Abstract
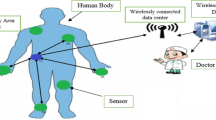
Wireless body area networks (WBANs) play a pivotal role in monitoring body movements and collecting crucial health metrics such as blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen levels, and physiological conditions. These health parameters are acquired through sensor clusters strategically deployed on the human body and subsequently transmitted to fog or cloud layers for essential decision-making processes. This research study commences by enhancing energy efficiency within WBANs through the introduction of an innovative weight-based algorithm known as the weight-based next neighbor selection algorithm (WBNN). WBNN assigns specific weights to each route connecting pairs of sensors by considering the distance between them. A small weight implies a small distance, while a high value of weight implies a high distance. The total weight of each route is then computed. During the forwarding mechanism, sensor nodes opt for routes with the smallest weight, signifying reduced energy consumption. Secondly, it provides insights into various clustering schemes and routing algorithms employed for data exchange among different sensors and network layers. Lastly, the suggested algorithm is compared with the latest routing algorithms on the basis of four parameters, i.e., network utilization, number of dead nodes, throughput and energy consumption. The results show that the described protocol surpasses traditional routing protocols by achieving superior outcomes, including a 6% reduction in energy consumption, a 72% increase in throughput, and a 68% decrease in number of dead nodes. These findings underscore the potential of the proposed protocol to significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of WBANs in the domain of smart healthcare applications.













Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Availability of data and material
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Aadil F, Song OY, Mushtaq M, Maqsood M, Sheikh SE, Baber J (2023) An efficient cluster optimization framework for internet of things (IoT) based wireless body area networks. J Enterp Inform Manag 36(3):839–860. https://doi.org/10.1108/JEIM-02-2020-0075/FULL/XML
Ahmad N, Awan MD, Khiyal MSH, Babar MI, Abdelmaboud A, Ibrahim HA, Hamed NO (2022a) Improved QoS aware routing protocol (IM-QRP) for WBAN based healthcare monitoring system. IEEE Access 10:121864–121885. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3223085
Ahmad N, Shahzad B, Arif M, Izdrui D, Ungurean I, Geman O (2022b) An energy-efficient framework for WBAN in health care domain. J Sens. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5823461
Al-Hiti AS, Ratna KZS, Harun SW, Obaid AN, Hamdi MM, Al-Shareeda MA (2023) Wireless body area networks: applications and congestion control technologies. Optim Robot Appl. https://doi.org/10.1109/HORA58378.2023.10156683
Aryai P, Khademzadeh A, Jassbi SJ, Hosseinzadeh M (2023a) SIMOF: Swarm intelligence multi-objective fuzzy thermal-aware routing protocol for WBANs. J Supercomput 79(10):10941–10976. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11227-023-05102-9/METRICS
Aryai P, Khademzadeh A, Jassbi SJ, Hosseinzadeh M, Hashemzadeh O, Shokouhifar M (2023b) Real-time health monitoring in WBANs using hybrid metaheuristic-driven machine learning routing protocol (MDML-RP). AEU-Int J Electron C 168(August):154723. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AEUE.2023.154723
Chavva SR, Sangam RS (2022) SIMPLE-DRR: a new energy-efficient multi-hop routing protocol in WBANs for health monitoring. Lect Notes Electric Eng 838:29–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-8550-7_4/COVER
Egert J, Kreutz C (2023) Rcall: an R interface for MATLAB. SoftwareX 21(February):101276. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SOFTX.2022.101276
Goyal R, Mittal N, Gupta L, Surana A (2023) Routing protocols in wireless body area networks: Architecture, challenges, and classification. Wirel Commun Mob Comput. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/9229297
Hai T, Zhou J, Masdari M, Marhoon HA (2023) A hybrid marine predator algorithm for thermal-aware routing scheme in wireless body area networks. J Bionic Eng 20(1):81–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/S42235-022-00263-4/METRICS
Karunanithy K, Velusamy B (2022) Edge device based efficient data collection in smart health monitoring system using wireless body area network. Biomed Signal Process Control 72(February):103280. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BSPC.2021.103280
Kiran MV, Nithya B (2023) Stable and energy-efficient next-hop router selection (SE-NRS) for wireless body area networks. Int J Inform Technol (singapore) 15(2):1189–1200. https://doi.org/10.1007/S41870-022-01083-9/METRICS
Liu Xu, Zhang Y, Wang X, Zhang J, Dong K, Wang F, Li H, Zheng H, Yonghui Wu, Wang ZL (2023) A battery-free wireless body area network towards state perception under all-weather conditions. Nano Energy 116(November):108856. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.NANOEN.2023.108856
Mohanty RK, Sahoo SP, Kabat MR (2023) Sustainable remote patient monitoring in wireless body area network with multi-hop routing and scheduling: a four-fold objective based optimization approach. Wirel Netw 29(5):2337–2351. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11276-023-03276-X/METRICS
Nyangaresi VO (2023) Privacy preserving three-factor authentication protocol for secure message forwarding in wireless body area networks. Ad Hoc Netw 142(April):103117. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ADHOC.2023.103117
Olatinwo DD, Abu-Mahfouz AM, Hancke GP (2021) Towards achieving efficient MAC protocols for WBAN-enabled IoT technology: a review. EURASIP J Wirel Commun Netw 2021(1):1–47. https://doi.org/10.1186/S13638-021-01919-1/TABLES/5
Preethichandra DMG, Piyathilaka L, Izhar U, Samarasinghe R, De Silva LC (2023) wireless body area networks and their applications—a review. IEEE Access 11:9202–9220. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3239008
Raayatpanah MA, Abyaneh AA, Elias J, Trotta A (2023) Optimal reliable design of energy-efficient wireless body area networks. Internet of Things 22(July):100727. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IOT.2023.100727
Raed S, Alabady SA (2022) CPAOR: control packet aware on-demand routing protocol for WBANs. Int J Sens Wirel Commun Control 12(5):402–414
Roshini A, Kiran KVD (2023) Hierarchical energy efficient secure routing protocol for optimal route selection in wireless body area networks. Int J Intell Netw 4(January):19–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJIN.2022.11.006
Selvaprabhu P, Chinnadurai S, Tamilarasan I, Venkatesan R, Kumaravelu VB (2022) Priority-Based resource allocation and energy harvesting for WBAN smart health. Wirel Commun Mob Comput. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8294149
Sharma P, Saini KS, Sidhu PK (2023) Fuzzy rule-based grey Wolf (GW-FIS) in wireless body area networks. In: 2023 IEEE 8th International Conference for Convergence in Technology, I2CT 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/I2CT57861.2023.10126361
Shyja V, Irine GR, Bindhu V (2023) Link quality and energy efficient optimal simplified cluster based routing scheme to enhance lifetime for wireless body area networks. Nano Commun Networks 37(September):100465. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.NANCOM.2023.100465
Singh S, Prasad D (2022) Wireless body area network (WBAN): a review of schemes and protocols. Mater Today Proc 49(January):3488–3496. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATPR.2021.05.564
Singla R, Kaur N, Koundal D, Lashari SA, Bhatia S, Rahmani MKI (2021) Optimized energy efficient secure routing protocol for wireless body area network. IEEE Access 9(1):116745–116759. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3105600
Yaghoubi M, Ahmed K, Miao Y (2022) Wireless body area network (WBAN): a survey on architecture, technologies, energy consumption, and security challenges. J Sens Actuator Netw 11(4):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/JSAN11040067
Zaman K, Zhaoyun S, Hussain A, Hussain T, Ali F, Shah SM, Ur Rahman H (2023) EEDLABA: energy-efficient distance- and link-aware body area routing protocol based on clustering mechanism for wireless body sensor network. Appl Sci 13(4):2190. https://doi.org/10.3390/APP13042190
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the Key Research and Development Project of Shaanxi Province, Grant Number: 2023-YBGY-014; General Research and Development Project of Shaanxi Province, Grant number:2023-YBGY-131.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jing, Y., Peng, H. & Liu, Z. WBNN: a weight-based next neighbor selection algorithm for wireless body area network. Soft Comput 28, 1803–1818 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-09511-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-09511-z