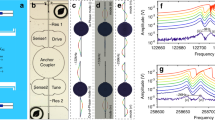
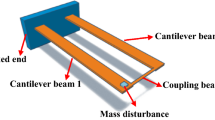
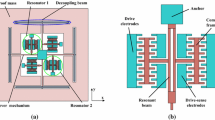
Abstract
The mode localization phenomenon is an effective technique to enhance sensor sensitivity, and some low noise floor mode-localized sensors, including accelerometers, mass sensors, and electrometers, have been successfully realized. To further improve the performance of the mode-localized accelerometer, we report a microelectromechanical system mode-localized accelerometer based on 4-degree of freedom (DoF) weakly coupled resonators (WCRs) with a stress-relief structure eliminating the thermal stress generated during the silicon-on-glass fabrication process. Experimental results show that compared with the state-of-the-art 3-DoF mode-localized accelerometer (4.40 g−1), the amplitude ratio-based sensitivity of the proposed accelerometer (119.36 V·g−1) is improved by 2612%. Moreover, the noise floor is 0.64 µg·Hz−1/2 from 0.01 to 3 Hz under the closed-loop circumstance. To the authors’ best knowledge, this is the lowest measured noise floor for mode-localized accelerometers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Middlemiss R P, Samarelli A, Paul D J, et al. Measurement of the earth tides with a MEMS gravimeter. Nature, 2016, 531: 614–617
Zou X D, Thiruvenkatanathan P, Seshia A A. A seismic-grade resonant MEMS accelerometer. J Microelectromech Syst, 2014, 23: 768–770
Boom B A, Bertolini A, Hennes E, et al. Nano-G accelerometer using geometric anti-springs. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Las Vegas, 2017. 33–36
Krishnamoorthy U, Olsson III R H, Bogart G R, et al. In-plane MEMS-based nano-g accelerometer with sub-wavelength optical resonant sensor. Sens Actuat A-Phys, 2008, 145–146: 283–290
Liu C-H, Kenny T W. A high-precision, wide-bandwidth micromachined tunneling accelerometer. J Microelectromech Syst, 2001, 10: 425–433
Spletzer M, Raman A, Wu A Q, et al. Ultrasensitive mass sensing using mode localization in coupled microcantilevers. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 88: 254102
Thiruvenkatanathan P, Yan J, Woodhouse J, et al. Ultrasensitive mode-localized mass sensor with electrically tunable parametric sensitivity. Appl Phys Lett, 2010, 96: 081913
Zhao C, Wood G S, Xie J, et al. A force sensor based on three weakly coupled resonators with ultrahigh sensitivity. Sens Actuat A-Phys, 2015, 232: 151–162
Manav M, Reynen G, Sharma M, et al. Ultrasensitive resonant MEMS transducers with tuneable coupling. J Micromech Microeng, 2014, 24: 055005
Zhang H, Li B, Yuan W, et al. An acceleration sensing method based on the mode localization of weakly coupled resonators. J Microelectromech Syst, 2016, 25: 286–296
Yang J, Zhong J, Chang H. A closed-loop mode-localized accelerometer. J Microelectromech Syst, 2018, 27: 210–217
Kang H, Yang J, Chang H. A closed-loop accelerometer based on three degree-of-freedom weakly coupled resonator with self-elimination of feedthrough signal. IEEE Sens J, 2018, 18: 3960–3967
Pandit M, Zhao C, Sobreviela G, et al. A mode-localized MEMS accelerometer with 7 µg bias stability. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Belfast, 2018. 968–971
Pandit M, Zhao C, Sobreviela G, et al. A high resolution differential mode-localized MEMS accelerometer. J Microelectromech Syst, 2019, 28: 782–789
Zhang H, Huang J, Yuan W, et al. A high-sensitivity micromechanical electrometer based on mode localization of two degree-of-freedom weakly coupled resonators. J Microelectromech Syst, 2016, 25: 937–946
Thiruvenkatanathan P, Yan J, Seshia A A. Ultrasensitive mode-localized micromechanical electrometer. In: Proceedings of 2010 IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium, Newport Beach, 2010. 91–96
Zhang H, Chang H, Yuan W. Characterization of forced localization of disordered weakly coupled micromechanical resonators. Microsyst Nanoeng, 2017, 3: 17023
Zhong J, Yang J, Chang H. The temperature drift suppression of mode-localized resonant sensors. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Belfast, 2018. 467–470
Thiruvenkatanathan P, Yan J, Seshia A A. Common mode rejection in electrically coupled MEMS resonators utilizing mode localization for sensor applications. In: Proceedings of 2009 IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium Joint with the 22nd European Frequency and Time Forum, Besancon, 2009. 358–363
Pandit M, Zhao C, Sobreviela G, et al. Practical limits to common mode rejection in mode localized weakly coupled resonators. IEEE Sens J, 2020, 20: 6818–6825
Zhang H, Zhong J, Yuan W, et al. Ambient pressure drift rejection of mode-localized resonant sensors. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Las Vegas, 2017. 1095–1098
Kang H, Yang J, Chang H. A mode-localized accelerometer based on four degree-of-freedom weakly coupled resonators. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Belfast, 2018. 960–963
Thomson W. Theory of Vibration With Application. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2018
Hao Y, Yuan W, Xie J, et al. Design and verification of a structure for isolating packaging stress in SOI MEMS devices. IEEE Sens J, 2017, 17: 1246–1254
Zhang H, Kang H, Chang H. Suppression on nonlinearity of mode-localized sensors using algebraic summation of amplitude ratios as the output metric. IEEE Sens J, 2018, 18: 7802–7809
Zhang H, Yang J, Yuan W, et al. Linear sensing for mode-localized sensors. Sens Actuat A-Phys, 2018, 277: 35–42
Gabrielson T B. Mechanical-thermal noise in micromachined acoustic and vibration sensors. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 1993, 40: 903–909
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2018YFB2002600), Shaanxi Key Research and Development Program (Grant No. 2019ZDLGY02-06), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 3102019JC002), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51805441).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, H., Ruan, B., Hao, Y. et al. Mode-localized accelerometer with ultrahigh sensitivity. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 65, 142402 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-020-3057-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-020-3057-y