever, cough, coryza, sore throat, bronchiolitis, bronchitis, pneumonia and croup | Aerosol | Only symptomatic | Worldwide |
| Severe acute respiratory disease | SARSr-CoV (SARS-CoV) | Humans | Flu-like prodrome, fever, dry cough, non–respiratory symptoms e.g. diarrhoea, myalgia, headache and chills/rigors | Aerosol | Symptomatic, antivirals | East Asia with further spreading to many countries |
Diagnosis
| Method | Species | Sample material | Detection target | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electron microscopy | Murine coronavirus (MHV) | Liver, brain | Particle morphology | Dumitrescu et al (1962) |
| DBT cell culture and immunofluorescence assay | Murine coronavirus (MHV) | Liver, brain | Viral antigens | Hirano et al (1976) |
| Immunoshostochemistry | Murine coronavirus (MHV) | Liver, brain | Viral antigens | Knobler et al (1981) |
| RT-PCR amplification of the membrane protein gene | Murine coronavirus (MHV, RtCoV) | Tissues | Viral RNA | Homberger et al (1991) |
| Nested PCR amplification of the nucleocapsid protein gene | Murine coronavirus (MHV) | Faeces | Viral RNA | Yamada et al (1998) |
| Real-time RT-PCR amplification of the membrane protein gene | Murine coronavirus (MHV, RtCoV) | Tissues, faeces, cage swipes | Viral RNA | Besselsen et al (2002) |
| HRT-18, MDBK or PK15 cell culture and immunofluorescence assay | Betacoronavirus-1 (BCoV, HCoV-OC43, PHEV, CRCoV, BuCoV, GiCoV, ECoV, ACoV, SACoV, WbCoV, SDCoV, WtDCoV, EkCoV) | Faeces, intestine, respiratory specimens | Viral antigens | Peterson et al (1976) |
| Electron microscopy | Betacoronavirus-1 (BCoV, HCoV-OC43, PHEV, CRCoV, BuCoV, GiCoV, ECoV, ACoV, SACoV, WbCoV, SDCoV, WtDCoV, EkCoV) | Faeces, intestine, respiratory specimens | Particle morphology | Chasey and Lucas (1977) |
| Protein A-colloidal gold immunoelectron microscopy | Betacoronavirus-1 (BCoV, HCoV-OC43, PHEV, CRCoV, BuCoV, GiCoV, ECoV, ACoV, SACoV, WbCoV, SDCoV, WtDCoV, EkCoV) | Faeces, intestine, respiratory samples | Viral antigens | Dea and Garzon (1991) |
| Haemagglutination using mouse or chicken erytrocytes | Betacoronavirus-1 (BCoV, HCoV-OC43, PHEV, CRCoV, BuCoV, GiCoV, ECoV, ACoV, SACoV, WbCoV, SDCoV, WtDCoV, EkCoV) | Faeces, intestine, respiratory specimens | Viral haemagglutinin | Storz et al (1992) |
| Monoclonal antibody ELISA | Betacoronavirus-1 (BCoV) | Faeces, intestine, respiratory specimens | Viral antigens | Thorns et al (1992) |
| Immunoistochemistry | Betacotonavirtus-1 (BCoV) | Paraffin-embedded, formalin-fixed intestines | Viral antigens | Zhang et al (1997) |
| Microimmunodot blot assay | Betacoronavirus-1 (BCoV) | Faeces, intestine, respiratory specimens | Viral antigens | Gaber and Kapil (1999) |
| Nested RT-PCR amplification of the nucleocapsid protein gene | Betacoronavirus-1 (BCoV) | Faeces, intestine, respiratory specimens | Viral RNA | Cho et al (2001) |
| Internally-controlled nested RT-PCR amplification of the nucleocapsid protein gene | Betacoronavirus-1 (BCoV) | Faeces, intestine, respiratory specimens | Viral RNA | Takiuchi et al (2006) |
| Real-time RT-PCR amplification of the membrane protein gene | Betacoronavirus-1 (BCoV, BuCoV, CRCoV) | Faeces, intestine, respiratory specimens | Viral RNA | Decaro et al (2008) |
| Nested RT-PCR amplification of the spike protein gene | Betacoronavirus-1 (PHEV) | Brain, faeces, intestine, respiratory specimens | Viral RNA | Sekiguchi et al (2004) |
| Real-time RT-PCR amplification of the nucleocapsid protein gene | Betacoronavirus-1 (CRCoV) | Respiratory specimens | Viral RNA | Mitchell et al (2009) |
| Immunofluorescence assay | Betacoronavirus-1 (HCoV-OC43) | Nasopharyngeal smears | Viral antigens | McIntosh et al (1978) |
| Monoclonal time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay | Betacoronavirus-1 (HCoV-OC43) | Respiratory specimens | Viral antigens | Hierholzer et al (1994) |
| Enzyme immunoassay | Betacoronavirus-1 (HCoV-OC43) | Respiratory specimens | Viral antigens | Hierholzer et al (1994) |
| Nested RT-PCR amplification of the nucleocapsid protein gene | Betacoronavirus-1 (HCoV-OC43) | Respiratory specimens | Viral RNA | Vabret et al (2001) |
| Real-time RT-PCR amplification of the membrane protein gene | Betacoronavirus-1 (HCoV-OC43) | Respiratory specimens | Viral RNA | Vijgen et al (2005) |
| Microarray using standard amplification and hybridization techniques | Betacoronavirus-1 (HCoV-OC43) | Respiratory specimens | Viral RNA | Lodes et al (2007) |
| RT-PCR amplification of the nucleocapsid protein gene | Betacoronavirus-1 (HCoV-OC43), HCoV-HKU1 | Respiratory specimens | Viral RNA | Dominguez et al (2009) |
| Nested PCR amplification of the nucleocapsid protein gene | Betacoronavirus-1 (HCoV-OC43), HCoV-HKU1 | Respiratory specimens | Viral RNA | Gaunt et al (2010) |
| Multiplex real-time RT-PCR amplification of the nucleocapsid protein gene | Betacoronavirus-1 (HCoV-OC43), HCoV-HKU1 | Respiratory specimens | Viral RNA | Gaunt et al (2010) |
| Vero or FRhK cell culture and immunofluorescence assay | SARSr-CoV (SARS-CoV) | Respiratory specimens | Viral antigens | Ksiazek et al (2003) |
| Electron microscopy | SARSr-CoV (SARS-CoV) | Respiratory specimens | Particle morphology | Ksiazek et al (2003) |
| Nested RT-PCR amplification of the RdRp (nsp1ab) gene | SARSr-CoV (SARS-CoV) | Respiratory specimens, faeces | Viral RNA | Drosten et al (2003) |
| RT-PCR amplification of the RdRp (nsp1ab) gene | SARSr-CoV (SARS-CoV) | Respiratory specimens, faeces | Viral RNA | Peiris et al (2003) |
| Real-time RT-PCR amplification of the RdRp (nsp1ab) gene | SARSe-CoV (SARS-CoV) | Respiratory specimens, faeces | Viral RNA | Poon et al (2003) |
| Real-time RT-PCR amplification of the RdRp (nsp1ab) gene | SARSr-CoV (SARS-CoV) | Respiratory specimens, faeces | Viral RNA | Kuiken, et al (2003) |
| Real-time RT-PCR amplification of the nucleocapsid protein gene | SARSr-CoV (SARS-CoV) | Respiratory specimens, faeces | Viral RNA | Kuiken, et al (2003) |
| Immunohistochemistry | SARSr-CoV (SARS-CoV) | Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues | Viral antigens | Kuiken et al (2003) |
| Indirect immunofluorescence assay | SARSr-CoV (SARS-CoV) | Serum | Anti-viral antibodies | Kuiken et al (2003) |
| ELISA test using whole virus | SARSr-CoV (SARS-CoV) | Serum | Anti-viral antibodies | Ksiazek et al (2003) |
| RT-PCR amplification of the nucleocapsid protein gene | SARSr-CoV (SARS-CoV) | Respiratory specimens, faeces | Viral RNA | Bermingham et al (2004) |
| Virus neutralising antibody test | SARSr-CoV (SARS-CoV) | Serum | Anti-viral antibodies | Zheng et al (2004) |
| Immunochromatographic test | SARSr-CoV (SARS-CoV) | Serum | Anti-viral antibodies | Wu et al (2004) |
| Western blot | SARSr-CoV (SARS-CoV) | Serum | Anti-viral antibodies | Wu et al (2004) |
| Dot blot enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay | SARSr-CoV (SARS-CoV) | Serum | Anti-viral antibodies | Chow et al (2004) |
| ELISA test using recombinant nucleocapsid protein | SARSr-CoV (SARS-CoV) | Serum | Anti-viral antibodies | Guo et al (2007) |
| Nucleocapsid-based human coronavirus immunoassay | SARSr-CoV (SARS-CoV) | Serum | Anti-nucleocapsid protein antibodies | Severance et al (2008) |
| Internally-controlled real-time RT-PCR amplification of the RdRp (nsp1ab) gene | SARSr-CoV (SARS-CoV) | Respiratory specimens, faeces | Viral RNA | Yu et al (2008) |
| Localized surface plasmon coupled fluorescence (LSPCF) fiber-optic biosensor | SARSr-CoV (SARS-CoV) | Serum | Viral antigens (nucleocapsid protein) | Huang et al (2009) |
| Surface plasmon resonance (SPR)-based biosensor | SARSr-CoV (SARS-CoV) | Serum | Anti-SARS-CoV surface antigen antibodies | Park et al (2009) |
| Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using chemiluminescence | SARSr-CoV (SARS-CoV) | Respiratory specimens, faeces | Viral antigens (nucleocapsid protein) | Fujimoto et al (2008) |
Vaccine Strains
| Strain | Attenuation process | Additional information | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Betacoronavirus-1 BCoV many strains | Inactivated vaccines | Do not prevent respiratory diseases | Saif (2010) |
| Betacoronavirus-1 BCoV many strains | Passage in cell culture | Do not prevent respiratory disease | Saif (2010) |
| SARSr-CoV SARS-CoV strain Utah | Double-inactivated, whole-virus vaccine | Not yet licenced; reached the phase 1 clinical trial testing | Spruth et al (2006) |
| VRC-SRSDNA015-00-VP vaccine containing the spike gene of SARS-CoV strain Urbani | DNA vaccine expressing the spike protein | Not yet licenced; reached the phase 1 clinical trial testing | Martin et al (2008) |
Vector Constructs
| Vector name | Backbone strain | Application | Insertion capacity (kb) | Additional information | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p25HE | Murine coronavirus MHV-JHM | Expression | 1.4 | Helper-dependent expression system | Liao et al (1995) |
| MHV-GFP | Murine coronavirus MHV-A59 | Expression | 0.5 | Genome vector generated by recombination | Fischer et al (1997) |
| pMH54 | Murine coronavirus MHV-A59 | Reverse genetics | 10.2 | Used for targeted RNA recombination to obtain chimeric MHVs | Kuo et al (2000) |
| pJHM | Murine coronavirus MHV-JHM | Reverse genetics | 10.2 | Used for targeted RNA recombination to obtain chimeric MHVs | Ontiveros et al (2001) |
| icMHV-A59 | Murine coronavirus MHV-A59 | Reverse genetics | 31.5 | Full-length genome infectious clone constructed through ligation of seven inserts | Yount et al (2002) |
| icSARS-CoV | SARsr-CoV SARS-CoV Urbani | Reverse genetics | 29.7 | Full-length genome infectious clone constructed through ligation of six inserts | Yount et al (2003) |
| vMHV-inf-1 | Murine coronavirus MHV-A59 | Reverse genetics | 31.4 | Recombinant vaccinia virus containing the full-length genome of MHV | Coley et al (2005) |
| pBAC-SARS-CoV | SARSr-CoV SARS-CoV Urbani | Reverse genetics | 30 | Infectious bacterial artificial chromosome | Almazan et al (2006) |
| pBAC-OC43(FL) | Betacoronavirus-1 HCoV-OC43 | Reverse genetics | 30 | Infectious bacterial artificial chromosome | St-Jean et al (2006) |
Betacoronavirus-1 (BCoV). Fig. 1.
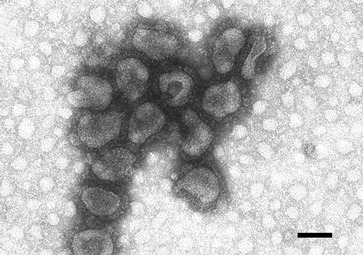
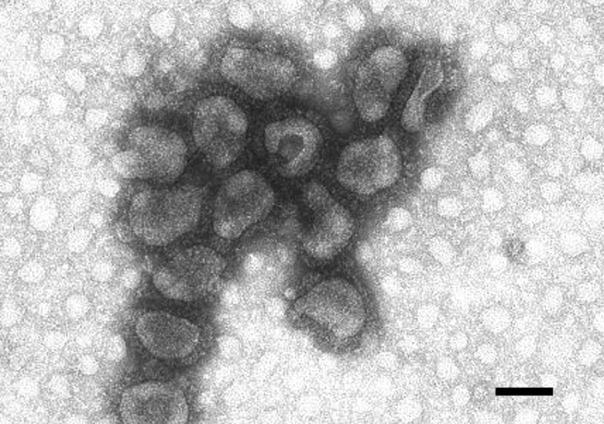
Transmission electron micrograph, negative staining of purified virus. Length of bar (nm): 100 (Courtesy of Dr. A. Lavazza, Istituto Zooprofilattico di Lombardia ed Emilia Romagna, Italy)
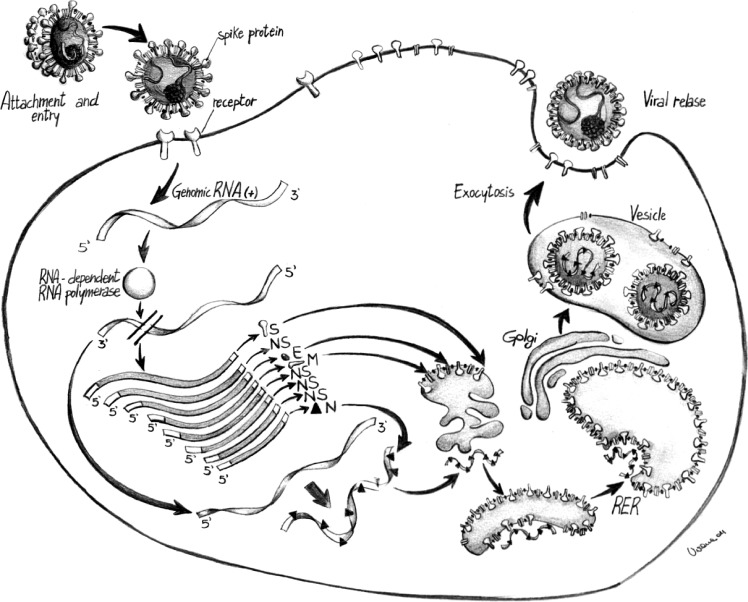
Alpha-, Beta-, and Gammacoronavirus replication cycle. Fig. 2.
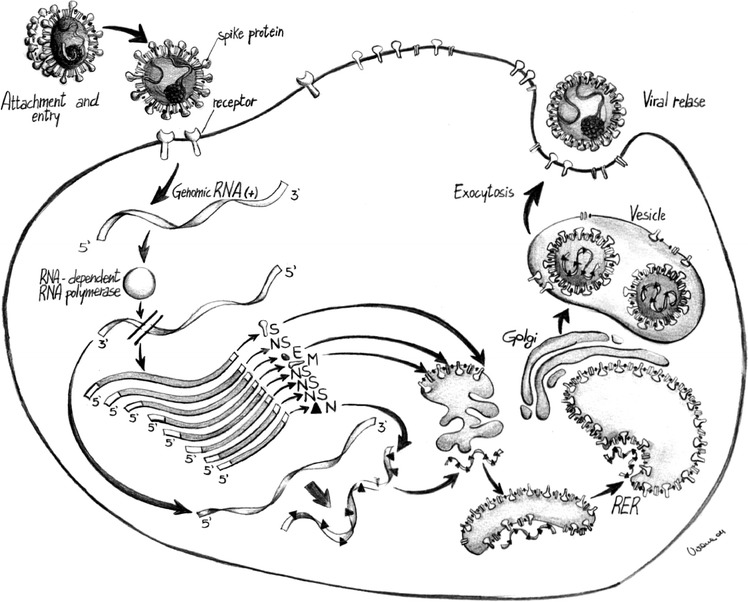
HE protein is present only in some Betacoronaviruses (Courtesy of Dr Viviana Tarallo, Department of Veterinary Public Health, Valenzano, Italy)
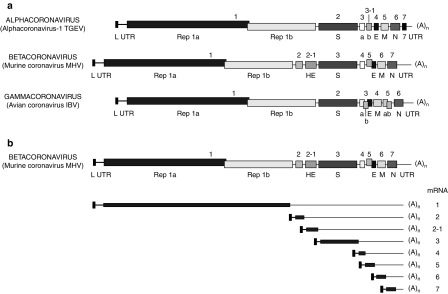
Genome organization of Alpha-, Beta-, and Gammacoronavirus prototypes (A) and transcription map of Murine coronavirus MHV (B). Fig. 3.
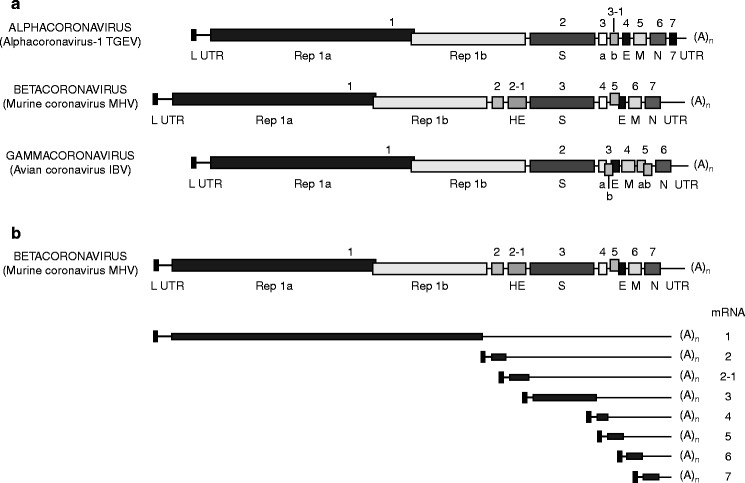
Numbers above bars ORFs, L leader, UTR untranslated region, Rep replicase, (A)n poly A (Modified from Springer Index of Viruses, 1st edition, with permission)
Footnotes
‡This chapter was reprinted from the first edition of the Springer Index of Viruses. Taxonomy and classification of the virus species described in this chapter may have changed.
References
- Carstens (2010)
- Cavanagh (1997)
- Enjuanes L, Siddell SG, Spaan WJ. Coronaviruses and arteriviruses. New York: Plenum; 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Enjuanes L, Brian D, Cavanagh D, Holmes K, Lai MMC, Laude H, Masters P, et al. et al. Coronaviridae. In: Murphy FA, et al.et al., editors. Virus taxonomy. New York: Academic; 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Enjuanes L, Spaan SE, Cavanagh D, et al. Nidovirales. In: Murphy FA, et al., editors. Virus taxonomy. New York: Academic; 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes KV, Lai MMC. Coronaviridae: the viruses and their replication. In: Fields BN, Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Fundamental virology. New York: Academic; 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Lai and Cavanagh (1997)
- Perlman S, Gallagher T, Snijder EJ. Nidovirales. Washington, DC: ASM; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Siddell SG. In: The coronaviridae. Fraenkel-Conrat H, Wagner RR, editors. Plenum: New York; 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sturman and Holmes (1983)