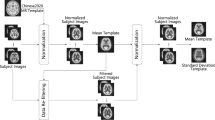
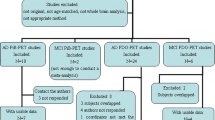
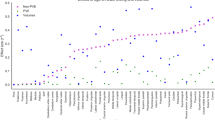
Abstract
[18F]-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) Positron Emission Tomography (PET) is a widely used diagnostic tool that can detect and quantify pathophysiology, as assessed through changes in cerebral glucose metabolism. [18F]-FDG PET scans can be analyzed using voxel-based statistical methods such as Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM) that provide statistical maps of brain abnormalities in single patients. In order to perform SPM, a “spatial normalization” of an individual’s PET scan is required to match a reference PET template. The PET template currently used for SPM normalization is based on [15O]-H2O images and does not resemble either the specific metabolic features of [18F]-FDG brain scans or the specific morphological characteristics of individual brains affected by neurodegeneration. Thus, our aim was to create a new [18F]-FDG PET aging and dementia-specific template for spatial normalization, based on images derived from both age-matched controls and patients. We hypothesized that this template would increase spatial normalization accuracy and thereby preserve crucial information for research and diagnostic purposes. We investigated the statistical sensitivity and registration accuracy of normalization procedures based on the standard and new template—at the single-subject and group level—independently for subjects with Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), probable Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) and dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB). We found a significant statistical effect of the population-specific FDG template-based normalisation in key anatomical regions for each dementia subtype, suggesting that spatial normalization with the new template provides more accurate estimates of metabolic abnormalities for single-subject and group analysis, and therefore, a more effective diagnostic measure.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert, M. S., DeKosky, S. T., Dickson, D., Dubois, B., Feldman, H. H., Fox, N. C., et al. (2011). The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging–Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 7(3), 270–279.
Anchisi, D., Borroni, B., Franceschi, M., Kerrouche, N., Kalbe, E., Beuthien-Beumann, B., Cappa, S., et al. (2005). Heterogeneity of brain glucose metaboism in mild cognitive impairment and clinical progression to Alzheimer disease. Archives of Neurology, 62(11), 1728–1733.
Ashburner, J. (2007). A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. NeuroImage, 38(1), 95–113.
Ashburner, J., & Friston, K. J. (1999). Nonlinear spatial normalization using basis functions. Human Brain Mapping, 7(4), 254–266.
Bartenstein, P., Asenbaum, S., Catafau, A., Halldin, C., Pilowski, L., Pupi, A., et al. (2002). European Association of Nuclear Medicine procedure guidelines for brain imaging using [(18)F]FDG. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, 29(10), BP43–BP48.
Berti, V., Osorio, R. S., Mosconi, L., Li, Y., De Santi, S., & de Leon, M. J. (2010). Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease with PET imaging. Neurodegenerative Diseases, 7(1–3), 131–135.
Bornebroek, M., & Bretelera, M. B. (2004). Epidemiology of non-AD dementia. Clinical Neuroscience Reserach, 3, 349–361.
Buchert, R., Wilke, F., Chakrabarti, B., Martin, B., Brenner, W., Mester, J., & Clausen, M. (2005). Adjusted scaling of FDG positron emission tomography images for statistical evaluation in patients with suspected Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Neuroimaging, 15, 348–355.
Caroli, A., Prestia, A., Chen, K., Ayutyanont, N., Landau, S. M., Madison, C. M., et al. (2012). Summary metrics to assess Alzheimer disease-related hypometabolic pattern with 18F-FDG PET: head-to-head comparison. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 53(4), 592–600.
Chételat, G., Desgranges, B., de la Sayette, V., Viader, F., Eustache, F., & Baron, J. C. (2003). Mild cognitive impairment: Can FDG-PET predict who is to rapidly convert to Alzheimer’s disease? Neurology, 60(8), 1374–1377.
Crivello, F., Schormann, T., Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., Roland, P. E., Zilles, K., & Mazoyer, B. M. (2002). Comparison of spatial normalization procedures and their impact on functional maps. Human Brain Mapping, 16(4), 228–250.
Dubois, B., Feldman, H. H., Jacova, C., Cummings, J. L., Dekosky, S. T., Barberger-Gateau, P., et al. (2010). Revising the definition of Alzheimer’s disease: a new lexicon. Lancet Neurology, 9(11), 1118–1127.
Eickhoff, S., Stephan, K. E., Mohlberg, H., Grefkes, C., Fink, G. R., Amunts, K., et al. (2005). A new SPM toolbox for combining probabilistic cytoarchitectonic maps and functional imaging data. NeuroImage, 25(4), 1325–1335.
Evans, A. C., Collins, D. L., Mills, S. R., Brown, E. D., Kelly, R. L., & Peters, T. M. (1993). 3D statistical neuroanatomical models from 305 MRI volumes. IEEE-Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference Proceeding, 1813–1817.
Foster, N. L., Heidebrink, J. L., Clark, C. M., Jagust, W. J., Arnold, S. E., Barbas, N. R., et al. (2007). FDG-PET improves accuracy in distinguishing frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Brain, 130(Pt10), 2616–2635.
Friston, K. J., Holmes, A. P., Worsley, K. J., Poline, J. P., Frith, C. D., & Frackowiak, R. S. (1994). Statistical parametric maps in functional imaging: a general linear approach. Human Brain Mapping, 2(4), 189–210.
Gispert, J. D., Pascau, J., Reig, S., Martinez-Lazaro, R., Molina, V., Garcia-Barreno, P., et al. (2003). Influence of the normalization template on the outcome of statistical parametric mapping of PET scans. NeuroImage, 19(3), 601–612.
Good, C. D., Johnsrude, I. S., Ashburner, J., Henson, R. N., Friston, K. J., & Frackowiak, R. S. (2001). A voxel-based morphometric study of ageing in 465 normal adult human brains. NeuroImage, 14(1 Pt1), 21–36.
Herholz, K., Salmon, E., Perani, D., Baron, J.-C., Holthoff, V., Frölich, L., Schönknecht, P., et al. (2002). Discrimination between Alzheimer dementia and controls by automated analysis of multicenter FDG PET. NeuroImage, 17(1), 302–316.
Ishii, K., Willoch, F., Minoshima, S., Drzezga, A., Ficaro, E. P., Cross, D. J., et al. (2001). Statistical brain mapping of 18F-FDG PET in Alzheimer’s disease: validation of anatomic standardization for atrophied brains. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 42(4), 548–557.
Jack, C. R., Jr., Albert, M. S., Knopman, D. S., McKhann, G. M., Sperling, R. A., Carrillo, M. C., et al. (2011). Introduction to the recommendations from the National Institute on Aging–Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 7(3), 257–262.
Kherif, F., Poline, J. P., Mériaux, S., Benali, H., Flandin, G., & Brett, M. (2003). Group analysis in functional neuroimaging: selecting subjects using similarity measures. NeuroImage, 20(4), 2197–2208.
Krishnan, S., Slavin, M. J., Tran, T. T., Doraiswamy, P. M., & Petrella, J. R. (2006). Accuracy of spatial normalization of the hippocampus: implications for fMRI research in memory disorders. NeuroImage, 31(2), 560–571.
Magistretti, P. J. (2000). Cellular bases of functional brain imaging: insights from neuron-glia metabolic coupling. Brain Research, 886(1–2), 108–112.
Markiewicz, P. J., Matthews, J. C., Declerck, J., & Herholz, K. (2009). Robustness of multivariate image analysis assessed by resampling techniques and applied to FDG-PET scans of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage, 46(2), 472–485.
Martino, M. E., Guzman de Villoria, J., Lacalle-Aurioles, M., Olazaran, J., Cruz, I., Navarro, E., et al. (2013). Comparison of different methods of spatial normalization of FDG-PET brain images in the voxel-wise analysis of MCI patients and controls. Annals of Nuclear Medicine. doi:10.1007/s12149-013-0723-7.
McKeith, I. G., Dickson, D. W., Lowe, J., Emre, M., O’Brien, J. T., Feldman, H., et al. (2005). Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: third report of the DLB Consortium. Neurology, 65(12), 1863–1872.
McKhann, G. M., Albert, M. S., Grossman, M., Miller, B., Dickson, D., & Trojanowski, J. Q. (2001). Clinical and pathological diagnosis of frontotemporal dementia: report of the Work Group on Frontotemporal Dementia and Pick’s Disease. Archives of Neurology, 58, 1803–1809.
McKhann, G. M., Knopman, D. S., Chertkow, H., Hyman, B. T., Jack, C. R., Jr., Kawas, C. H., Klunk, W. E., et al. (2011). The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging– Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 7(3), 263–269.
Minoshima, S., Frey, K. A., Koeppe, R. A., Foster, N. L., & Kuhl, D. E. (1995). A diagnostic approach in Alzheimer’s disease using three-dimensional stereotactic surface projections of fluorine-18-FDG PET. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 36(7), 1238–1248.
Minoshima, S., Giordani, B., Berent, S., Frey, K. A., Foster, N. L., & Kuhl, D. E. (1997). Metabolic reduction in the posterior cingulate cortex in very early Alzheimer’s disease. Annals of Neurology, 42(1), 85–94.
Minoshima, S., Foster, N. L., Sima, A. A., Frey, K. A., Albin, R. L., & Kuhl, D. E. (2001). Alzheimer’s disease versus dementia with Lewy bodies: cerebral metabolic distinction with autopsy confirmation. Annals of Neurology, 50(3), 358–365.
Morbelli, S., Drzezga, A., Perneczky, R., Frisoni, G. B., Caroli, A., van Berckel, B. N., et al. (2012). Resting metabolic connectivity in prodromal Alzheimer’s disease. A European Alzheimer Disease Consortium (EADC) project. Neurobiology of Aging, 33(11), 2533–2550.
Mori, T., Ikeda, M., Fukuhara, R., Nestor, P. J., & Tanabe, H. (2006). Correlation of visual hallucinations with occipital rCBF changes by donepezil in DLB. Neurology, 66(6), 935–937.
Mosconi, L., Tsui, W. H., Herholz, K., Pupi, A., Drzezga, A., Lucignani, G., et al. (2008). Multicenter standardized 18F-FDG PET diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer’s disease, and other dementias. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 49(3), 390–398.
Neary, D., Snowden, J. S., Gustafson, L., Passant, U., Stuss, D., Black, S., et al. (1998). Frontotemporal lobar degeneration: a consensus on clinical diagnostic criteria. Neurology, 51, 1546–1554.
Patterson, J. C., Lilien, D. L., Takalkar, A., & Pinkston, J. B. (2011). Early detection of brain pathology suggestive of early AD using objective evaluation of FDG-PET scans. International Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease. doi:10.4061/2011/946590.
Perani, D. (2008). Functional neuroimaging of cognition. In: M. J. Aminoff, F. Boller, & D. F. Swaab (Eds.), Handbook of Clinical Neurology (pp.61–111). Elsevier.
Prince, M., Bryce, R., & Ferr, C. (2011). The benefits of early diagnosis and intervention. In: Alzheimer’s Disease International World Alzheimer Report 2011. Institute of Psychiatry. King’s College London. Alzheimer’s Disease International.
Rascovsky, K., Hodges, J. R., Knopman, D., Mendez, M. F., Kramer, J. H., Neuhaus, J., et al. (2011). Sensitivity of revised diagnostic criteria for the behavioural variant of frontotemporal dementia. Brain, 134(Pt9), 2456–2477.
Ridgway, G., Omar, R., Ourselin, S., Hill, D., Warren, J., & Fox, N. (2009). Issues with threshold masking in voxel-based morphometry of atrophied brains. NeuroImage, 44(1), 99–111.
Rorden, C., Bonilha, L., Fridriksson, J., Bender, B., & Karnath, H. O. (2012). Age-specific CT and MRI templates for spatial normalization. NeuroImage, 61(4), 957–965.
Salmon, E., Garraux, G., Delbeuck, X., Collette, F., Kalbe, E., Zuendorf, G., et al. (2003). Predominant ventromedial frontopolar metabolic impairment in frontotemporal dementia. NeuroImage, 20(1), 435–440.
Salmon, E., Kerrouche, N., Perani, D., Lekeu, F., Holthoff, V., Beuthien- Baumann, B., et al. (2009). On the multivariate nature of brain metabolic impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 30(2), 186–197.
Sestini, S., Castagnoli, A., & Mansi, L. (2010). The new FDG brain revolution: the neurovascular unit and the default network. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, 37(5), 913–916.
Signorini, M., Paulesu, E., Friston, K., Perani, D., Colleluori, A., Lucignani, G., et al. (1999). Rapid assessment of regional cerebral metabolic abnormalities in single subjects with quantitative and nonquantitative [18F]FDG PET: a clinical validation of statistical parametric mapping. NeuroImage, 9(1), 63–80.
Spence, J. S., Carmack, P. S., Gunst, R. F., Schucany, W. R., Woodward, W. A., & Haley, R. W. (2006). Using a white matter reference to remove the dependency of global signal on experimental conditions in SPECT analyses. NeuroImage, 32(1), 49–53.
Sperling, R. A., Aisen, P. S., Beckett, L. A., Bennett, D. A., Craft, S., Fagan, A. M., et al. (2011). Towards defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 7(3), 280–292.
Teipel, S. J., Sabri, O., Grothe, M., Barthel, H., Prvulovic, D., Buerger, K., et al. (2013). Perspectives for multimodal neurochemical and imaging biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 33(S1), S329–S347.
Teune, L. K., Bartels, A. L., de Jong, B. M., Willemsen, A. T., Eshuis, S. A., de Vries, J. J., et al. (2010). Typical cerebral metabolic patterns in neurodegenerative brain diseases. Movement Disorders, 25(14), 2395–2404.
Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., Landeau, B., Papathanassiou, D., Crivello, F., Etard, O., Delcroix, N., et al. (2002). Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. NeuroImage, 15(1), 273–289.
Wenzel, F., Young, S., Wilke, F., Apostolova, I., Arlt, S., Jahn, H., et al. (2010). B-spline-based stereotactical normalization of brain FDG PET scans in suspected neurodegenerative disease: impact on voxel-based statistical single-subject analysis. NeuroImage, 50(3), 994–1003.
Winblad, B., Palmer, K., Kivipelto, M., Jelic, V., Fratiglioni, L., Wahlund, L. O., et al. (2004). Mild cognitive impairment-beyond controversies, towards a consensus: report of the International Working Group on Mild Cognitive Impairment. Journal of Internal Medicine, 256(3), 240–246.
Yakushev, I., Hammers, A., Fellgiebel, A., Schmidtmann, I., Scheurich, A., Buchholz, H. G., et al. (2009). SPM-based count normalization provides excellent discrimination of mild Alzheimer’s disease and amnesic mild cognitive impairment from healthy aging. NeuroImage, 44(1), 43–50.
Acknowledgments
We thank the EADC-PET Consortium (Alexander Drzezga and Robert Perneczky [Munich], Mira Didic and Eric Guedj [Marseilles], Bart N. Van Berckel and Rik Ossenkoppele [Amsterdam], Flavio Nobili and Silvia Morbelli [Genoa], Giovanni Frisoni, Anna Caroli [Brescia]) for kindly providing EADC-PET imaging data for the purposes of the current study. This study was supported in part by the 6th European Framework Program Network of Excellence “DIMI” LSHB-CT-2005-512146, and the 7th Framework Programme for Research and Technological Development “DECIDE” RI-261593 and in part by the Italian Ministry of Education in the framework of the Project of Strategic National Interest “Invecchiamento: innovazioni tecnologiche e molecolari per un miglioramento della salute dell’anziano” allocated to the National Research Council. Karl Friston and John Ashburner are based at The Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging, which is supported by core funding from the Wellcome Trust [091593/Z/10/Z].
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding authors
Additional information
*Alexander Drzezga and Robert Perneczky [Munich], Mira Didic and Eric Guedj [Marseilles], Bart N. Van Berckel and Rik Ossenkoppele [Amsterdam], Flavio Nobili and Silvia Morbelli [Genoa]
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table 1
(DOC 39 kb)
ESM 1
(DOCX 470 kb)
ESM 2
(DOC 25 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Della Rosa, P.A., Cerami, C., Gallivanone, F. et al. A Standardized [18F]-FDG-PET Template for Spatial Normalization in Statistical Parametric Mapping of Dementia. Neuroinform 12, 575–593 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-014-9235-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-014-9235-4