Abstract
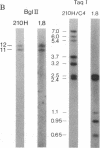
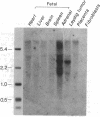
The gene encoding human adrenal steroid 21-hydroxylase (P450c21) and its highly similar pseudogene are duplicated in tandem with the two genes encoding the fourth component of human serum hemolytic complement (C4). This 60-kilobase gene complex, which lies within the major histocompatibility complex on the short arm of human chromosome 6, has been studied in considerable detail because genetic disorders in steroid 21-hydroxylation and in C4 are common. We have cloned a cDNA encoded by a previously unidentified gene in this region. This gene lies on the strand of DNA opposite from the strand containing the P450c21 and C4 genes, and it overlaps the last exon of P450c21. The newly identified gene encodes mRNAs of 3.5 and 1.8 kilobases that are expressed in the adrenal and in a Leydig cell tumor but are not expressed in nonsteroidogenic tissues. The sequence of the longest cDNA (2.7 kilobases) shows no similarity to known sequences available in two computerized data bases. The 5' end of this sequence is characterized by three repeats, each encoding about 100 amino acids flanked by potential sites for proteolytic cleavage. Although numerous studies have shown that gene deletions causing congenital adrenal hyperplasia occur in this region, none of these gene deletions extends into this newly identified gene, suggesting that it encodes an essential function.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman J. P., Bond C. T., Douglass J., Herbert E. Two mammalian genes transcribed from opposite strands of the same DNA locus. Science. 1987 Mar 20;235(4795):1514–1517. doi: 10.1126/science.3547652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belt K. T., Carroll M. C., Porter R. R. The structural basis of the multiple forms of human complement component C4. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):907–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Savouret J. F., Mendez B., West B. L., Karin M., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. A method for isolation of intact, translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA. 1983;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin D. D., Galbraith L. J., Seidman J. G., White P. C., Parker K. L. Nucleotide sequence analysis of murine 21-hydroxylase genes: mutations affecting gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9601–9605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung B. C., Matteson K. J., Miller W. L. Structure of a bovine gene for P-450c21 (steroid 21-hydroxylase) defines a novel cytochrome P-450 gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4243–4247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Keene M. A., Fechtel K., Fristrom J. W. Gene within a gene: nested Drosophila genes encode unrelated proteins on opposite DNA strands. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):33–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90482-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Tanae A., Inoue H., Hiromasa T., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Aberrant splicing and missense mutations cause steroid 21-hydroxylase [P-450(C21)] deficiency in humans: possible gene conversion products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7486–7490. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Yoshioka H., Yamane M., Gotoh O., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Complete nucleotide sequence of two steroid 21-hydroxylase genes tandemly arranged in human chromosome: a pseudogene and a genuine gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2841–2845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar M. A., Hodin R. A., Darling D. S., Chin W. W. A novel member of the thyroid/steroid hormone receptor family is encoded by the opposite strand of the rat c-erbA alpha transcriptional unit. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1128–1136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteson K. J., Chung B. C., Urdea M. S., Miller W. L. Study of cholesterol side-chain cleavage (20,22 desmolase) deficiency causing congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia using bovine-sequence P450scc oligodeoxyribonucleotide probes. Endocrinology. 1986 Apr;118(4):1296–1305. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-4-1296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteson K. J., Phillips J. A., 3rd, Miller W. L., Chung B. C., Orlando P. J., Frisch H., Ferrandez A., Burr I. M. P450XXI (steroid 21-hydroxylase) gene deletions are not found in family studies of congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5858–5862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L., Leisti S., Johnson L. K. Synthesis of growth hormone, prolactin, and proopiomelanocortin by intact adult ovine pituitary tissue in vitro. Endocrinology. 1982 Oct;111(4):1358–1367. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-4-1358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L., Levine L. S. Molecular and clinical advances in congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Pediatr. 1987 Jul;111(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80334-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L. Molecular biology of steroid hormone synthesis. Endocr Rev. 1988 Aug;9(3):295–318. doi: 10.1210/edrv-9-3-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima N., Horiuchi R., Shibuya Y., Fukushige S., Matsubara K., Toyoshima K., Yamamoto T. Two erbA homologs encoding proteins with different T3 binding capacities are transcribed from opposite DNA strands of the same genetic locus. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):31–39. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90169-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel Y., André J., Uring-Lambert B., Hauptmann G., Bétuel H., Tossi M., Forest M. G., David M., Bertrand J., Miller W. L. Rearrangements and point mutations of P450c21 genes are distinguished by five restriction endonuclease haplotypes identified by a new probing strategy in 57 families with congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):527–536. doi: 10.1172/JCI113914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Adesnik M., Coon M. J., Estabrook R. W., Gonzalez F. J., Guengerich F. P., Gunsalus I. C., Johnson E. F., Kemper B., Levin W. The P450 gene superfamily: recommended nomenclature. DNA. 1987 Feb;6(1):1–11. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Nelson D. R., Adesnik M., Coon M. J., Estabrook R. W., Gonzalez F. J., Guengerich F. P., Gunsalus I. C., Johnson E. F., Kemper B. The P450 superfamily: updated listing of all genes and recommended nomenclature for the chromosomal loci. DNA. 1989 Jan-Feb;8(1):1–13. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picado-Leonard J., Miller W. L. Homologous sequences in steroidogenic enzymes, steroid receptors and a steroid binding protein suggest a consensus steroid-binding sequence. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Nov;2(11):1145–1150. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-11-1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentice H. L., Schneider P. M., Strominger J. L. C4B gene polymorphism detected in a human cosmid clone. Immunogenetics. 1986;23(4):274–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00373024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer C. A., Gietz R. D., Hodgetts R. B. Overlapping transcription units in the dopa decarboxylase region of Drosophila. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):279–281. doi: 10.1038/322279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Huarte J., Belin D., Vassalli A., Rickles R. J., Vassalli J. D. Antisense RNA directed against the 3' noncoding region prevents dormant mRNA activation in mouse oocytes. Science. 1988 Aug 5;241(4866):680–684. doi: 10.1126/science.2456615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voutilainen R., Miller W. L. Coordinate tropic hormone regulation of mRNAs for insulin-like growth factor II and the cholesterol side-chain-cleavage enzyme, P450scc [corrected], in human steroidogenic tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1590–1594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voutilainen R., Miller W. L. Developmental expression of genes for the stereoidogenic enzymes P450scc (20,22-desmolase), P450c17 (17 alpha-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase), and P450c21 (21-hydroxylase) in the human fetus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Nov;63(5):1145–1150. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-5-1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., New M. I., Dupont B. Structure of human steroid 21-hydroxylase genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5111–5115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T., Fried M. A mouse locus at which transcription from both DNA strands produces mRNAs complementary at their 3' ends. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):275–279. doi: 10.1038/322275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Davis C. G., Brown M. S., Schneider W. J., Casey M. L., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. The human LDL receptor: a cysteine-rich protein with multiple Alu sequences in its mRNA. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Krol A. R., Mol J. N., Stuitje A. R. Modulation of eukaryotic gene expression by complementary RNA or DNA sequences. Biotechniques. 1988 Nov-Dec;6(10):958–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]