Abstract
We present the recent development of hybridizable and embedded discontinuous Galerkin (DG) methods for wave propagation problems in fluids, solids, and electromagnetism. In each of these areas, we describe the methods, discuss their main features, display numerical results to illustrate their performance, and conclude with bibliography notes. The main ingredients in devising these DG methods are (1) a local Galerkin projection of the underlying partial differential equations at the element level onto spaces of polynomials of degree k to parametrize the numerical solution in terms of the numerical trace; (2) a judicious choice of the numerical flux to provide stability and consistency; and (3) a global jump condition that enforces the continuity of the numerical flux to obtain a global system in terms of the numerical trace. These DG methods are termed hybridized DG methods, because they are amenable to hybridization (static condensation) and hence to more efficient implementations. They share many common advantages of DG methods and possess some unique features that make them well-suited to wave propagation problems.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Strictly speaking, the finite element mesh can only partition the problem domain if \(\partial \Omega \) is piecewise p-th degree polynomial. For simplicity of exposition, and without loss of generality, we assume hereinafter that \(\mathcal {T}_h\) actually partitions \(\Omega \).
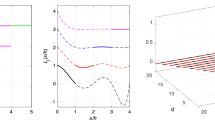
Note the amplification factor \(N_1\) in the y-axis is a logarithmic quantity.
Note the amplitude of the instabilities in Fig. 3 is non-dimensionalized with respect to the freestream velocity.
References
Ahnert, T., Bärwolff, G.: Numerical comparison of hybridized discontinuous Galerkin and finite volume methods for incompressible flow. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 76(5), 267–281 (2014)
Alexander, R.: Diagonally implicit Runge–Kutta methods for stiff ODEs. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 14, 1006–1021 (1977)
Balan, A., Woopen, M., May, G.: Adjoint-based hp-adaptation for a class of high-order hybridized finite element schemes for compressible flows. In: 21st AIAA Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference (2013)
Bonnasse-Gahot, M., Calandra, H., Diaz, J., Lanteri, S.: Hybridizable discontinuous galerkin method for the 2-d frequency-domain elastic wave equations. Geophys. J. Int. 213(1), 637–659 (2018)
Bui-Thanh, T.: From Godunov to a unified hybridized discontinuous Galerkin framework for partial differential equations. J. Comput. Phys. 295, 114–146 (2015)
Cai, X.C., Sarkis, M.: A restricted additive Schwarz preconditioner for general sparse linear systems. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 21, 792–797 (1999)
Celiker, F., Cockburn, B., Shi, K.: Hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin methods for Timoshenko beams. J. Sci. Comput. 44(1), 1–37 (2010)
Cesmelioglu, A., Cockburn, B., Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J.: Analysis of HDG methods for Oseen equations. J. Sci. Comput. 55, 392–431 (2013)
Cesmelioglu, A., Cockburn, B., Qiu, W.: Analysis of a hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method for the steady-state incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. Math. Comput. 86(306), 1643–1670 (2017)
Chabaud, B., Cockburn, B.: Uniform-in-time superconvergence of HDG methods for the heat equation. Math. Comput. 81, 107–129 (2012)
Chaurasia, H.K.: A time-spectral hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method for periodic flow problems. Ph.D. thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (2014)
Chaurasia, H.K., Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J.: A Time-spectral hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method for periodic flow problems. In: 21st AIAA Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference, Fluid Dynamics and Co-located Conferences, AIAA 2013-2861. American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (2013)
Chen, G., Xie, X.: A robust weak galerkin finite element method for linear elasticity with strong symmetric stresses. Comput. Methods Appl. Math. 16(3), 389–408 (2016)
Chen, H., Qiu, W., Shi, K., Solano, M.: A superconvergent HDG method for the Maxwell equations. J. Sci. Comput. 70(3), 1010–1029 (2017)
Christophe, A., Descombes, S., Lanteri, S.: An implicit hybridized discontinuous Galerkin method for the 3D time-domain Maxwell equations. Appl. Math. Comput. 319(Supplement C), 395–408 (2018)
Ciuca, C.: Implicit hybridized discontinuous Galerkin methods for magnetohydrodynamics. Master’s thesis, Imperial College London (2018)
Cockburn, B., Dong, B., Guzmán, J.: A superconvergent LDG-hybridizable Galerkin method for second-order elliptic problems. Math. Comput. 77, 1887–1916 (2008)
Cockburn, B., Dong, B., Guzmán, J., Restelli, M., Sacco, R.: A hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method for steady-state convection-diffusion-reaction problems. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 31(5), 3827–3846 (2009)
Cockburn, B., Fu, G.: Superconvergence by \(m\)-decompositions. Part ii: construction of two-dimensional finite elements. ESAIM Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 51(1), 165–186 (2017)
Cockburn, B., Fu, G.: Superconvergence by \(m\)-decompositions. Part iii: construction of three-dimensional finite elements. ESAIM Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 51(1), 365–398 (2017)
Cockburn, B., Fu, G.: Devising superconvergent hdg methods with symmetric approximate stresses for linear elasticity by M-decompositions. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 38(2), 566–604 (2018)
Cockburn, B., Fu, G., Qiu, W.: A note on the devising of superconvergent hdg methods for stokes flow by m-decompositions. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 37(2), 730–749 (2017)
Cockburn, B., Fu, G., Sayas, F.: Superconvergence by \(m\)-decompositions. Part i: general theory for hdg methods for diffusion. Math. Comput. 86(306), 1609–1641 (2017)
Cockburn, B., Fu, Z., Hungria, A., Ji, L., Sánchez, M.A., Sayas, F.-J.: Stormer-Numerov HDG methods for acoustic waves. J. Sci. Comput. 75(2), 597–624 (2017)
Cockburn, B., Gopalakrishnan, J., Lazarov, R.: Unified hybridization of discontinuous Galerkin, mixed, and continuous Galerkin methods for second order elliptic problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 47(2), 1319–1365 (2009)
Cockburn, B., Gopalakrishnan, J., Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J., Sayas, F.-J.: Analysis of HDG methods for Stokes flow. Math. Comput. 80, 723–760 (2011)
Cockburn, B., Gopalakrishnan, J., Sayas, F.-J.: A projection-based error analysis of HDG methods. Math. Comput. 79, 1351–1367 (2010)
Cockburn, B., Guzmán, J., Wang, H.: Superconvergent discontinuous Galerkin methods for second-order elliptic problems. Math. Comput. 78, 1–24 (2009)
Cockburn, B., Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J.: A comparison of HDG methods for Stokes flow. J. Sci. Comput. 45(1–3), 215–237 (2010)
Cockburn, B., Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J.: A comparison of HDG methods for Stokes flow. J. Sci. Comput. 45(1), 215–237 (2010)
Cockburn, B., Qiu, W., Shi, K.: Conditions for superconvergence of hdg methods for second-order elliptic problems. Math. Comput. 81(279), 1327–1353 (2012)
Cockburn, B., Qiu, W., Shi, K.: Superconvergent hdg methods on isoparametric elements for second-order elliptic problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 50(3), 1417–1432 (2012)
Cockburn, B., Quenneville-Bélair, V.: Uniform-in-time superconvergence of HDG methods for the acoustic wave equation. Math. Comput. 83, 65–85 (2014)
Cockburn, B., Sayas, F.J.: Divergence-conforming HDG methods for Stokes flow. Math. Comput. 83, 1571–1598 (2014)
Cockburn, B., Shi, K.: Conditions for superconvergence of HDG methods for Stokes flow. Math. Comput. 82, 651–671 (2013)
Cockburn, B., Shi, K.: Superconvergent HDG methods for linear elasticity with weakly symmetric stresses. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 33(3), 747–770 (2013)
Cockburn, B., Di Pietro, D.A., Ern, A.: Bridging the hybrid high-order and hybridizable discontinuous galerkin methods. ESAIM Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 50(3), 635–650 (2016)
Cui, J., Zhang, W.: An analysis of HDG methods for the Helmholtz equation. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 34(1), 279–295 (2014)
Dahm, J.P.S., Fidkowski, K.J.: Error estimation and adaptation in hybridized discontinuous Galerkin methods. In: 52nd Aerospace Sciences Meeting, AIAA 2014-0078 (2014)
Dedner, A., Kemm, F., Kröner, D., Munz, C.D., Schnitzer, T., Wesenberg, M.: Hyperbolic divergence cleaning for the MHD equations. J. Comput. Phys. 175(2), 645–673 (2002)
Di Pietro, D.A., Ern, A.: A hybrid high-order locking-free method for linear elasticity on general meshes. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 283, 1–21 (2015)
Dong, B.: Optimally convergent HDG method for third-order Korteweg-de Vries type equations. J. Sci. Comput. 73(2), 712–735 (2017)
Evans, C.R., Hawley, J.F.: Simulation of magnetohydrodynamic flows: a constrained transport method. Astrophys. J. 332(2), 659–677 (1988)
Eyck, A.T., Celiker, F., Lew, A.: Adaptive stabilization of discontinuous Galerkin methods for nonlinear elasticity: motivation, formulation, and numerical examples. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 197, 1–21 (2007)
Eyck, A.T., Celiker, F., Lew, A.: Adaptive stabilization of discontinuous Galerkin methods for nonlinear elasticity: analytical estimates. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 197, 2989–3000 (2008)
Feng, X., Lu, P., Xu, X.: A hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method for the time-harmonic Maxwell equations with high wave number. Comput. Methods Appl. Math. 16(3), 429–445 (2016)
Feng, X., Xing, Y.: Absolutely stable local discontinuous Galerkin methods for the Helmholtz equation with large wave number. Math. Comput. 82(283), 1269–1296 (2012)
Fernandez, P.: The hybridized discontinuous Galerkin methods for large-eddy simulation of transitional and turbulent flows. PhD thesis, Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (2018)
Fernandez, P., Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J.: Subgrid-scale modeling and implicit numerical dissipation in DG-based Large-Eddy Simulation. In: 23rd AIAA Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference, AIAA 2017-3951, Denver, Colorado, USA (2017)
Fernandez, P., Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J.: The hybridized discontinuous Galerkin method for implicit large-eddy simulation of transitional turbulent flows. J. Comput. Phys. 336, 308–329 (2017)
Fernandez, P., Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J.: A physics-based shock capturing method for unsteady laminar and turbulent flows. In: 56th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Orlando, Florida, Jan 2018. American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (2018)
Fernandez, P., Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J.: Entropy-stable hybridized discontinuous Galerkin methods for the compressible Euler and Navier–Stokes equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. (Under Review). arXiv preprint arXiv:1808.05066 (2018)
Fernandez, P., Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J.: A physics-based shock capturing method for large-eddy simulation. J. Comput. Phys. (Under Review). arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.06449 (2018)
Fernandez, P., Nguyen, N.C., Roca, X., Peraire, J.: Implicit large-eddy simulation of compressible flows using the interior embedded discontinuous Galerkin method. In: 54th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, San Diego, California, USA, Jan 2016. American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (2016)
Fernandez, P., Moura, R., Mengaldo, G., Peraire, J.: Non-modal analysis of spectral element methods: towards accurate and robust large-eddy simulations. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.09712 (2018)
Fidkowski, K.J.: A hybridized discontinuous Galerkin method on mapped deforming domains. Comput. Fluids 139, 80–91 (2016)
Fu, G., Cockburn, B., Stolarski, H.: Analysis of an HDG method for linear elasticity. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 102(3–4), 551–575 (2015)
Giorgiani, G., Fernández-Méndez, S., Huerta, A.: Hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin p-adaptivity for wave propagation problems. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 72(12), 1244–1262 (2013)
Giorgiani, G., Fernández-Méndez, S., Huerta, A.: Hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin with degree adaptivity for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. Comput. Fluids 98, 196–208 (2014)
Gopalakrishnan, J., Li, F., Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J.: Spectral approximations by the HDG method. Math. Comput. 84(293), 1037–1059 (2015)
Griesmaier, R., Monk, P.: Error analysis for a hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method for the Helmholtz equation. J. Sci. Comput. 49(3), 291–310 (2011)
Gürkan, C., Kronbichler, M., Fernández-Méndez, S.: Extended hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin with heaviside enrichment for heat bimaterial problems. J. Sci. Comput. 72(2), 542–567 (2017)
Güzey, S., Cockburn, B., Stolarski, H.K.: The embedded discontinuous Galerkin methods: application to linear shells problems. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 70, 757–790 (2007)
Hungria, A., Prada, D., Sayas, F.-J.: HDG methods for elastodynamics. Comput. Math. Appl. 74(11), 2671–2690 (2017)
Huynh, L.N.T., Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J., Khoo, B.C.: A high-order hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method for elliptic interface problems. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 93(2), 183–200 (2013)
Jaust, A., Schütz, J.: A temporally adaptive hybridized discontinuous Galerkin method for time-dependent compressible flows. Comput. Fluids 98, 177–185 (2014)
Kabaria, H., Lew, A., Cockburn, B.: A hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin formulation for non-linear elasticity. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 283, 303–329 (2015)
Kolkman, L.N.: Implementation of an implicit-explicit scheme for hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin methods. Master’s thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (2018)
Lehrenfeld, C., Schöberl, J.: High order exactly divergence-free hybrid discontinuous Galerkin methods for unsteady incompressible flows. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 307, 339–361 (2016)
Li, F., Xu, L., Yakovlev, S.: Central discontinuous Galerkin methods for ideal MHD equations with the exactly divergence-free magnetic field. J. Comput. Phys. 230(12), 4828–4847 (2011)
Li, L., Lanteri, S., Mortensen, N.A., Wubs, M.: A hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method for solving nonlocal optical response models. Comput. Phys. Commun. 219, 99–107 (2017)
Li, L., Lanteri, S., Perrussel, R.: A hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method combined to a Schwarz algorithm for the solution of 3d time-harmonic Maxwell’s equations. J. Comput. Phys. 256, 563–581 (2014)
Li, L., Lanteri, S., Perrussel, R.: A class of locally well-posed hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin methods for the solution of time-harmonic Maxwell’s equations. Comput. Phys. Commun. 192, 23–31 (2015)
Lu, P., Chen, H., Qiu, W.: An absolutely stable hp-HDG method for the time-harmonic Maxwell equations with high wave number. Math. Comput. 86(306), 1553–1577 (2017)
McGhee, R., Walker, B., Millard, B.: Experimental Results for the Eppler 387 airfoil at Low Reynolds Number in the Langley Low-Turbulence Pressure Tunnel. Technical Report, NASA Langley Research Center, Langley (1988)
Moro, D., Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J.: Navier–Stokes Solution Using Hybridizable Discontinuous Galerkin methods. Hawaii, Technical Report, Honolulu (2011)
Moro, D., Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J.: Dilation-based shock capturing for high-order methods. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 82(7), 398–416 (2016)
Moro, D., Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J., Drela, M.: Advances in the development of a high order, viscous-inviscid interaction solver. In: 21st AIAA Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference, AIAA 2013-2943, San Diego (2013)
Moro, D., Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J., Drela, M.: Mesh topology preserving boundary-layer adaptivity method for steady viscous flows. AIAA J. 55(6), 1970–1985 (2017)
Munz, C.D., Omnes, P., Schneider, R., Sonnendrücker, E., Voß, U.: Divergence correction techniques for Maxwell solvers based on a hyperbolic model. J. Comput. Phys. 161(2), 484–511 (2000)
Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J., Cockburn, B.: Hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin methods. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Spectral and High Order Methods, Trondheim (2009)
Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J., Cockburn, B.: A hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. In: Proceedings of the 48th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, AIAA 2010-362, Orlando (2010)
Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J.: An adaptive shock-capturing HDG method for compressible flows. In: 20th AIAA Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference, AIAA 2011–3060, Reston, Virigina, 2011. American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (2011)
Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J.: Hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin methods for partial differential equations in continuum mechanics. J. Comput. Phys. 231(18), 5955–5988 (2012)
Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J., Cockburn, B.: An implicit high-order hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method for linear convection diffusion equations. J. Comput. Phys. 228(9), 3232–3254 (2009)
Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J., Cockburn, B.: An implicit high-order hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method for nonlinear convection diffusion equations. J. Comput. Phys. 228(23), 8841–8855 (2009)
Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J., Cockburn, B.: A hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method for Stokes flow. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 199(9–12), 582–597 (2010)
Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J., Cockburn, B.: An implicit high-order hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 230(4), 1147–1170 (2011)
Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J., Cockburn, B.: High-order implicit hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin methods for acoustics and elastodynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 230(10), 3695–3718 (2011)
Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J., Cockburn, B.: Hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin methods for the time-harmonic Maxwell’s equations. J. Comput. Phys. 230(19), 7151–7175 (2011)
Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J., Cockburn, B.: A class of embedded discontinuous Galerkin methods for computational fluid dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 302, 674–692 (2015)
Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J., Reitich, F., Cockburn, B.: A phase-based hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method for the numerical solution of the Helmholtz equation. J. Comput. Phys. 290, 318–335 (2015)
Nguyen, N.C., Roca, X., Moro, D., Peraire, J.: A hybridized multiscale discontinuous Galerkin method for compressible flows. In: 51st AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting iIncluding the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition, AIAA-2013-689 (2013)
Park, H.-R., Chen, X., Nguyen, N.C., Oh, S.-H., Peraire, J.: Nanogap-enhanced Terahertz sensing of 1-nm-thick dielectric films. ACS Photonics 2(3), 417–424 (2015)
Peraire, J., Nguyen, N.C., Cockburn, B.: A hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method for the compressible Euler and Navier–Stokes equations. In: 48th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting Including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition, AIAA 2010-363 (2010)
Peraire, J., Nguyen, N.C., Cockburn, B.: An embedded discontinuous Galerkin method for the compressible Euler and Navier–Stokes equations. In 20th AIAA Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference, AIAA 2011-3228, Reston, Virigina, Jun 2011. American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (2011)
Qiu, W., Shen, J., Shi, K.: An HDG method for linear elasticity with strong symmetric stresses. Math. Comput. 87(309), 69–93 (2018)
Qiu, W., Shi, K.: A superconvergent HDG method for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations on general polyhedral meshes. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 36(4), 1943–1967 (2016)
Rhebergen, S., Cockburn, B.: A space-time hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method for incompressible flows on deforming domains. J. Comput. Phys. 231(11), 4185–4204 (2012)
Roca, X., Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J.: Scalable parallelization of the hybridized discontinuous Galerkin method for compressible flow. In: 21st AIAA Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference, AIAA-2013-2939 (2013)
Saad, Y., Schultz, M.H.: GMRES: a generalized minimal residual algorithm for solving nonsymmetric linear systems. SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput. 7, 856–869 (1986)
Samii, A., Dawson, C.: An explicit hybridized discontinuous Galerkin method for Serre–Green–Naghdi wave model. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 330(Supplement C), 447–470 (2018)
Sánchez, M.A., Ciuca, C., Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J., Cockburn, B.: Symplectic Hamiltonian HDG methods for wave propagation phenomena. J. Comput. Phys. 350(Supplement C), 951–973 (2017)
Schütz, J., May, G.: A hybrid mixed method for the compressible Navier–Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 240, 58–75 (2013)
Schutz, J., May, G.: An adjoint consistency analysis for a class of hybrid mixed methods. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 34, 1222–1239 (2013)
Sheldon, J.P., Miller, S.T., Pitt, J.S.: A hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method for modeling fluid-structure interaction. J. Comput. Phys. 326(Supplement C), 91–114 (2016)
Soon, S.-C.: Hybridizable discontinuosu Galerkin methods for solid mechanics. Ph.D thesis, University of Minnesota (2008)
Soon, S.-C., Cockburn, B., Stolarski, H.K.: A hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method for linear elasticity. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 80(8), 1058–1092 (2009)
Stanglmeier, M., Nguyen, N.C., Peraire, J., Cockburn, B.: An explicit hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method for the acoustic wave equation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 300, 748–769 (2016)
Terrana, S., Vilotte, J.-P., Guillot, L.: A spectral hybridizable discontinuous galerkin method for elastic–acoustic wave propagation. Geophys. J. Int. 213(1), 574–602 (2018)
Ueckermann, M.P., Lermusiaux, P.F.J.: High-order schemes for 2D unsteady biogeochemical ocean models. Ocean Dyn. 60(6), 1415–1445 (2010)
Ueckermann, M.P., Lermusiaux, P.F.J.: Hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin projection methods for Navier–Stokes and Boussinesq equations. J. Comput. Phys. 306, 390–421 (2016)
Vidal-Codina, F., Nguyen, N.C., Oh, S.-H., Peraire, J.: A hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method for computing nonlocal electromagnetic effects in three-dimensional metallic nanostructures. J. Comput. Phys. 355, 548–565 (2018)
Williams, D.: An entropy stable, hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method for the compressible Navier–Stokes equations. Math. Comput. 87(309), 95–121 (2018)
Woopen, M., Balan, A., May, G.: A hybridized hiscontinuous Galerkin method for three-dimensional compressible flow problems. In: 52nd Aerospace Sciences Meeting, AIAA 2014-0938 (2014)
Woopen, M., Balan, A., May, G., Schütz, J.: A comparison of hybridized and standard DG methods for target-based hp-adaptive simulation of compressible flow. Comput. Fluids 98, 3–16 (2014)
Woopen, M., May, G., Schütz, J.: Adjoint-based error estimation and mesh adaptation for hybridized discontinuous Galerkin methods. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 76(11), 811–834 (2014)
Yoo, D., Nguyen, N.C., Martin-Moreno, L., Mohr, D.A., Carretero-Palacios, S., Shaver, J., Peraire, J., Ebbesen, T.W., Oh, S.H.: High-throughput fabrication of resonant metamaterials with ultrasmall coaxial apertures via atomic layer lithography. Nano Lett. 16(3), 2040–2046 (2016)
Zhu, L., Huang, T.Z., Li, L.: A hybrid-mesh hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method for solving the time-harmonic Maxwell’s equations. Appl. Math. Lett. 68, 109–116 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (FA9550-15-1-0276 and FA9550-16-1-0214), the NASA (NNX16AP15A), and Pratt & Whitney for supporting this work. P. Fernandez also acknowledges the financial support from the Zakhartchenko and “la Caixa” Fellowships.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernandez, P., Christophe, A., Terrana, S. et al. Hybridized Discontinuous Galerkin Methods for Wave Propagation. J Sci Comput 77, 1566–1604 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-018-0811-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-018-0811-x