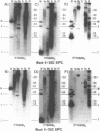
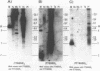
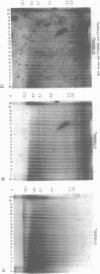
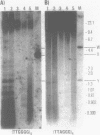
Abstract
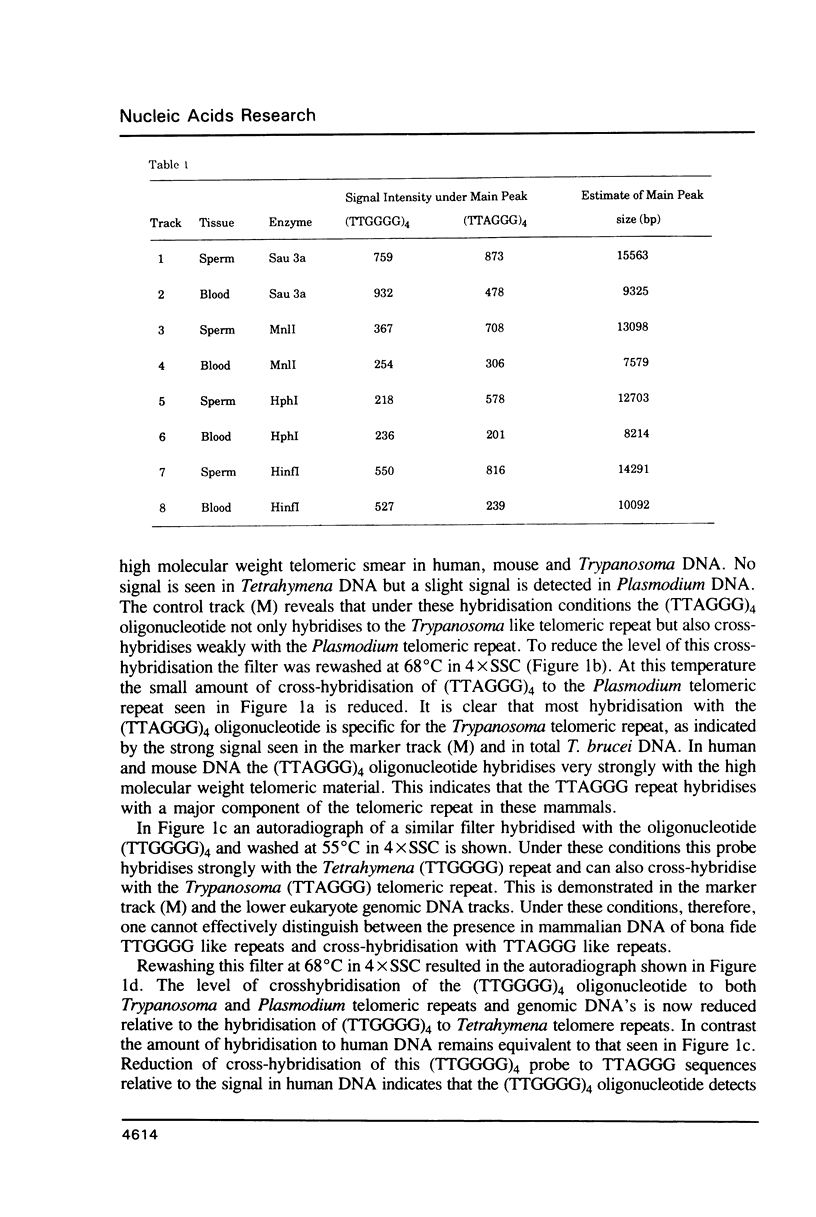
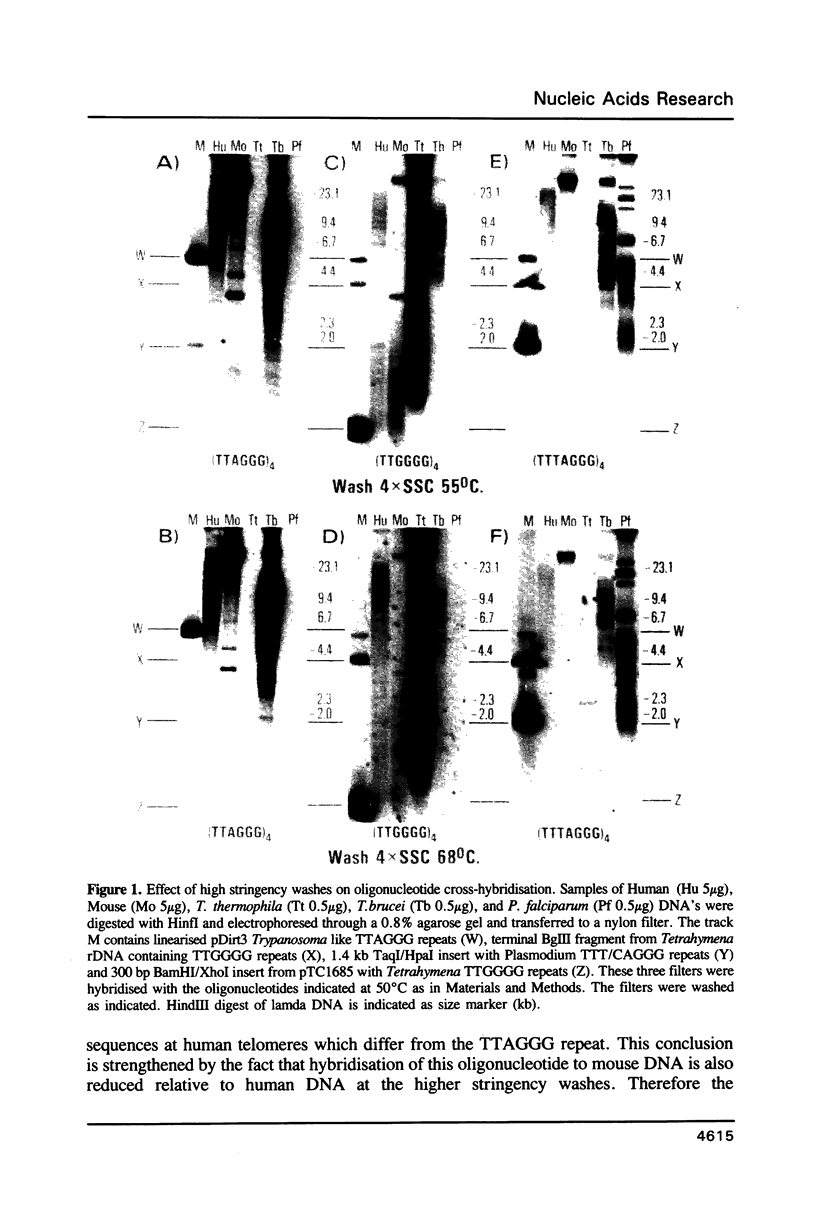
Using a combination of different oligonucleotides and restriction enzymes we have examined the gross organisation of repeats within the most distal region of human chromosomes. We demonstrate here that human telomeres do not contain a pure uniform 6 base pair repeat unit but that there are at least three types of repeat. These three types of repeat are present at the ends of most or all human chromosomes. The distribution of each type of repeat appears to be non-random. Each human telomere has a similar arrangement of these repeats relative to the ends of the chromosome. This could reflect differences in the functions that they perform, or might result from the mutation and correction processes occurring at human telomeres. The number of repeat units, the repeat types and arrangement differs at mouse telomeres. Analysing the change in length of the telomeric repeat region between an individuals blood and germline DNA reveals that this is due to variable amounts of the TTAGGG repeat and not the other repeat types. This organization of repeat units at human telomeres will only be confirmed upon the isolation and sequencing of full length (10-15 kb), intact human telomeres.
Full text
PDF



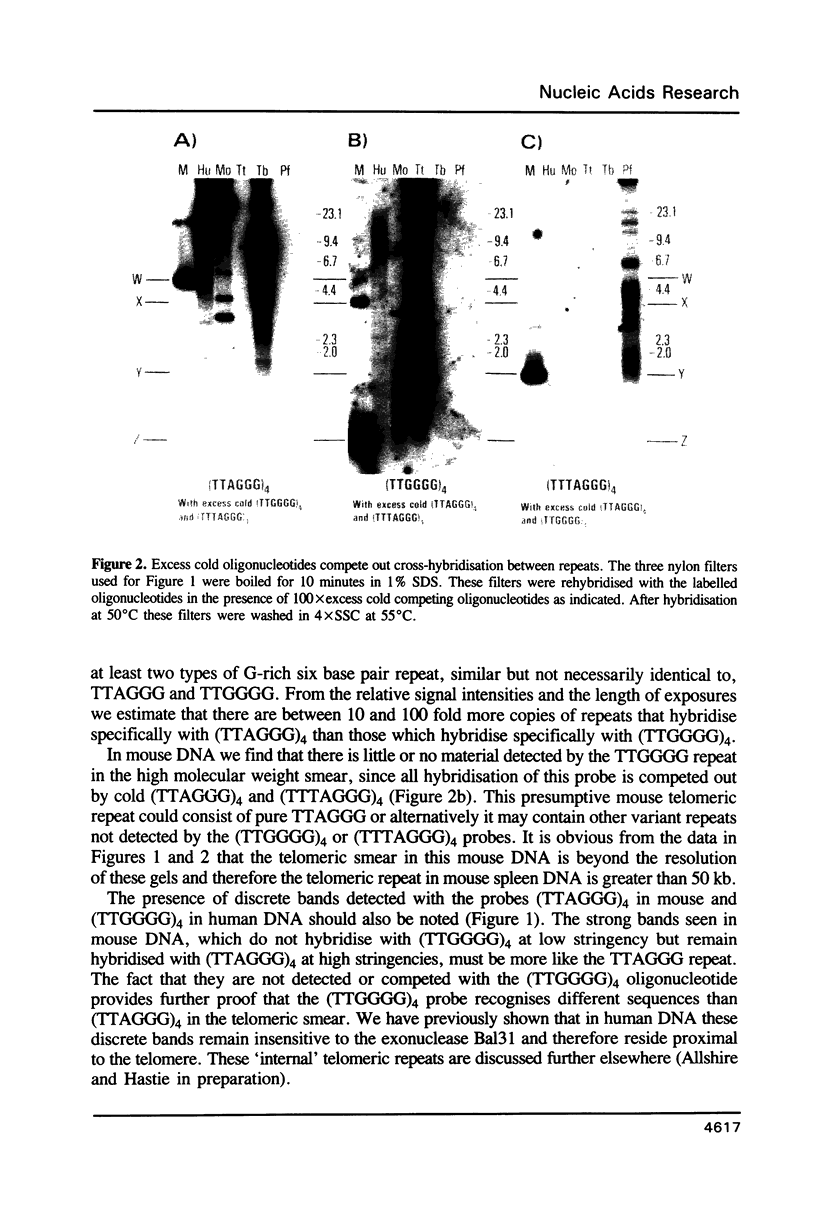


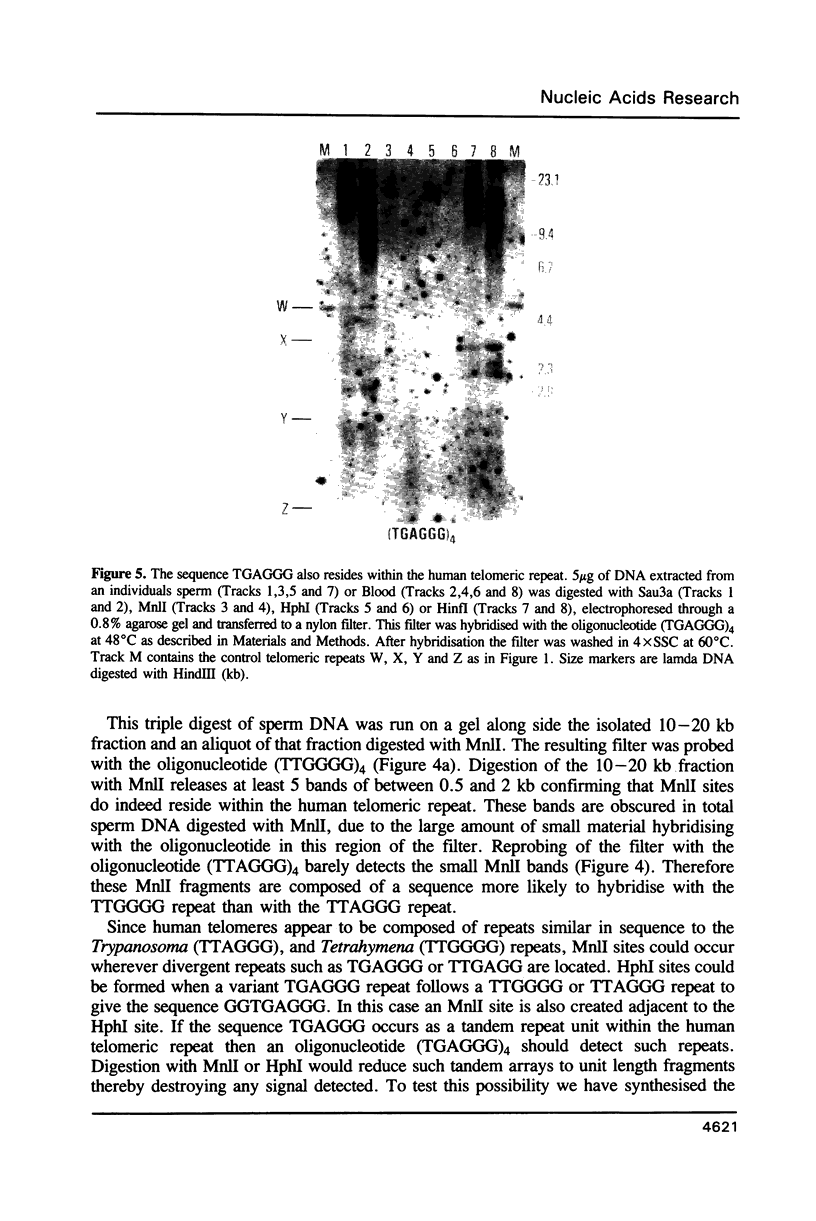

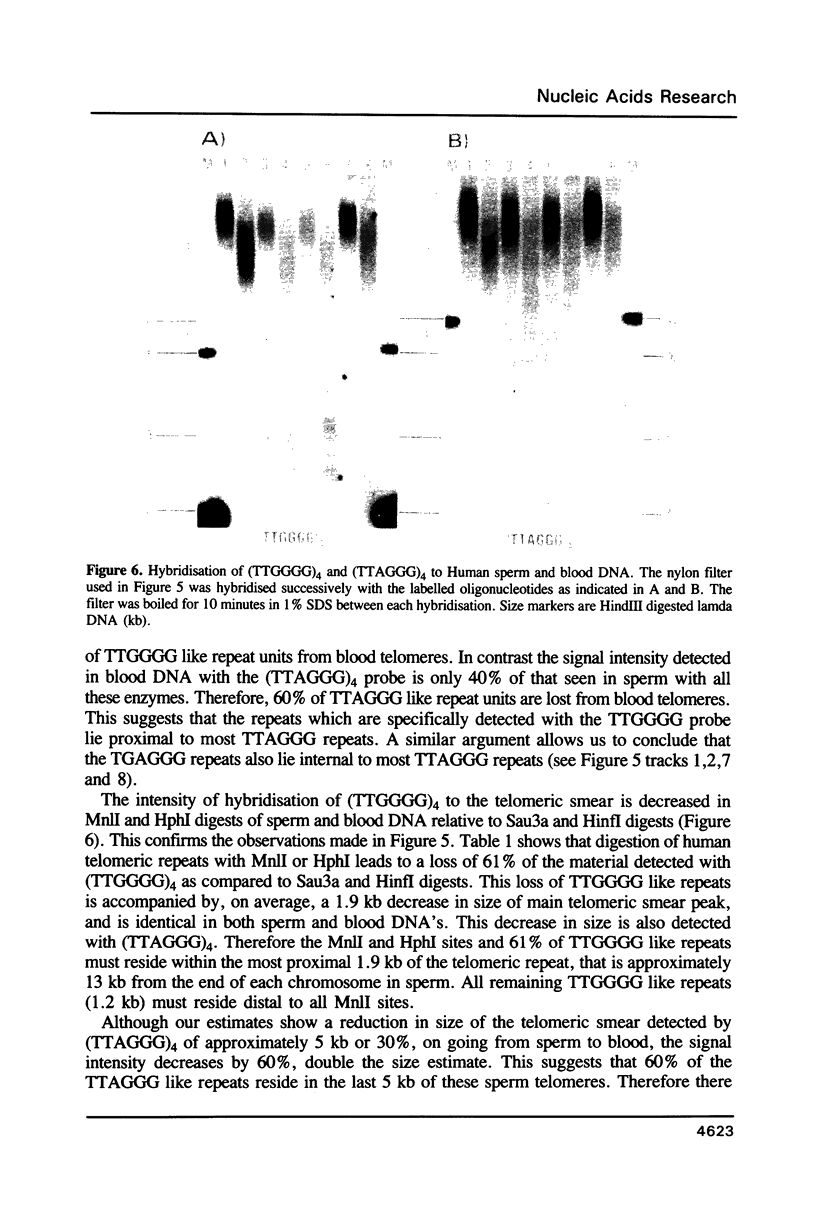




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agard D. A., Sedat J. W. Three-dimensional architecture of a polytene nucleus. Nature. 1983 Apr 21;302(5910):676–681. doi: 10.1038/302676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allshire R. C., Gosden J. R., Cross S. H., Cranston G., Rout D., Sugawara N., Szostak J. W., Fantes P. A., Hastie N. D. Telomeric repeat from T. thermophila cross hybridizes with human telomeres. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):656–659. doi: 10.1038/332656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baroin A., Prat A., Caron F. Telomeric site position heterogeneity in macronuclear DNA of Paramecium primaurelia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1717–1728. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergold P. J., Campbell G. R., Littau V. C., Johnson E. M. Sequence and hairpin structure of an inverted repeat series at termini of the Physarum extrachromosomal rDNA molecule. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1287–1299. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90310-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. The molecular structure of centromeres and telomeres. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:163–194. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R. Molecular cloning of human telomeres in yeast. Nature. 1989 Apr 27;338(6218):774–776. doi: 10.1038/338774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H. J., Smith B. A. Variability at the telomeres of the human X/Y pseudoautosomal region. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):213–219. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross S. H., Allshire R. C., McKay S. J., McGill N. I., Cooke H. J. Cloning of human telomeres by complementation in yeast. Nature. 1989 Apr 27;338(6218):771–774. doi: 10.1038/338771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. K., Green D. K., Southern E. M. Automatic reading of DNA sequencing gel autoradiographs using a large format digital scanner. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):417–424. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forney J. D., Blackburn E. H. Developmentally controlled telomere addition in wild-type and mutant paramecia. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):251–258. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forney J., Henderson E. R., Blackburn E. H. Identification of the telomeric sequence of the acellular slime molds Didymium iridis and Physarum polycephalum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9143–9152. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry K., Salser W. Nucleotide sequences of HS-alpha satellite DNA from kangaroo rat Dipodomys ordii and characterization of similar sequences in other rodents. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1069–1084. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90170-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosden J. R., Gosden C. M., Christie S., Cooke H. J., Morsman J. M., Rodeck C. H. The use of cloned Y chromosome-specific DNA probes for fetal sex determination in first trimester prenatal diagnosis. Hum Genet. 1984;66(4):347–351. doi: 10.1007/BF00287639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. A telomeric sequence in the RNA of Tetrahymena telomerase required for telomere repeat synthesis. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):331–337. doi: 10.1038/337331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. Identification of a specific telomere terminal transferase activity in Tetrahymena extracts. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. The telomere terminal transferase of Tetrahymena is a ribonucleoprotein enzyme with two kinds of primer specificity. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90576-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson D. D., Spangler E. A., Blackburn E. H. Dynamics of telomere length variation in Tetrahymena thermophila. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):477–483. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90501-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazrimas J. A., Hatch F. T. Similarity of satilite DNA properties in the order Rodentia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Sep;4(9):3215–3227. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.9.3215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyzis R. K., Buckingham J. M., Cram L. S., Dani M., Deaven L. L., Jones M. D., Meyne J., Ratliff R. L., Wu J. R. A highly conserved repetitive DNA sequence, (TTAGGG)n, present at the telomeres of human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6622–6626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluta A. F., Zakian V. A. Recombination occurs during telomere formation in yeast. Nature. 1989 Feb 2;337(6206):429–433. doi: 10.1038/337429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzi M., Pace T., Dore E., Frontali C. Identification of a telomeric DNA sequence in Plasmodium berghei. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2991–2995. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04034.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards E. J., Ausubel F. M. Isolation of a higher eukaryotic telomere from Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90494-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. J. Restriction enzymes and their isoschizomers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987;15 (Suppl):r189–r217. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.suppl.r189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen D., Gilbert W. Formation of parallel four-stranded complexes by guanine-rich motifs in DNA and its implications for meiosis. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):364–366. doi: 10.1038/334364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shampay J., Blackburn E. H. Generation of telomere-length heterogeneity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):534–538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shampay J., Szostak J. W., Blackburn E. H. DNA sequences of telomeres maintained in yeast. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):154–157. doi: 10.1038/310154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Base sequence and evolution of guinea-pig alpha-satellite DNA. Nature. 1970 Aug 22;227(5260):794–798. doi: 10.1038/227794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szybalski W. Universal restriction endonucleases: designing novel cleavage specificities by combining adapter oligodeoxynucleotide and enzyme moieties. Gene. 1985;40(2-3):169–173. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walmsley R. M., Szostak J. W., Petes T. D. Is there left-handed DNA at the ends of yeast chromosomes? Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):84–86. doi: 10.1038/302084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild M. A., Gall J. G. An intervening sequence in the gene coding for 25S ribosomal RNA of Tetrahymena pigmentosa. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):565–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]