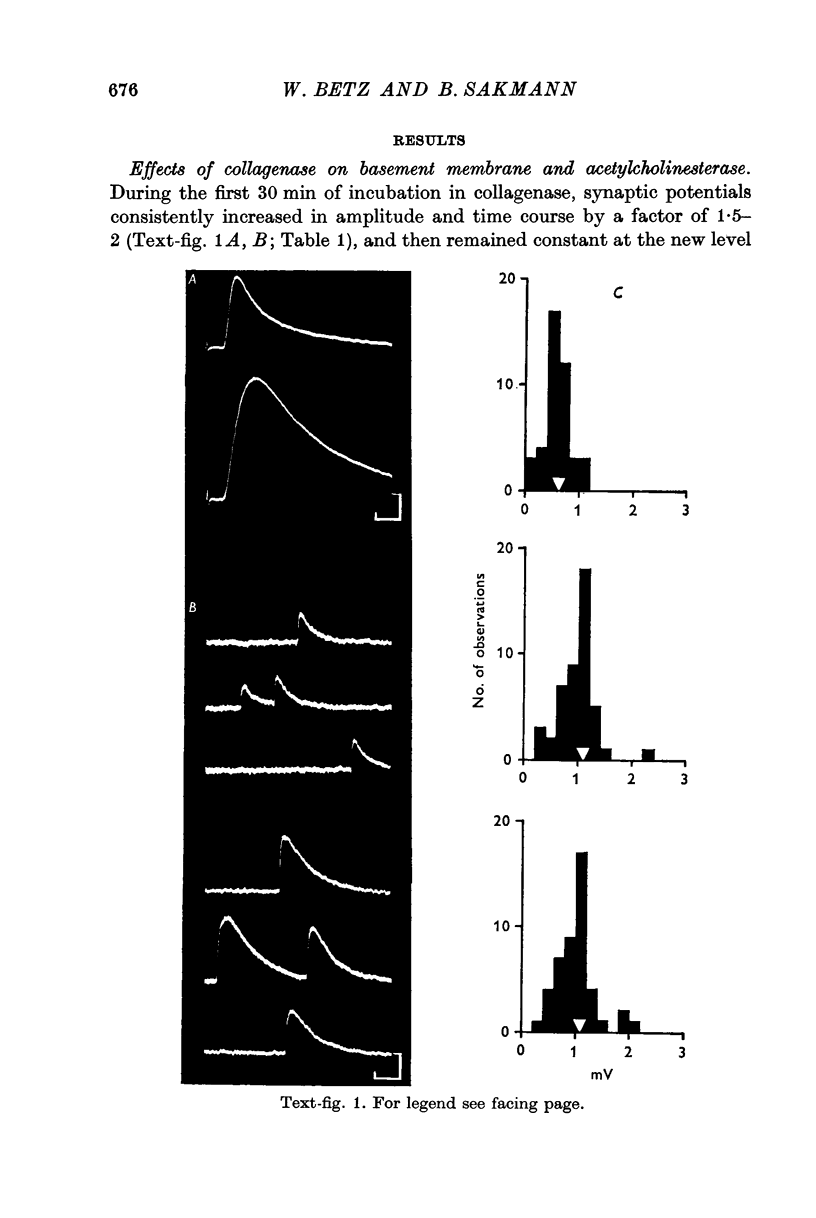
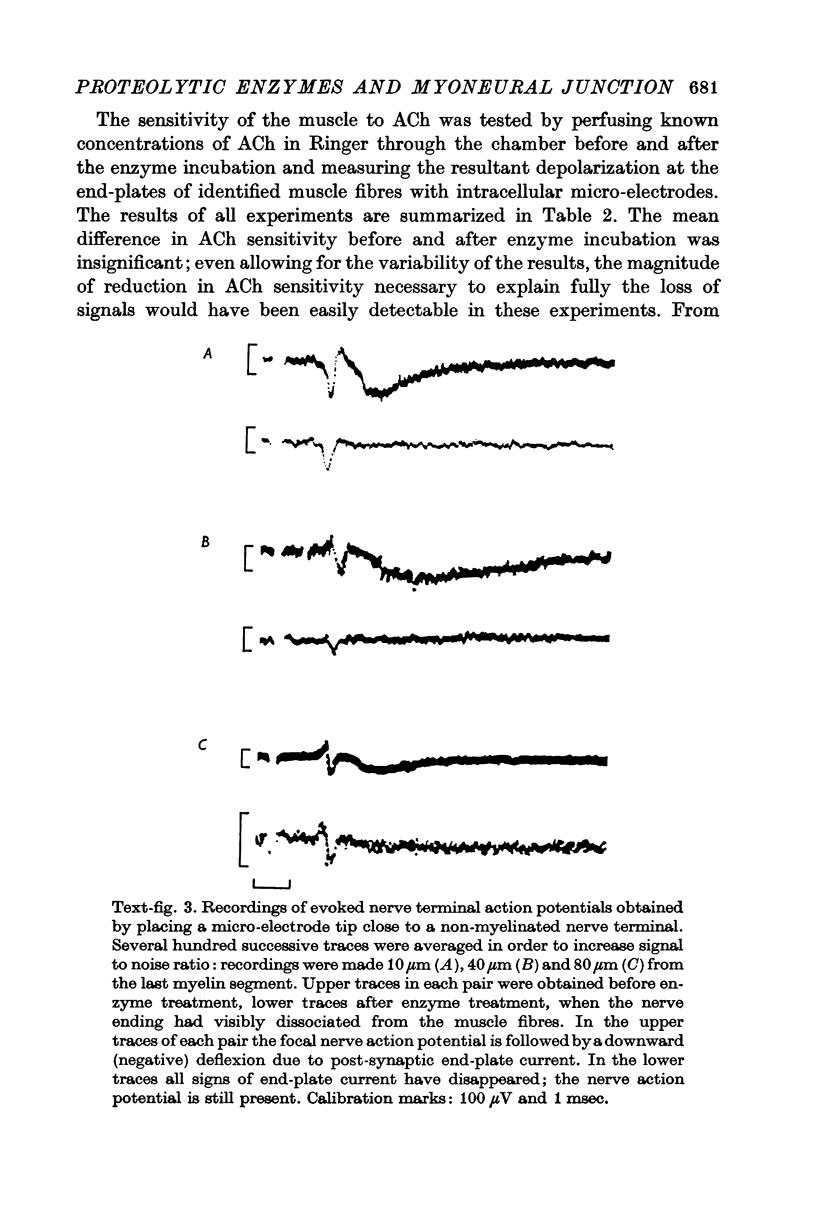
Abstract
1. Frog cutaneous pectoris nerve-muscle preparations were incubated with collagenase and protease and examined with electrophysiological and electron microscopic techniques.
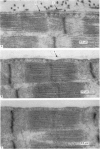
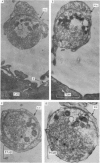
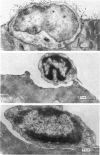
2. The physiological properties and intracellular ultrastructural appearance of individual muscle and nerve cells were not affected by the enzyme treatment. However, neuromuscular transmission and the morphology of the nerve-muscle junction were altered.
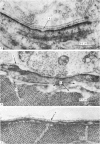
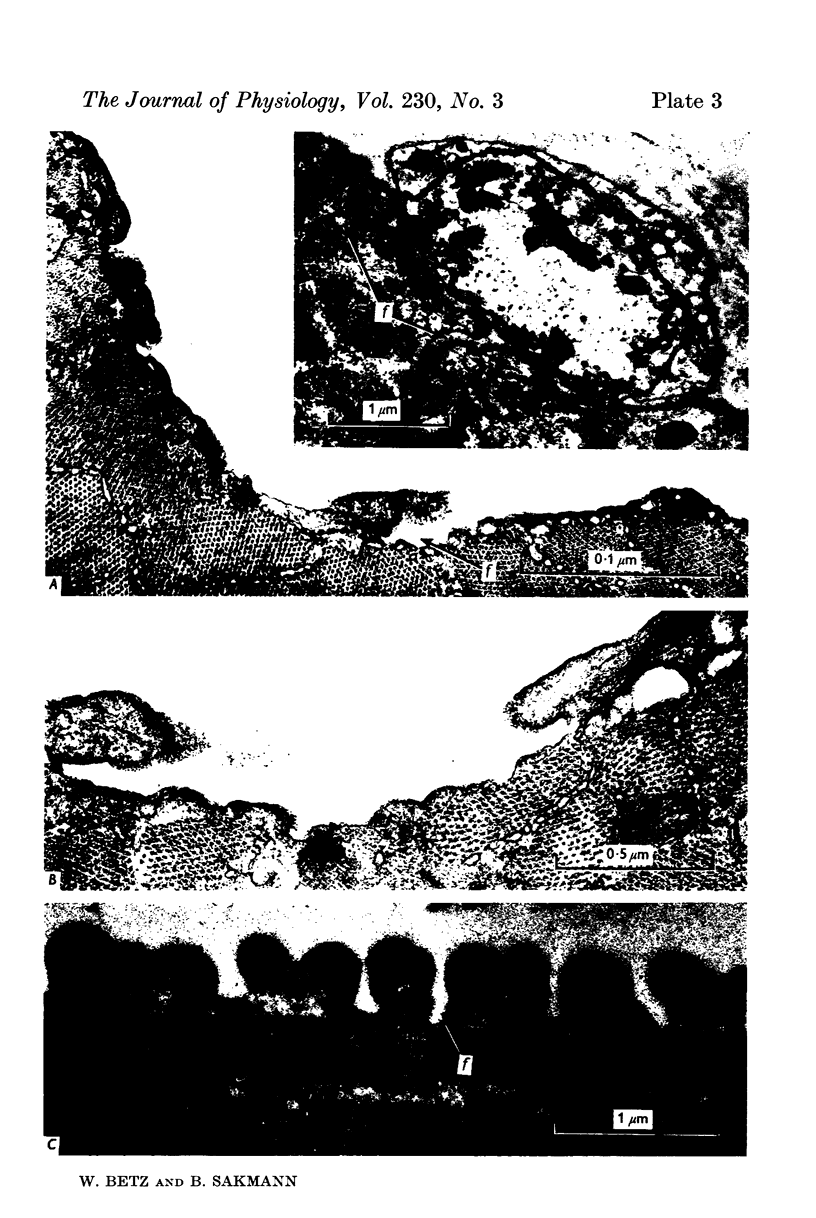
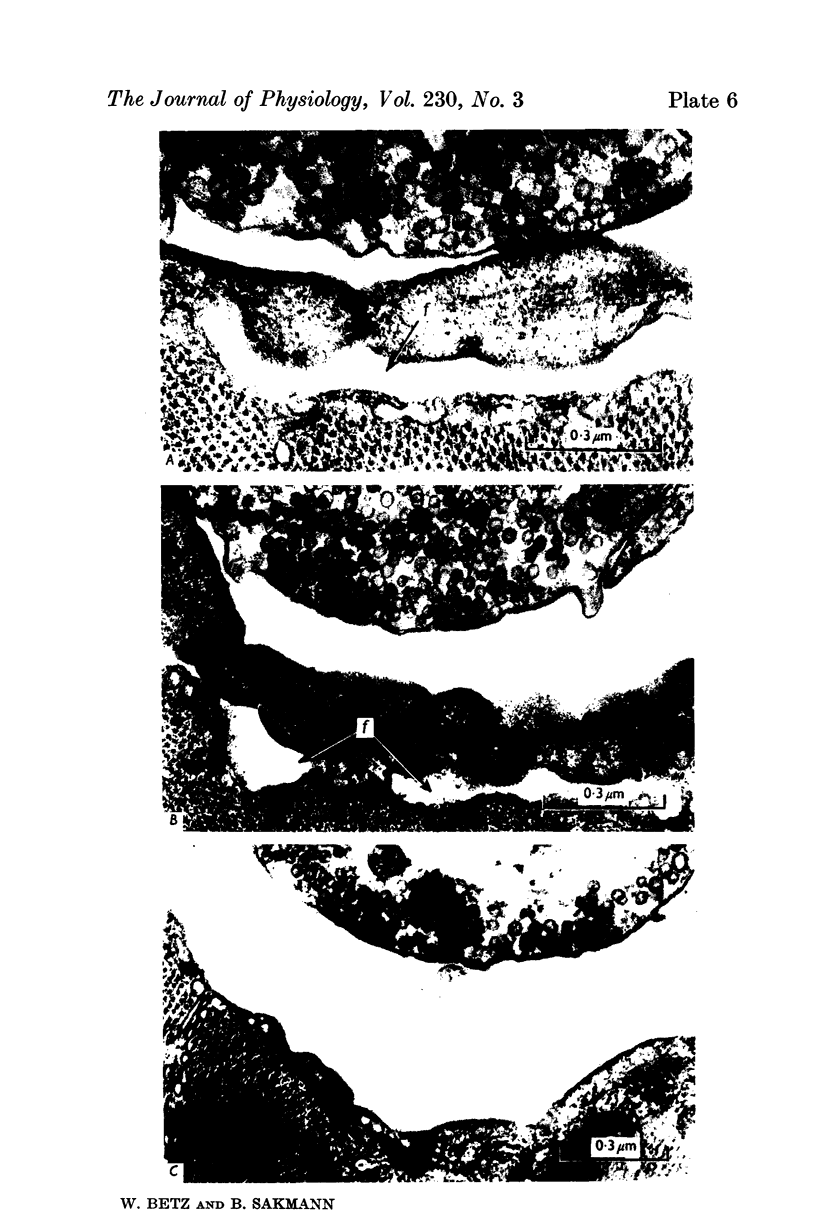
3. Collagenase produced an irreversible loss of activity of end-plate cholinesterase and a partial loss of stainable `synaptic cleft material'.
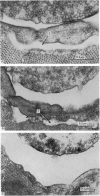
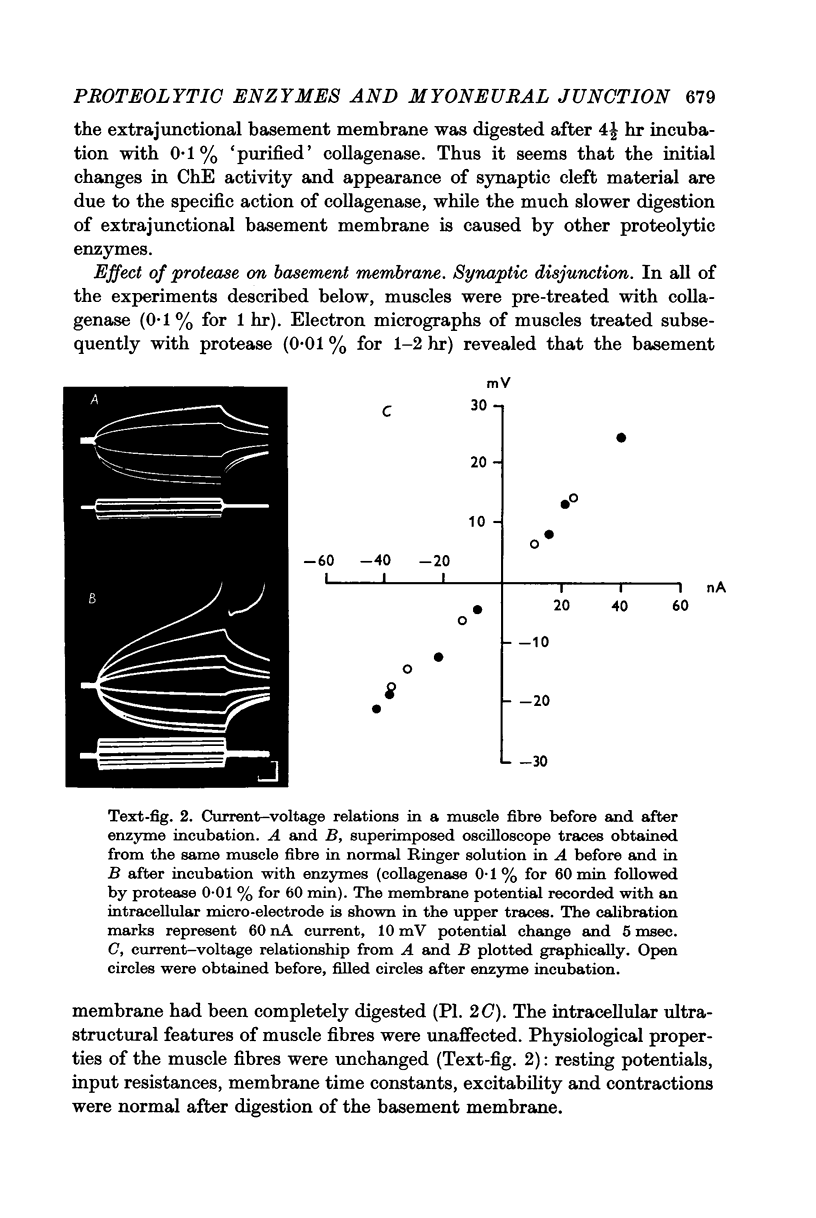
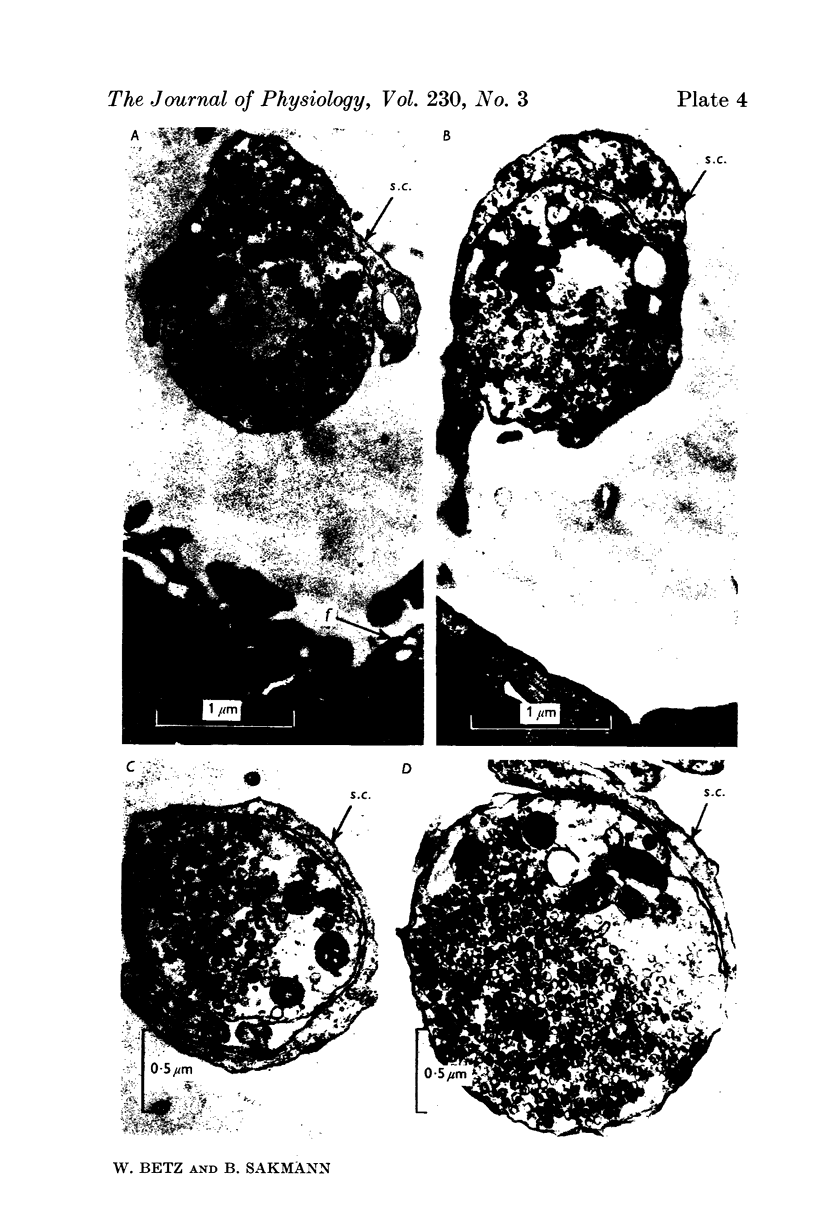
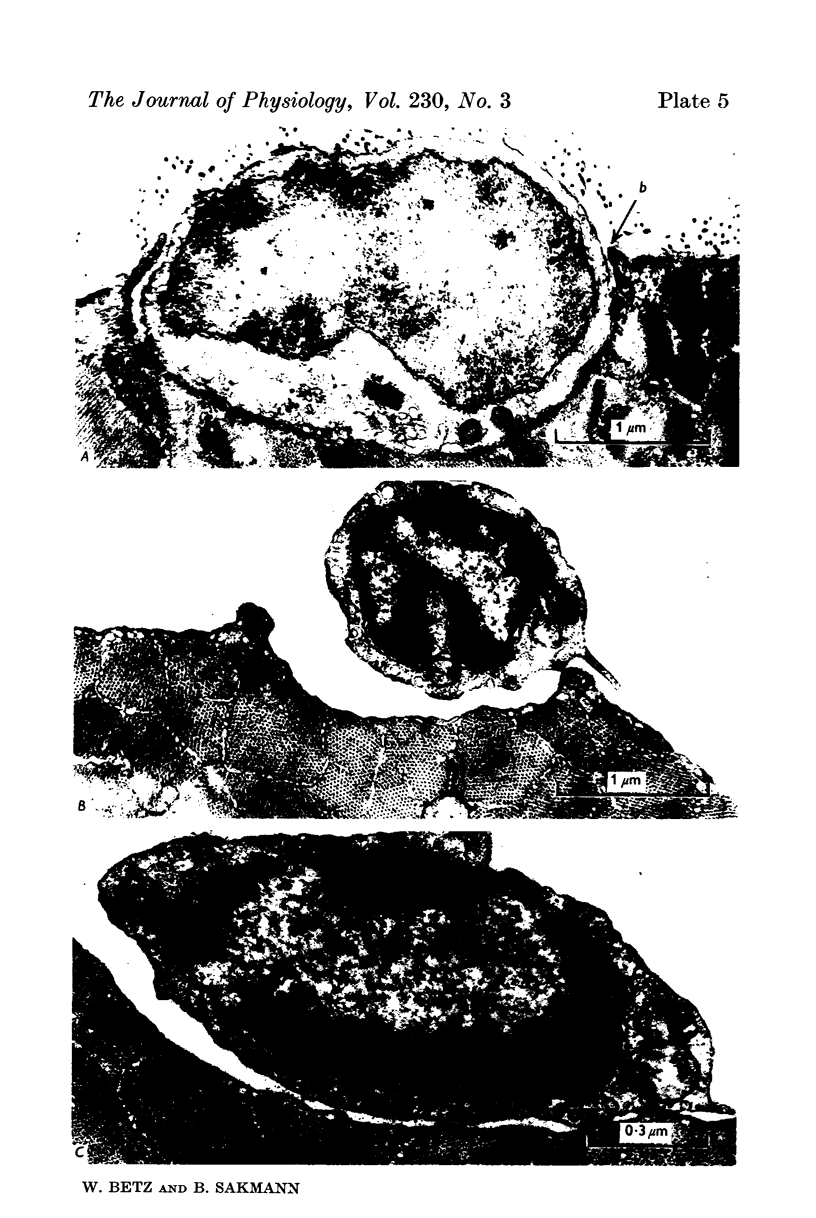
4. Protease produced these changes and, in addition, the entire basement membrane was digested, which led to `synaptic disjunction' of nerve terminals and muscle end-plates.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albuquerque E. X., Sokoll M. D., Sonesson B., Thesleff S. Studies on the nature of the cholinergic receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1968 Aug;4(1):40–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(68)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRKS R., KATZ B., MILEDI R. Dissociation of the 'surface membrane complex' in atrophic muscle fibres. Nature. 1959 Nov 7;184(Suppl 19):1507–1508. doi: 10.1038/1841507a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz W., Sakmann B. "Disjunction" of frog neuromuscular synapses by treatment with proteolytic enzymes. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 21;232(29):94–95. doi: 10.1038/newbio232094a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom F. E., Aghajanian G. K. Fine structural and cytochemical analysis of the staining of synaptic junctions with phosphotungstic acid. J Ultrastruct Res. 1968 Mar;22(5):361–375. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(68)90027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondareff W. Demonstration of an intercellular substance in mouse cerebral cortex. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1967;81(3):366–373. doi: 10.1007/BF00342761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G. Effects of descending impulses on transmission through the spinocervical tract. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(1):103–125. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G., Franz D. N. Responses of spinocervical tract neurones to natural stimulation of identified cutaneous receptors. Exp Brain Res. 1969;7(3):231–249. doi: 10.1007/BF00239031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., KOSTYUK P. G., SCHMIDT R. F. Presynaptic inhibition of the central actions of flexor reflex afferents. J Physiol. 1962 May;161:258–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erulkar S. D., Sprague J. M., Whitsel B. L., Dogan S., Jannetta P. J. Organization of the vestibular projection to the spinal cord of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1966 Jul;29(4):626–664. doi: 10.1152/jn.1966.29.4.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farquhar M. G., Palade G. E. Cell junctions in amphibian skin. J Cell Biol. 1965 Jul;26(1):263–291. doi: 10.1083/jcb.26.1.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fetz E. E. Pyramidal tract effects on interneurons in the cat lumbar dorsal horn. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Jan;31(1):69–80. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAY E. D., REVEL J. P. Autoradiographic studies of the origin of the basement lamella in Ambystoma. Dev Biol. 1963 Mar;6:152–168. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(63)90114-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall Z. W., Kelly R. B. Enzymatic detachment of endplate acetylcholinesterase from muscle. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 14;232(28):62–63. doi: 10.1038/newbio232062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanak H., Böck P. Die Feinstruktur der Muskel-Sehnenverbindung von Skelett- und Herzmuskel. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Jul;36(1):68–85. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)80089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Jankowska E., Lundberg A. Post-synaptic excitation and inhibition from primary afferents in neurones of the spinocervical tract. J Physiol. 1968 Dec;199(3):569–592. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. J. THE LOCALIZATION OF CHOLINESTERASE ACTIVITY IN RAT CARDIAC MUSCLE BY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1964 Nov;23:217–232. doi: 10.1083/jcb.23.2.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. PROPAGATION OF ELECTRIC ACTIVITY IN MOTOR NERVE TERMINALS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Feb 16;161:453–482. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kefalides N. A. Isolation and characterization of the collagen from glomerular basement membrane. Biochemistry. 1968 Sep;7(9):3103–3112. doi: 10.1021/bi00849a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAPORTE Y., LUNDBERG A., OSCARSSON O. Functional organization of the dorsal spino-cerebellar tract in the cat. I. Recording of mass discharge in dissected Flechsig's fasciculus. Acta Physiol Scand. 1956 Mar 24;36(1-2):175–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1956.tb01316.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBERG A., OSCARSSON O. Three ascending spinal pathways in the dorsal part of the lateral funiculus. Acta Physiol Scand. 1961 Jan;51:1–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1961.tb02108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAURO A. Satellite cell of skeletal muscle fibers. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:493–495. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massoulié J., Rieger F., Tsuji S. Solubilisation de l'acetylcholinestérase des organes électriques de gymnote. Action de la trypsine. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jul;14(3):430–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel F. M., Baker R. F., Wayland H. Quantitation of human red blood cell fixation by glutaraldehyde. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jan;48(1):91–100. doi: 10.1083/jcb.48.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfenninger K. H. The cytochemistry of synaptic densities. II. Proteinaceous components and mechanism of synaptic connectivity. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Jun;35(5):451–475. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)80005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON J. D. Some features of the ultrastructure of reptilian skeletal muscle. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1956 Jul 25;2(4):369–380. doi: 10.1083/jcb.2.4.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUDIN D. O., EISENMAN G. A method for dissection and electrical study in vitro of mammalian central nervous tissue. Science. 1951 Sep 21;114(2960):300–302. doi: 10.1126/science.114.2960.300-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambourg A., Leblond C. P. Electron microscope observations on the carbohydrate-rich cell coat present at the surface of cells in the rat. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jan;32(1):27–53. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoumura K. Patterns of fiber degeneration in the lateral wall of the suprasylvian gyrus (Clare-Bishop area) following lesions in the visual cortex in cats. Brain Res. 1972 Aug 11;43(1):264–267. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90293-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAUB A. LOCAL, SEGMENTAL AND SUPRASPINAL INTERACTION WITH A DORSOLATERAL SPINAL CUTANEOUS AFFERENT SYSTEM. Exp Neurol. 1964 Oct;10:357–374. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(64)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENABLE J. H., COGGESHALL R. A SIMPLIFIED LEAD CITRATE STAIN FOR USE IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1965 May;25:407–408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall P. D. The laminar organization of dorsal horn and effects of descending impulses. J Physiol. 1967 Feb;188(3):403–423. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]