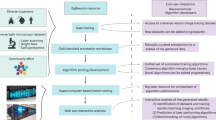
Abstract
The study of neuronal morphology in relation to function, and the development of effective medicines to positively impact this relationship in patients suffering from neurodegenerative diseases, increasingly involves image-based high-content screening and analysis. The first critical step toward fully automated high-content image analyses in such studies is to detect all neuronal cells and distinguish them from possible non-neuronal cells or artifacts in the images. Here we investigate the performance of well-established machine learning techniques for this purpose. These include support vector machines, random forests, k-nearest neighbors, and generalized linear model classifiers, operating on an extensive set of image features extracted using the compound hierarchy of algorithms representing morphology, and the scale-invariant feature transform. We present experiments on a dataset of rat hippocampal neurons from our own studies to find the most suitable classifier(s) and subset(s) of features in the common practical setting where there is very limited annotated data for training. The results indicate that a random forests classifier using the right feature subset ranks best for the considered task, although its performance is not statistically significantly better than some support vector machine based classification models.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderl, J.L., Redpath, S., Ball, A.J. (2009). A neuronal and astrocyte co-culture assay for high content analysis of neurotoxicity. Journal of Visualized Experiments, 5(27), 1173.
Antony, P.M.A., Trefois, C., Stojanovic, A., Baumuratov, A.S., Kozak, K. (2013). Light microscopy applications in systems biology: opportunities and challenges. Cell Communication and Signaling, 11(24), 1–19.
Arganda-Carreras, I., Kaynig, V., Rueden, C., Eliceiri, K.W., Schindelin, J., Cardona, A., Seung, H.S. (2017). Trainable Weka Segmentation: a machine learning tool for microscopy pixel classification. Bioinformatics, 33(15), 2424–2426.
Ascoli, G.A. (2015). Trees of the brain, roots of the mind. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Bianchini, M., & Scarselli, F. (2014). On the complexity of neural network classifiers: a comparison between shallow and deep architectures. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 25(8), 1553–1565.
Bischl, B., Mersmann, O., Trautmann, H., Weihs, C. (2012). Resampling methods for meta-model validation with recommendations for evolutionary computation. Evolutionary Computation, 20(2), 249–275.
Bischl, B., Lang, M., Kotthoff, L., Schiffner, J., Richter, J., Jones, Z., Casalicchio, G. (2016). mlr: Machine Learning in R. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=mlr.
Bishop, C.M. (2006). Pattern recognition and machine learning. New York: Springer.
Boser, B.E., Guyon, I.M., Vapnik, V.N. (1992). A training algorithm for optimal margin classifiers. In Proceedings of the 5th Annual ACM Workshop on Computational Learning Theory (pp. 144–152).
Bougen-Zhukov, N., Loh, S.Y., Lee, H.K., Loo, L.H. (2017). Large-scale image-based screening and profiling of cellular phenotypes. Cytometry Part A, 91(2), 115–125.
Branco, P., Torgo, L., Ribeiro, R.P. (2016). A survey of predictive modeling on imbalanced domains. ACM Computing Surveys, 49(2), 31:1–31:50.
Bredenbeek, P.J., Frolov, I., Rice, C.M., Schlesinger, S. (1993). Sindbis virus expression vectors: packaging of RNA, replicons by using defective helper RNAs. Journal of Virology, 67(11), 6439–6446.
Breiman, L. (2001). Random forests. Machine Learning, 45(1), 5–32.
Burges, C.J.C. (1998). A tutorial on support vector machines for pattern recognition. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2(2), 121–167.
Charoenkwan, P., Hwang, E., Cutler, R.W., Lee, H.C., Ko, L.W., Huang, H.L., Ho, S.Y. (2013). HCS-Neurons: identifying phenotypic changes in multi-neuron images upon drug treatments of high-content screening. BMC Bioinformatics, 14(S16), S12.
Chawla, N.V., Bowyer, K.W., Hall, L.O., Kegelmeyer, W.P. (2002). SMOTE: Synthetic minority over-sampling technique. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 16(1), 321–357.
Chawla, N.V., Japkowicz, N., Kotcz, A. (2004). Editorial: Special issue on learning from imbalanced data sets. ACM SIGKDD Explorations Newsletter, 6(1), 1–6.
Cover, T., & Hart, P. (1967). Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 13(1), 21–27.
Cristianini, N., & Shawe-Taylor, J. (2000). An introduction to support vector machines and other Kernel-Based learning methods. Cambridge: University Press.
Cuesto, G., Enriquez-Barreto, L., Caramés, C., Cantarero, M., Gasull, X., Sandi, C., Ferrús, A., Acebes, Á., Morales, M. (2011). Phosphoinositide-3-kinase activation controls synaptogenesis and spinogenesis in hippocampal neurons. Journal of Neuroscience, 31(8), 2721–2733.
Dalal, N., & Triggs, B. (2005). Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 886–893).
Daskalaki, S., Kopanas, I., Avouris, N. (2006). Evaluation of classifiers for an uneven class distribution problem. Applied Artificial Intelligence, 20(5), 381–417.
Dehmelt, L., Poplawski, G., Hwang, E., Halpain, S. (2011). NeuriteQuant: an open source toolkit for high content screens of neuronal morphogenesis. BMC Neuroscience, 12(100), 1–13.
Dragunow, M. (2008). High-content analysis in neuroscience. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 9(10), 779–788.
Ebrahimpour, M.K., Zare, M., Eftekhari, M., Aghamolaei, G. (2017). Occam’s razor in dimension reduction: using reduced row Echelon, form for finding linear independent features in high dimensional microarray datasets. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 62, 214–221.
Enriquez-Barreto, L., Cuesto, G., Dominguez-Iturza, N., Gavilán, E., Ruano, D., Sandi, C., Fernández-Ruiz, A., Martín-Vázquez, G., Herreras, O., Morales, M. (2014). Learning improvement after PI3K, activation correlates with de novo formation of functional small spines. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience, 6, 54.
Enriquez-Barreto, L., & Morales, M. (2016). The PI3K, signaling pathway as a pharmacological target in autism related disorders and schizophrenia. Molecular and Cellular Therapies, 4, 2.
Fawcett, T. (2006). An introduction to ROC, analysis. Pattern Recognition Letters, 27(8), 861–874.
Fei-Fei, L., & Perona, P. (2005). A Bayesian hierarchical model for learning natural scene categories. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, (Vol. 2 pp. 524–531).
Fernandez-Lozano, C., Gestal, M., Munteanu, C.R., Dorado, J., Pazos, A. (2016). A methodology for the design of experiments in computational intelligence with multiple regression models. PeerJ, 4, e2721.
Finner, H. (1993). On a monotonicity problem in step-down multiple test procedures. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 88(423), 920–923.
Forman, G., & Scholz, M. (2010). Apples-to-apples in cross-validation studies: pitfalls in classifier performance measurement. ACM SIGKDD Explorations Newsletter, 12(1), 49–57.
Friedman, M. (1940). A comparison of alternative tests of significance for the problem of m rankings. Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 11(1), 86–92.
Friedman, J., Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R. (2010). Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent. Journal of Statistical Software, 33(1), 1–22.
Gabor, D. (1946). Theory of communication. Journal of the Institution of Electrical Engineers — Part III: Radio and Communication Engineering, 93(26), 429–457.
García, S., Fernández, A., Luengo, J., Herrera, F. (2010). Advanced nonparametric tests for multiple comparisons in the design of experiments in computational intelligence and data mining: experimental analysis of power. Information Sciences, 180(10), 2044–2064.
García, V., Mollineda, R.A., Sȧnchez, J.S. (2014). A bias correction function for classification performance assessment in two-class imbalanced problems. Knowledge-Based Systems, 59, 66–74.
Ghosh, A., Kumar, H., Sastry, P.S. (2017). Robust loss functions under label noise for deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (pp. 1919–1925).
Goslin, K., Asumussen, H., Banker, G. (1998). Rat hippocampal neurons in low-density culture. In Culturing Nerve cells (pp. 339–370). Cambridge: The MIT Press.
Gosain, A., & Sardana, S. (2017). Handling class imbalance problem using oversampling techniques: a review, In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (pp. 79–85).
Gradshteyn, I.S., & Ryzhik, I.M. (1994). Table of integrals, series and products. New York: Academic Press.
Greenspan, H., van Ginneken, B., Summers, R.M. (2016). Deep learning in medical imaging: overview and future promise of an exciting new technique. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 35(5), 1153–1159.
Gupta, P., Batra, S.S., Jayadeva. (2017). Sparse short-term time series forecasting models via minimum model complexity. Neurocomputing, 243, 1–11.
Hadjidementriou, E., Grossberg, M., Nayar, S. (2001). Spatial information in multiresolution histograms. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. I.702–I.709).
Haixiang, G., Yijing, L., Shang, J., Mingyun, G., Yuanyue, H., Bing, G. (2017). Learning from class-imbalanced data: review of methods and applications. Expert Systems with Applications, 73, 220–239.
Haralick, R.M., Shanmugam, K., Dinstein, I. (1973). Textural features for image classification. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 3(6), 610–621.
He, H., & Garcia, E.A. (2009). Learning from imbalanced data. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 21(9), 1263–1284.
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J. (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 770–778).
Hechenbichler, K., & Schliep, K. (2004). Weighted k-nearest-neighbor techniques and ordinal classification. Sonderforschungsbereich, 386(399), 1–16.
Hong, X., Gao, J., Chen, S., Harris, C.J. (2013). Particle swarm optimisation assisted classification using elastic net prefiltering. Neurocomputing, 122, 210–220.
Horvath, P., Wild, T., Kutay, U., Csucs, G. (2011). Machine learning improves the precision and robustness of high-content screens: using nonlinear multiparametric methods to analyze screening results. Journal of Biomolecular Screening, 16(9), 1059–1067.
Iacca, G., Neri, F., Mininno, E., Ong, Y.S., Lim, M.H. (2012). Ockham’s razor in memetic computing: three stage optimal memetic exploration. Information Sciences, 188, 17–43.
Jain, S., van Kesteren, R.E., Heutink, P. (2012). High content screening in neurodegenerative diseases. Journal of Visualized Experiments, 59, e3452.
Jiang, R.M., Crookes, D., Luo, N., Davidson, M.W. (2010). Live-cell tracking using SIFT, features in DIC microscopic videos. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 57(9), 2219–2228.
Kingma, D.P., & Ba, J. (2014). Adam: a method for stochastic optimization, Computing Research Repository arXiv:1412.6980.
Kraus, O.Z., & Frey, B.J. (2016). Computer vision for high content screening. Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 51(2), 102–109.
Krawczyk, B. (2016). Learning from imbalanced data: open challenges and future directions. Progress in Artificial Intelligence, 5(4), 221–232.
Kuminski, E., George, J., Wallin, J., Shamir, L. (2014). Combining human and machine learning for morphological analysis of galaxy images. Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 126(944), 959–967.
Lazebnik, S., Schmid, C., Ponce, J. (2006). Beyond bags of features: Spatial pyramid matching for recognizing natural scene categories. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, (Vol. 2 pp. 2169–2178).
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., Hinton, G. (2015). Deep learning. Nature, 521(7553), 436–444.
Lee, D.H., Lee, D.W., Han, B.S. (2016). Possibility study of scale invariant feature transform (SIFT), algorithm application to spine magnetic resonance imaging. PLOS ONE, 11(4), 1–9.
Li, J., Fong, S., Wong, R.K., Chu, V.W. (2018). Adaptive multi-objective swarm fusion for imbalanced data classification. Information Fusion, 39, 1–24.
Liaw, A., & Wiener, M. (2002). Classification and regression by randomForest. R News, 2(3), 18–22.
Litjens, G., Kooi, T., Bejnordi, B.E., Setio, A.A.A., Ciompi, F., Ghafoorian, M., van der Laak, J.A.W.M., van Ginneken, B., Sánchez, C.I. (2017). A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Medical Image Analysis, 42, 60–88.
Lowe, D.G. (2004). Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. International Journal of Computer Vision, 60(2), 91–110.
MacQueen, J. (1967). Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. In Proceedings of the 5th Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability — Volume 1: Statistics (pp. 281–297). Berkeley: University of California Press.
Mata, G., Radojević, M., Smal, I., Morales, M., Meijering, E., Rubio, J. (2016). Automatic detection of neurons in high-content microscope images using machine learning approaches. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro (pp. 330–333).
MathWorks. (2016). Version 9.0.0.341360 (R2016a). Natick: MA.
Meijering, E. (2010). Neuron tracing in perspective. Cytometry Part A, 77(7), 693–704.
Meijering, E., Carpenter, A.E., Peng, H., Hamprecht, F.A., Olivo-Marin, J.C. (2016). Imagining the future of bioimage analysis. Nature Biotechnology, 34(12), 1250–1255.
Meyer, D., Dimitriadou, E., Hornik, K., Weingessel, A., Leisch, F. (2017). e1071: Misc Functions of the Department of Statistics, Probability Theory Group (Formerly: E1071), TU Wien. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=e1071.
Mualla, F., Scholl, S., Sommerfeldt, B., Maier, A., Hornegger, J. (2013). Automatic cell detection in bright-field microscope images using SIFT, random forests, and hierarchical clustering. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 32(12), 2274–2286.
Ni, D., Chui, Y.P., Qu, Y., Yang, X.S., Qin, J., Wong, T.T., Ho, S.S.H., Heng, P.A. (2009). Reconstruction of volumetric ultrasound panorama based on improved 3D, SIFT. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, 33(7), 559–566.
Orlov, N., Shamir, L., Macura, T., Johnston, J., Eckley, D.M., Goldberg, I.G. (2008). WND-CHARM: Multi-purpose image classification using compound image transforms. Pattern Recognition Letters, 29(11), 1684–1693.
Otsu, N. (1979). A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 9(1), 62–66.
van Pelt, J., van Ooyen, A., Uylings, H. (2001). The need for integrating neuronal morphology databases and computational environments in exploring neuronal structure and function. Anatomy and Embryology, 204(4), 255–265.
Prewitt, J.M.S. (1970). Object enhancement and extraction. In Picture Processing and psychopictorics (pp. 75–149). New York: Academic Press.
R Core Team. (2016). R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria, https://www.R-project.org/.
Radio, N. (2012). Neurite outgrowth assessment using high content analysis methodology. Methods in Molecular Biology, 846, 247–260.
Ramón y Cajal, S. (2007). Histología del sistema nervioso del hombre y de los vertebrados. CSIC Madrid reprinted in.
Saeys, Y., Inza, I., Larrañaga, P. (2007). A review of feature selection techniques in bioinformatics. Bioinformatics, 23(19), 2507–2517.
Sáez, J.A., Luengo, J., Stefanowski, J., Herrera, F. (2015). SMOTE-IPF: Addressing the noisy and borderline examples problem in imbalanced classification by a re-sampling method with filtering. Information Sciences, 291, 184–203.
Samworth, R.J. (2012). Optimal weighted nearest neighbour classifiers. The Annals of Statistics, 40(5), 2733–2763.
Schliep, K., & Hechenbichler, K. (2016). kknn: Weighted k-Nearest Neighbors. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=kknn.
Shaikhina, T., & Khovanova, N.A. (2017). Handling limited datasets with neural networks in medical applications: a small-data approach. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 75, 51–63.
Shamir, L., Orlov, N., Eckley, D.M., Macura, T., Johnston, J., Goldberg, I.G. (2008). Wndchrm – an open source utility for biological image analysis. Source Code for Biology and Medicine, 3(1), 1–13.
Shamir, L., Delaney, J.D., Orlov, N., Eckley, D.M., Goldberg, I.G. (2010). Pattern recognition software and techniques for biological image analysis. PLOS Computational Biology, 6(11), e1000974.
Shamir, L. (2012a). Automatic detection of peculiar galaxies in large datasets of galaxy images. Journal of Computational Science, 3(3), 181–189.
Shamir, L., & Tarakhovsky, J.A. (2012b). Computer analysis of art. Journal on Computing and Cultural Heritage, 5(2), 7.
Shapiro, S.S., & Wilk, M.B. (1965). An analysis of variance test for normality (complete samples). Biometrika, 52(3-4), 591– 611.
Shen, D., Wu, G., Suk, H.I. (2017). Deep learning in medical image analysis. Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering, 19, 221– 248.
Simon, R. (2007). Resampling strategies for model assessment and selection. In Fundamentals of Data Mining in Genomics and Proteomics (pp. 173–186). Boston: Springer.
Simonyan, K., & Zisserman, A. (2014). Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. Computing Research Repository arXiv:1409.1556.
Singh, S., Carpenter, A.E., Genovesio, A. (2014). Increasing the content of high-content screening: an overview. Journal of Biomolecular Screening, 19(5), 640–650.
Smafield, T., Pasupuleti, V., Sharma, K., Huganir, R.L., Ye, B., Zhou, J. (2015). Automatic dendritic length quantification for high throughput screening of mature neurons. Neuroinformatics, 13(4), 443–458.
Sommer, C., & Gerlich, D.W. (2013). Machine learning in cell biology – teaching computers to recognize phenotypes. Journal of Cell Science, 126(24), 5529–5539.
Squire, L.R. (1992). Memory and the hippocampus: a synthesis from findings with rats, monkeys, and humans. Psychological Review, 99(2), 195–231.
Strobl, C., Hothorn, T., Zeileis, A. (2009). A new, conditional variable importance measure for random forests available in the party package. The R Journal, 1(2), 14–17.
Tajbakhsh, N., Shin, J.Y., Gurudu, S.R., Hurst, R.T., Kendall, C.B., Gotway, M.B., Liang, J. (2016). Convolutional neural networks for medical image analysis: full training or fine tuning?. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 35(5), 1299–1312.
Tamura, H., Mori, S., Yamawaki, T. (1978). Textural features corresponding to visual perception. IEEE Transactions on Systems Man, and Cybernetics, 8(6), 460–473.
Tibshirani, R. (1996). Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Statistical Methodology), 58(1), 267–288.
Uhlmann, V., Singh, S., Carpenter, A.E. (2016). CP-CHARM: segmentation-free image classification made accessible. BMC Bioinformatics, 17(1), 51.
Vallotton, P., Lagerstrom, R., Sun, C., Buckley, M., Wang, D., Silva, M.D., Tan, S.S., Gunnersen, J.M. (2007). Automated analysis of neurite branching in cultured cortical neurons using HCA-Vision. Cytometry Part A, 71(10), 889–895.
Vapnik, V.N. (1998). Statistical learning theory. New York: Wiley.
Vapnik, V.N. (1999). The nature of statistical learning theory. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Vedaldi, A., & Fulkerson, B. (2008). VLFeat: An Open and Portable Library of Computer Vision Algorithms. http://www.vlfeat.org/.
Vert, J.P., Tsuda, K., Schölkopf, B. (2004). A primer on kernel methods. In Kernel Methods in Computational Biology (pp. 35–70). Cambridge: MIT Press.
Wickham, H. (2009). Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. New York: Springer.
Wu, C., Schulte, J., Sepp, K.J., Littleton, J.T., Hong, P. (2010). Automatic robust neurite detection and morphological analysis of neuronal cell cultures in high-content screening. Neuroinformatics, 8(2), 83–100.
Xia, X., & Wong, S.T.C. (2012). Concise review: a high-content screening approach to stem cell research and drug discovery. Stem Cells, 30(9), 1800–1807.
Yang, J., Yu, K., Gong, Y., Huang, T. (2009). Linear spatial pyramid matching using sparse coding for image classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 1794–1801).
Yu, D., Yang, F., Yang, C., Leng, C., Cao, J., Wang, Y., Tian, J. (2016). Fast rotation-free feature-based image registration using improved N-SIFT, and GMM-based parallel optimization. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 63(8), 1653–1664.
Zhang, Y., Zhou, X., Degterev, A., Lipinski, M., Adjeroh, D., Yuan, J., Wong, S.T.C. (2007). A novel tracing algorithm for high throughput imaging: screening of neuron-based assays. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 160(1), 149–162.
Zhang, R., Zhou, W., Li, Y., Yu, S., Xie, Y. (2013). Nonrigid registration of lung CT images based on tissue features. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2013, 834192.
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the Spanish Ministry of Economy, Industry and Competitiveness (project numbers MTM2014-54151-P, UNLC08-1E-002, UNLC13-13-3503), the University of La Rioja (project number FPI-UR-13), the European Regional Development Fund (FEDER) of the European Union, the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Reseach (project number 612.001.018), and the Erasmus University Medical Center Fellowship Program. Carlos Fernandez-Lozano was supported by a Juan de la Cierva postdoctoral fellowship grant (Spanish Ministry of Economy, Industry and Competitiveness, FJCI-2015-26071).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Gadea Mata, Miroslav Radojević and Carlos Fernandez-Lozano contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mata, G., Radojević, M., Fernandez-Lozano, C. et al. Automated Neuron Detection in High-Content Fluorescence Microscopy Images Using Machine Learning. Neuroinform 17, 253–269 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-018-9399-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-018-9399-4