Abstract
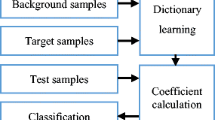
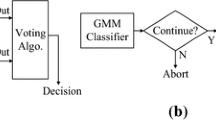
This paper presents Program Guardian, which is a speaker recognition-based screening system for smart TV. The system identifies a specific person from his or her voice such that the smart TV can provide suitable programs for that person. This system is based on a robust speaker recognition system that uses robust principal component analysis (RPCA) and a sparse representation classifier (SRC). First, i-vectors that are generated from supervectors of Gaussian mixture models (GMMs) are used to generate the basic atoms of an over-complete dictionary. The i-vectors are then transformed using RPCA. The SRC is produced from transformed i-vector-based RPCA vectors. Finally, the sparse representation classifier corresponding to the target speaker with the least reconstruction error is constructed. NIST speaker recognition evaluation data base is used in our experiment. The results show that the proposed speaker recognition system is feasible and offers advantages over accuracy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahari MH, McLaren M, Hamme HV, Leeuwen DV (2012) Age estimation from telephone speech using i-vectors. In Proceedings of INTERSPEECH 2012, pp. 506–509
Campbell WM, Sturim DE, Reynolds DA (2006) Support vector machines using GMM supervectors for speaker verification. IEEE Signal Process Lett 13(5):308–311
Campbell WM, Sturim DE, Reynolds DA, Solomonoff A (2006) SVM-based speaker verification using a GMM supervector kernel and NAP variability compensation. In Proceedings of the 2006 I.E. International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. I-97–I-100
Candès E, Li X, Ma Y, Wright J (2011) Robust principal component analysis? J ACM 58(3):11:1–11:37
Chen CF, Wei CP, Wang YCF (2012) Low-rank matrix recovery with structural incoherence for robust face recognition. In Proceedings of the 2012 I.E. Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2618–2625
De la Torre F, Black M (2001) Robust principal component analysis for computer vision. In Proceedings of the Eighth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 362–369
De la Torre F, Black M (2003) A framework for robust subspace learning. Int J Comput Vis 54(1):117–142
Gauvain JL, Lee CH (1994) Maximum a posteriori estimation for multivariate Gaussian mixture observations of Markov chains. IEEE Trans Speech Audio Process 2(2):291–298
Han Y, Park K, Lee YK (2011) Confident wrapper-type semi-supervised feature selection using an ensemble classifier. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Management Science and Electronic Commerce (AIMSEC), pp. 4581–4586.
Huanjun B, Fang Z (2008) Combined GMM-UBM and SVM speaker identification system. J Tsinghua Univ (Sci Technol) 48(S1):693–698
Jeong JW, Lee DH (2014) Inferring search intents from remote control movement patterns: a new content search method for smart TV. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 92–98
Kanagasundaram A, Vogt R, Dean D, Sridharan S, Mason M (2011) i-vector based speaker recognition on short utterances. In Proceedings of INTERSPEECH 2011, pp. 2341–2344
Ke Q, Kanade T (2005) Robust L1 norm factorization in the presence of outliers and missing data by alternative convex programming. In Proceedings of the 2005 I.E. Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 739–746
Kenny P, Ouellet P, Dehak N, Gupta V, Dumouchel P (2008) A study of interspeaker variability in speaker verification. IEEE Trans Audio, Speech, Lang Process 16(5):980–988
Lin Z, Chen M, Ma Y (2010) The augmented lagrange multiplier method for exact recovery of corrupted low-rank matrices. UIUC Technical Report UILU-ENG-09-2215, 2009
Liu G, Lin Z, Yu Y (2010) Robust subspace segmentation by low-rank representation. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1–8
Liu G, Lin Z, Yan S, Sun J, Yu Y, Ma Y (2013) Robust recovery of subspace structures by low-rank representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(1):171–184
Naseem I, Togneri R, Bennamoun M (2010) Sparse representation for speaker identification. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, pp. 4460–4463
Potamitis I, Georgila K, Fakotakis N, Kokkinakis G (2003) An integrated system for smart-home control of appliances based on remote speech interaction. In Proceedings of INTERSPEECH 2003, pp. 2197–2200
Povey D, Chu SM, Varadarajan B (2008) Universal background model based speech recognition. In Proceedings of the 2008 I.E. International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 4561–4564
Vergin R, O’Shaughnessy D, Farhat A (1999) Generalized mel frequency cepstral coefficients for largevocabulary speaker-independent continuous-speech recognition. IEEE Trans Speech Audio Process 7(5):525–532
Wright J, Yang AY, Ganesh A, Sastry SS, Ma Y (2009) Robust face recognition via sparse representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 31(2):210–227
Yan C, Zhang Y, Xu J, Dai F, Zhang J, Fai Q, Wu F (2014) Efficient parallel framework for HEVC motion estimation on many-core processors. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 2077–2089
Yan C, Zhang Y, Dai F, Wang X, Li L, Dai Q (2014) Parallel deblocking filter for HEVC on many-core processor. Electron Lett 367–368
Zeinali H, Sameti H, Khaki H, BabaAli B (2012) A fast two-level speaker identification method employing sparse representation and GMM-based methods. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Information Science, Signal Processing and their Applications (ISSPA), pp. 45–48
Zuo F, de With PHN (2005) Real-time embedded face recognition for smart home. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 51(1):183–190
Zuo F, de With PHN (2005) Real-time face recognition for smart home applications. In Proceedings of the 2005 International Conference on Consumer, pp. 35–36
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chin, YH., Tai, TC., Zhao, JH. et al. Program Guardian: screening system with a novel speaker recognition approach for smart TV. Multimed Tools Appl 76, 13881–13896 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3764-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3764-9