Abstract
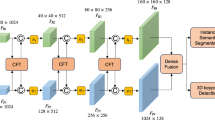
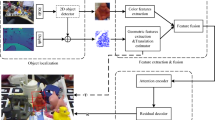
We propose a feature-fusion network for pose estimation directly from RGB images without any depth information in this study. First, we introduce a two-stream architecture consisting of segmentation and regression streams. The segmentation stream processes the spatial embedding features and obtains the corresponding image crop. These features are further coupled with the image crop in the fusion network. Second, we use an efficient perspective-n-point (E-PnP) algorithm in the regression stream to extract robust spatial features between 3D and 2D keypoints. Finally, we perform iterative refinement with an end-to-end mechanism to improve the estimation performance. We conduct experiments on two public datasets of YCB-Video and the challenging Occluded-LineMOD. The results show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in both the speed and the accuracy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Brachmann E, Krull A, Michel F, Gumhold S, Shotton J, Rother C. Learning 6D object pose estimation using 3D object coordinates. In Proc. the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Sept. 2014, pp.536-551. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10605-2_35.
Hinterstoisser S, Holzer S, Cagniart C, Ilic S, Konolige K, Navab N, Lepetit V. Multimodal templates for real-time detection of texture-less objects in heavily cluttered scenes. In Proc. the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Nov. 2011, pp.858-865. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2011.6126326.
Hinterstoisser S, Lepetit V, Ilic S, Holzer S, Bradski G, Konolige K, Navab N. Model based training, detection and pose estimation of texture-less 3D objects in heavily cluttered scenes. In Proc. the 11th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Nov. 2012, pp.548-562. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-37331-2_42.
Kehl W, Milletari F, Tombari F, Ilic S, Navab N. Deep learning of local RGB-D patches for 3D object detection and 6D pose estimation. In Proc. the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Oct. 2016, pp.205-220. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46487-9_13.
Rios-Cabrera R, Tuytelaars T. Discriminatively trained templates for 3D object detection: A real time scalable approach. In Proc. the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Dec. 2013, pp.2048-2055. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2013.256.
Tejani A, Tang D, Kouskouridas R, Kim T K. Latent-class hough forests for 3D object detection and pose estimation. In Proc. the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Sept. 2014, pp.462-477. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10599-4_30.
Wohlhart P, Lepetit V. Learning descriptors for object recognition and 3D pose estimation. In Proc. the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, June 2015, pp.3109-3118. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298930.
Cao Y, Ju T, Xu J, Hu S. Extracting sharp features from RGB-D images. Computer Graphics Forum, 2017, 36(8): 138-152. https://doi.org/10.1111/cgf.13069.
Wang C, Xu D, Zhu Y, Martin R, Lu C, Li F, Savarese S. DenseFusion: 6D object pose estimation by iterative dense fusion. In Proc. the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, June 2019, pp.3343-3352. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00346.
Fischler M A, Bolles R C. Random sample consensus: A paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Communications of the ACM, 1981, 24(6): 381-395. https://doi.org/10.1145/358669.358692.
Xiang Y, Schmidt T, Narayanan V, Fox D. PoseCNN: A convolutional neural network for 6D object pose estimation in cluttered scenes. In Proc. the 14th Robotics: Science and Systems, June 2018. 10.15607/RSS.2018.XIV.019.
Krull A, Brachmann E, Michel F, Yang M Y, Gumhold S, Rother C. Learning analysis-by-synthesis for 6D pose estimation in RGB-D images. In Proc. the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Dec. 2015, pp.954-962. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.115.
Qi C R, Su H, Mo K, Guibas L J. PointNet: Deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation. In Proc. the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, July 2017, pp.652-660. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.16.
Hu Y, Hugonot J, Fua P, Salzmann M. Segmentation-driven 6D object pose estimation. In Proc. the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, June 2019, pp.3385-3394. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00350.
Xu D, Anguelov D, Jain A. PointFusion: Deep sensor fusion for 3D bounding box estimation. In Proc. the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, June 2018, pp.244-253. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00033.
Qi C R, Liu W, Wu C, Su H, Guibas L J. Frustum PointNets for 3D object detection from RGB-D data. In Proc. the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, June 2018, pp.7918-7927. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00102.
Yang X L, Jia X H. 6D pose estimation with two-stream net. In Proc. the 2020 ACM SIGGRAPH, Aug. 2020, Article No. 40. https://doi.org/10.1145/3388770.3407423.
Song S, Xiao J. Sliding shapes for 3D object detection in depth images. In Proc. the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Sept. 2014, pp.634-651. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10599-4_41.
Song S, Xiao J. Deep sliding shapes for Amodal 3D object detection in RGB-D images. In Proc. the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, June 2016, pp.808-816. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.94.
Geiger A, Lenz P, Urtasun R. Are we ready for autonomous driving? The KITTI vision benchmark suite. In Proc. the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, June 2012, pp.3354-3361. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2012.6248074.
Aubry M, Maturana D, Efros A A, Russell B C, Sivic J. Seeing 3D chairs: Exemplar part-based 2D-3D alignment using a large dataset of CAD models. In Proc. the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, June 2014, pp.3762-3769. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2014.487.
Collet A, Martinez M, Srinivasa S S. The MOPED framework: Object recognition and pose estimation for manipulation. International Journal of Robotics Research, 2011, 30(10): 1284-1306. https://doi.org/10.1177/0278364911401765.
Ferrari V, Tuytelaars T, Gool L V. Simultaneous object recognition and segmentation from single or multiple model views. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2006, 67(2): 159-188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-005-3964-7.
Rothganger F, Lazebnik S, Schmid C, Ponce J. 3D object modeling and recognition using local affine-invariant image descriptors and multi-view spatial constraints. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2006, 66(3): 231-259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-005-3674-1.
Zhu M, Derpanis K G, Yang Y, Brahmbhatt S, Zhang M, Phillips C, Lecce M, Daniilidis K. Single image 3D object detection and pose estimation for grasping. In Proc. the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, May 31-June 7, 2014, pp.3936-3943. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2014.6907430.
Nakajima Y, Saito H. Robust camera pose estimation by viewpoint classification using deep learning. Computational Visual Media, 2017, 3(2): 189-198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41095-016-0067-z.
Suwajanakorn S, Snavely N, Tompson J J, Norouzi M. Discovery of latent 3D keypoints via end-to-end geometric reasoning. In Proc. the 2018 Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Dec. 2018, pp.2059-2070.
Tekin B, Sinha S N, Fua P. Real-time seamless single shot 6D object pose prediction. In Proc. the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, June 2018, pp.292-301. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00038.
Tremblay J, To T, Sundaralingam B, Xiang Y, Fox D, Birchfield S. Deep object pose estimation for semantic robotic grasping of household objects. In Proc. the 2nd Conference on Robot Learning, Oct. 2018, pp.306-316.
Schwarz M, Schulz H, Behnke S. RGB-D object recognition and pose estimation based on pre-trained convolutional neural network features. In Proc. the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, May 2015, pp.1329-1335. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2015.7139363.
Tulsiani S, Malik J. Viewpoints and keypoints. In Proc. the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, June 2015, pp.1510-1519. 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298758.
Mousavian A, Anguelov D, Flynn J, Kosecka J. 3D bounding box estimation using deep learning and geometry. In Proc. the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, July 2017, pp.7074-7082. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.597.
Sundermeyer M, Marton Z C, Durner M, Brucker M, Triebel R. Implicit 3D orientation learning for 6D object detection from RGB images. In Proc. the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Sept. 2018, pp.699-715. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01231-1_43.
Billings G, Johnson-Roberson M. SilhoNet: An RGB method for 6D object pose estimation. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2019, 4(4): 3727-3734. https://doi.org/10.1109/LRA.2019.2928776.
Park K, Patten T, Vincze M. Pix2Pose: Pixel-wise coordinate regression of objects for 6D pose estimation. In Proc. the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Oct. 27-Nov. 2, 2019, pp.7668-7677. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00776.
Castro P, Armagan A, Kim T K. Accurate 6D object pose estimation by pose conditioned mesh reconstruction. arXiv:1910.10653, 2019. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1910.10653.pdf, Jan. 2022.
Kalchbrenner N, Grefenstette E, Blunsom P. A convolutional neural network for modelling sentences. arXiv:1404.2188, 2014. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1404.2188.pdf, Jan. 2022.
Badrinarayanan V, Kendall A, Cipolla R. SegNet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(12): 2481-2495. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615.
Li C, Bai J, Hager G D. A unified framework for multi-view multi-class object pose estimation. In Proc. the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Sept. 2018, pp.254-269. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01270-0_16.
Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLOv3: An incremental improvement. arXiv:1804.02767, 2018. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1804.02767.pdf, Jan. 2022.
Bochkovskiy A, Wang C, Liao H M. YOLOv4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv:2004.10934, 2020. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2004.10934.pdf, Jan. 2022.
Lin T, Goyal P, Girshick R, He K, Dollar P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proc. the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Oct. 2017, pp.2980-2988. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.324.
Lepetit V, Moreno-Noguer F, Fua P. EPnP: An accurate O(n) solution to the PnP problem. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2009, 81(2): Article No. 155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-008-0152-6.
Rad M, Lepetit V. BB8: A scalable, accurate, robust to partial occlusion method for predicting the 3D poses of challenging objects without using depth. In Proc. the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Oct. 2017, pp.3828-3836. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.413.
Oberweger M, Rad M, Lepetit V. Making deep heatmaps robust to partial occlusions for 3D object pose estimation. In Proc. the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Sept. 2018, pp.119-134. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01267-0_8.
Peng S, Liu Y, Huang Q, Zhou X, Bao H. PVNet: Pixel-wise voting network for 6DoF pose estimation. In Proc. the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, June 2019, pp.4561-4570. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00469.
Li Z, Wang G, Ji X. CDPN: Coordinates-based disentangled pose network for real-time RGB-based 6-DoF object pose estimation. In Proc. the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Oct. 27-Nov. 2, 2019, pp.7678-7687. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00777.
Everingham M, Van Gool L, Williams C K I, Winn J, Zisserman A. The Pascal visual object classes (VOC) challenge. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2010, 88(2): 303-338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-009-0275-4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 2145 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, XL., Jia, XH., Liang, Y. et al. 6D Object Pose Estimation in Cluttered Scenes from RGB Images. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 37, 719–730 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11390-021-1311-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11390-021-1311-2