Abstract
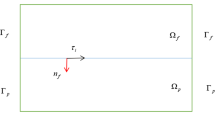
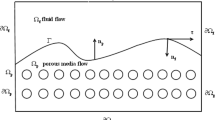
In this paper, by combining a partition of unity with backtracking technique, a modified local and parallel finite element method (MLPFEM) is proposed and investigated for the coupled Stokes-Darcy problem with the Beavers-Joseph (BJ) interface condition. The well-posedness of the coupled Stokes-Darcy model with BJ interface condition is established when the parameter αBJ is small enough in Cao et al. (Commun. Math. Sci. 8(1), 1–25 2010). The MLPFEM is adopted based on its significant advantages that we only need to solve a series of local subproblems once the coarse approximation is derived. Compared with the global discontinuous solution by the algorithm in Du and Zuo (2017), the main features of our algorithm are as follows: (1) partition of unity functions are utilized to gather local approximations computed on a fine grid by local and parallel procedures to generate a global continuous solution; (2) a further global coarse correction, namely the backtracking technique, is considered to obtain optimal error bounds of the velocity field and the piezometric head in L2 norm. Optimal error bounds are derived and numerical tests are carried out to support the theoretical analysis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao, Y., Gunzburger, M., He, X., Wang, X.: Robin-Robin domain decomposition methods for the steady-state Stokes-Darcy system with the Beavers-Joseph interface condition. Numer. Math. 117(4), 601–629 (2011)
Cao, Y., Gunzburger, M., He, X., Wang, X.: Parallel, non-iterative, multi-physics domain decomposition methods for time-dependent Stokes-Darcy systems. Math. Comput. 83(288), 1617–1644 (2014)
Cao, Y., Gunzburger, M., Hua, F., Wang, X.: Coupled Stokes-Darcy model with Beavers-Joseph interface boundary condition. Commun. Math. Sci. 8(1), 1–25 (2010)
Chen, W., Gunzburger, M., Hua, F., Wang, X.: A parallel Robin-Robin domain decomposition method for the Stokes-Darcy system. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 49(3), 1064–1084 (2011)
Discacciati, M., Quarteroni, A., Valli, A.: Robin-Robin domain decomposition methods for the Stokes-Darcy coupling. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 45(3), 1246–1268 (2007)
Du, G., Zuo, L.: A two-grid method with backtracking for the mixed Stokes/Darcy model. J. Numer. Math. 29(1), 39–46 (2021)
Du, G., Li, Q., Zhang, Y.: A two-grid method with backtracking for the mixed Navier-Stokes/Darcy model. Numer. Methods Partial Diff. Equa. 36(6), 1601–1610 (2020)
Du, G., Zuo, L.: A parallel partition of unity scheme based on two-grid discretizations for the Navier-Stokes problem. J. Sci. Comput. 75(3), 1445–1462 (2018)
Du, G., Zuo, L.: A parallel iterative finite element method for the linear elliptic equations. J. Sci. Comput. 85(2), 35 (2020)
Du, G., Zuo, L., Zhang, Y.: A new local and parallel finite element method for the coupled Stokes-Darcy model. J. Sci. Comput. 90(1), 43 (2022)
Du, G., Zuo, L.: Local and parallel finite element method for the mixed Navier-Stokes/Darcy model with Beavers-Joseph interface conditions. Acta Math. Sci. 37(5), 1331–1347 (2017)
Du, G., Zuo, L.: Local and parallel finite element methods for the coupled Stokes/Darcy model. Numer. Algor., 1593-1611 (2021)
Du, G.: Expandable parallel finite element methods for linear elliptic problems. Acta Math. Sci. 40B(2), 572–588 (2020)
Du, G., Zuo, L.: Local and parallel finite element post-processing scheme for the Stokes problem. Comput. Math. Applic., 129–140 (2017)
He, Y., Xu, J., Zhou, A.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms for the Navier-Stokes problem. J. Comput. Math., 227–238 (2006)
He, Y., Xu, J., Zhou, A., Li, J.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms for the Stokes problem. Numer. Math. 109(3), 415–434 (2008)
Hou, Y.: Optimal error estimates of a decoupled scheme based on two-grid finite element for mixed Stokes-Darcy model. Appl. Math. Lett. 57, 90–96 (2016)
Jiang, B.: A parallel domain decomposition method for coupling of surface and groundwater flows. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 198(9-12), 947–957 (2009)
Li, Q., Du, G.: Local and parallel finite element methods based on two-grid discretizations for the nonstationary Navier-Stokes equations. Numer. Algor. 88(4), 1915–1936 (2021)
Li, Q., Du, G.: Local and parallel finite element methods based on two-grid discretizations for unsteady convection-diffusion problem. Numer. Methods Partial Diff. Equa. 37(6), 3023–3041 (2021)
Li, R., Gao, Y., Li, J., Chen, Z.: A weak galerkin finite element method for a coupled Stokes-Darcy problem on general meshes. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 334, 111–127 (2018)
Li, Y., Hou, Y., Layton, W., Zhao, H.: Adaptive partitioned method for the time-accurate approximation of the evolutionary Stokes-Darcy system. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 364, 112923 (2020)
Mu, M., Xu, J.: A two-grid method of a mixed Stokes-Darcy model for coupling fluid flow with porous media flow. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 45 (5), 1801–1813 (2007)
Qin, Y., Hou, Y., Huang, P., Wang, Y.: Numerical analysis of two grad-div stabilization methods for the time-dependent Stokes/Darcy model. Comput. Math. Applic. 73(9), 817–832 (2020)
Shan, L., Zheng, H.: Partitioned time stepping method for fully evolutionary Stokes-Darcy flow with Beavers-Joseph interface conditions. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 51(2), 813–839 (2013)
Shang, Y., Wang, K.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms based on two-grid discretizations for the transient Stokes equations. Numer. Algor. 54(2), 195–218 (2010)
Shang, Y., He, Y.: Parallel iterative finite element algorithms based on full domain partition for the stationary Navier-Stokes equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 60(7), 719–737 (2010)
Shang, Y., He, Y., Kim, D., Zhou, X.: A new parallel finite element algorithm for the stationary Navier-Stokes equations. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 47(11), 1262–1279 (2011)
Song, L., Li, P., Gu, Y., Fan, C.: Generalized finite difference method for solving stationary 2D and 3D stokes equations with a mixed boundary condition. Comput. Math. Applic. 80(6), 1726–1743 (2020)
Sun, Y., Sun, W., Zheng, H.: Domain decomposition method for the fully-mixed Stokes-Darcy coupled problem. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 374, 113578 (2021)
Vassilev, D., Wang, C., Yotov, I.: Domain decomposition for coupled Stokes and Darcy flows. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 268, 264–283 (2014)
Wang, X., Du, G., Zuo, L.: A novel local and parallel finite element method for the mixed Navier-Stokes-Darcy problem. Comput. Math. Applic. 90 (15), 73–79 (2021)
Xu, J., Zhou, A.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms based on two-grid discretizations. Math. Comput. 69(231), 881–909 (2000)
Yu, J., Shi, F., Zheng, H.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms based on the partition of unity for the Stokes problem. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 36(5), C547–C567 (2014)
Yu, J., Sun, Y., Shi, F., Zheng, H.: Nitsches type stabilized finite element method for the fully mixed Stokes-Darcy problem with Beavers-Joseph conditions. Appl. Math. Lett. 110, 106588 (2020)
Zheng, H., Yu, J., Shi, F.: Local and parallel finite element method based on the partition of unity for incompressible flow. J. Sci. Comput. 65(2), 512–532 (2015)
Zheng, H., Song, L., Hou, Y., Zhang, Y.: The partition of unity parallel finite element algorithm. Adv. Comput. Math. 41(4), 937–951 (2015)
Zuo, L., Du, G.: A parallel two-grid linearized method for the coupled Navier-Stokes-Darcy problem. Numer. Algor. 77(1), 151–165 (2018)
Zuo, L., Du, G.: A multi-grid technique for coupling fluid flow with porous media flow. Comput. Math. Applic. 75(11), 4012–4021 (2018)
Funding
This work is subsidized by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 12172202, 11701343, 12101494), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (Grant No. ZR2021MA063), the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (2021JQ-426), and the Scientific Research Program of Shaanxi Provincial Education Department (21JK0935).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Du, G. & Li, Y. A modified local and parallel finite element method for the coupled Stokes-Darcy model with the Beavers-Joseph interface condition. Numer Algor 93, 815–831 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-022-01442-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-022-01442-4