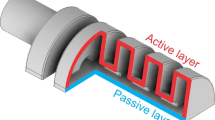
Abstract
Soft actuators have emerged as a promising solution for applications that conventional actuators are unable to address. Soft pneumatic actuators (SPAs) are widely used among various types of soft actuators due to their good performance and ease of use. However, the control of SPA movement poses challenges due to limited knowledge regarding their behaviours and characteristics, which are significantly influenced by the design. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the impact of three design parameters commonly modified during SPA design: chamber length, number, and wall thickness. Specifically, we examine their effects on the curvature and tip force generated by 3D printed SPAs. In this experimental study, we printed 21 SPAs using fused deposition modelling (FDM) 3D printing technology, employing varying chamber lengths, numbers, and wall thicknesses. The SPAs were then inflated with pressurized air, and the resulting outcomes were measured and analysed. Our findings reveal that increasing the chamber length leads to a reduction in the generated tip force, while also having a minor effect on reducing the curvature. Conversely, the addition of chambers enhances the curvature of the SPA, and diminishes the generated tip force, likely due to the presence of buckling chambers in the mid-body of the SPA. Notably, modifying the wall thickness of the chamber significantly affects the curvature, exerting a larger impact compared to the number of chambers. However, wall thickness does not significantly influence the generated tip force. These findings provide valuable insights for engineers to better comprehend the parameters affecting SPA characteristics, thereby reducing prototyping time and cost.







Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Adib, B.M.: “Analysis of The Effect of Volume, Wall Thickness, Number of Section, and Actuation Pressure on Tip-Force of 3D Printed Soft Pneumatic Actuator. Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta (2020)
Andrialovanirina, N., Ponton, D., Behivoke, F., Mahafina, J., Léopold, M.: A powerful method for measuring fish size of small-scale fishery catches using ImageJ. Fish Res. 223, 105425 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FISHRES.2019.105425
Calisti, M., Picardi, G., Laschi, C.: Fundamentals of soft robot locomotion. J. R. Soc. Interface 14(130), 20170101 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2017.0101
Chen, F., Wang, M.Y.: Design Optimization of Soft Robotics. IETE J. Res. 66(6), 731–732 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/03772063.2020.1842159
Chen, L., Yang, C., Wang, H., Branson, D.T., Dai, J.S., Kang, R.: Design and modeling of a soft robotic surface with hyperelastic material. Mech. Mach. Theory 130, 109–122 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2018.08.010
Cho, K.J., Koh, J.S., Kim, S., Chu, W.S., Hong, Y., Ahn, S.H.: Review of manufacturing processes for soft biomimetic robots. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 10(3), 171–181 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-009-0064-6
Cianchetti, M., Laschi, C., Menciassi, A., Dario, P.: Biomedical applications of soft robotics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 3(6), 143–153 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-018-0022-y
De Falco, I., Cianchetti, M., Menciassi, A.: A soft multi-module manipulator with variable stiffness for minimally invasive surgery. Bioinspir. Biomim. 12, 056008 (2017)
Decroly, G., et al.: Programmable stimuli-responsive actuators for complex motions in soft robotics: concept, design and challenges. Actuators 9(4), 1–44 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/act9040131
Elsayed, Y., et al.: Finite element analysis and design optimization of a pneumatically actuating silicone module for robotic surgery applications. Soft Robot. 1(4), 255–262 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1089/soro.2014.0016
eSUN, “eFlex(TPU-87A) filament__Natural.” https://www.esun3d.net/products/300.html (Accessed 29 Mar 2022)
Gajewski, M., Szczerba, R., Jemioło, S.: Modelling of elastomeric bearings with application of Yeoh hyperelastic material model. Procedia Eng. 111, 220–227 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2015.07.080
Gariya, N., Kumar, P., Prasad, B., Singh, T.: Soft pneumatic actuator with an embedded flexible polymeric piezoelectric membrane for sensing bending deformation. Mater. Today Commun. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2023.105910
Georgopoulou, A., Egloff, L., Vanderborght, B., Clemens, F.: A sensorized soft pneumatic actuator fabricated with extrusion-based additive manufacturing. Actuators 10(5), 102 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/act10050102
Gul, J.Z., et al.: 3D printing for soft robotics–A review. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 19(1), 243–262 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/14686996.2018.1431862
Herianto, H., Irawan, W., Ritonga, A.S., Prastowo, A.: Design and fabrication in the loop of soft pneumatic actuators using fused deposition modelling. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 298, 111556 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2019.111556
Hu, W., Mutlu, R., Li, W., Alici, G.: A structural optimisation method for a soft pneumatic actuator. Robotics 7(2), 1–16 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics7020024
Hyatt, P., Wingate, D., Killpack, M.D.: Model-based control of soft actuators using learned non-linear discrete-time models. Front. Robot. AI (2019). https://doi.org/10.3389/frobt.2019.00022
Id, E.H.S., et al.: Reverse pneumatic artificial muscles ( rPAMs ): Modeling , integration, and control. pp. 1–24, 2018.
Kim, S., Laschi, C., Trimmer, B.: Soft robotics: a bioinspired evolution in robotics. Trends Biotechnol. 31(5), 287–294 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TIBTECH.2013.03.002
Kim, W., Eom, J., Cho, K.-J.: A dual-origami design that enables the quasisequential deployment and bending motion of soft robots and grippers. Adv. Intell. Syst. 4(3), 2100176 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/aisy.202100176
Laschi, C., Mazzolai, B., Cianchetti, M.: Soft robotics: technologies and systems pushing the boundaries of robot abilities. Sci. Robot. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1126/scirobotics.aah3690
Li, D., Dornadula, V., Lin, K., Wehner, M.: Position control for soft actuators, next steps toward inherently safe interaction. Electronics (Switzerland) 10(9), 1116 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10091116
Li, M., Pal, A., Aghakhani, A., Pena-Francesch, A., Sitti, M.: Soft actuators for real-world applications. Nat. Rev. Mater. 7(3), 235–249 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-021-00389-7
Li, M., Pal, A., Aghakhani, A., Pena-Francesch, A., Sitti, M.: Soft actuators for real-world applications. Nat. Rev. Mater. 7(3), 235–249 (2022b). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-021-00389-7
Manns, M., Morales, J., Fo, P.F.: ScienceDirect ScienceDirect Additive manufacturing silicon based PneuNets soft robotic actuators 28th CIRP of *, functional Frohn b architecture of A new methodology to Martin analyze the and existing products for an assembly oriented family identificatio. Procedia CIRP 72, 328–333 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2018.03.186
Marchese, A.D., Tedrake, R., Rus, D.: Dynamics and trajectory optimization for a soft spatial fluidic elastomer manipulator. Int. J. Robot. Res. 35(8), 1000–1019 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1177/0278364915587926
Morrow, J., et al.: Improving Soft Pneumatic Actuator fingers through integration of soft sensors, position and force control, and rigid fingernails. In IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2016, pp. 5024–5031. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2016.7487707.
Mosadegh, B., et al.: Pneumatic networks for soft robotics that actuate rapidly. Adv. Funct. Mater. 24, 2163–2170 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201303288
Moseley, P., Florez, J.M., Sonar, H.A., Agarwal, G., Curtin, W., Paik, J.: Modeling, design, and development of soft pneumatic actuators with finite element method. Adv. Eng. Mater. 18(6), 978–988 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.201500503
Oshiro, T., Olson, G., Palmer, C.: Evaluation of 3D printed soft robots in radiation environments and comparison with molded counterparts. Front. Robot. AI 6, 1–14 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3389/frobt.2019.00040
Paterna, M., De Benedictis, C., Ferraresi, C.: The research on soft pneumatic actuators in Italy: Design solutions and applications. Actuators 11(11), 328 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/act11110328
Renaud, C., Cros, J.M., Feng, Z.Q., Yang, B.: The Yeoh model applied to the modeling of large deformation contact/impact problems. Int. J. Impact Eng. 36(5), 659–666 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2008.09.008
Ritonga, S.A.: Analysis of The Effect of Dimensions, Number of Chambers, and Geometry on Strength and Curvature of 3D Printed Soft Pneumatic Actuator As a Stroke Rehabilitation Glove. Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta (2019)
Robertson, M.A., Sadeghi, H., Florez, J.M., Paik, J.: Soft pneumatic actuator fascicles for high force and reliability. Soft Robot. 4(1), 23–32 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1089/soro.2016.0029
Robots, L., Muscles, A., Tawk, C., Spinks, G.M.: Bioinspired 3D printable soft vacuum actuators. Soft Robot. 00(00), 1–10 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1089/soro.2018.0021
Rus, D., Tolley, M.T.: Design, fabrication and control of soft robots. Nature 521(7553), 467–475 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14543
Salem, M.E.M., Wang, Q., Xu, M.H.: Application of neural network fitting for modeling the pneumatic networks bending soft actuator behavior. Engineering Research Express 4(1), 015032 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1088/2631-8695/ac58e7
Schaffner, M., Faber, J.A., Pianegonda, L., Rühs, P.A.: programmable bioinspired architectures. Nat. Commun. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03216-w
Selvadurai, A.P.S.: Deflections of a rubber membrane. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 54(6), 1093–1119 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmps.2006.01.001
Shepherd, R.F., et al.: Multigait soft robot. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1116564108
Shintake, J., Cacucciolo, V., Floreano, D., Shea, H.: Soft robotic grippers. Adv. Mater. 30(29), 1707035 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201707035
Sun, Y., Song, Y.S., Paik, J.: Characterization of silicone rubber based soft pneumatic actuators. IEEE Int. Conf. Intell. Robots Syst. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2013.6696995
Suzuki, T., et al.: Reliability of measurement using Image J for reach distance and movement angles in the functional reach test. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 33, 112–117 (2021)
Tan, N., Gu, X., Ren, H.: Design, characterization and applications of a novel soft actuator driven by flexible shafts. Mech Mach Theory 122, 197–218 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2017.12.021
Tang, X., et al.: A review of soft actuator motion: actuation, design, manufacturing and applications. Actuators 11(11), 331 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/act11110331
Tawk, C., Alici, G.: Finite element modeling in the design process of 3D printed pneumatic soft actuators and sensors. Robotics (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/ROBOTICS9030052
Tawk, C., Alici, G.: A review of 3D-printable soft pneumatic actuators and sensors: research challenges and opportunities. Adv. Intell. Syst. 3(6), 2000223 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/aisy.202000223
Tawk, C., Mutlu, R., Alici, G.: A 3D printed modular soft gripper integrated with metamaterials for conformal grasping. Front. Robot. AI 8, 1–13 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3389/frobt.2021.799230
Thalman, C., Artemiadis, P.: A review of soft wearable robots that provide active assistance: trends, common actuation methods, fabrication, and applications. Wearable Technol. 1, 1–27 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1017/wtc.2020.4
Treratanakulchai, S., Franco, E., Garriga-Casanovas, A., Minghao, H., Kassanos, P., Baena, F.R.y.: Development of a 6 DOF Soft Robotic Manipulator with Integrated Sensing Skin. In IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Kyoto, Japan, 2022, pp. 6944–6951.
Trimmer, B.: Soft robots. Curr. Biol. 23(15), R639–R641 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2013.04.070
Wakimoto, S., Suzumori, K., Ogura, K.: Miniature pneumatic curling rubber actuator generating bidirectional motion with one air-supply tube. Adv. Robot. 25(9–10), 1311–1330 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1163/016918611X574731
Wallin, R.F., Pikul, T.J., Shepherd, J.: 3D printing of soft robotic systems. Nat. Rev. Mat. 3, 84–100 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-018-0002-2
Wang, T., Ge, L., Gu, G.: Programmable design of soft pneu-net actuators with oblique chambers can generate coupled bending and twisting motions. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 271, 131–138 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2018.01.018
Whitesides, G.M.: Soft robotics. Angewandte Chemie – Int. Edn. 57(16), 4258–4273 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201800907
Yap, H.K., Ng, H.Y., Yeow, C.H.: High-force soft printable pneumatics for soft robotic applications. Soft Robot. 3(3), 144–158 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1089/soro.2016.0030
Zan, Y., et al.: Soft actuators based on spin-crossover particles embedded in thermoplastic polyurethane. Adv. Intell. Syst. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/aisy.202200432
Zolfagharian, M., Denk, A., Bodaghi, M.: Topology-optimized 4D printing of a soft Actuator. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 33, 418–430 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10338-019-00137-z
Zolfagharian, A., et al.: Actuators: fabrication, modelling, and control and control. Virt. Phys. Prototyp. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/17452759.2020.1795209
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ritonga, S.A., Herianto, Muzhaffar, A. et al. Analysis of design parameters’ effect on 3D printed soft pneumatic actuator generated curvature and tip force. Int J Intell Robot Appl 7, 752–762 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41315-023-00296-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41315-023-00296-w