Abstract
Photonic quantum key distribution (QKD) is commonly implemented using interferometers, devices that inherently cause the addition of vacuum ancillas, thus enlarging the quantum space in use. This enlargement sometimes exposes the implemented protocol to new kinds of attacks that have not yet been analyzed.
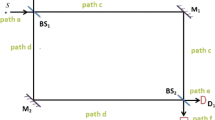
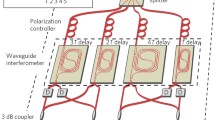
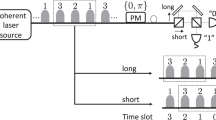
We consider several QKD implementations that use interferometers, and analyze the enlargement of the quantum space caused by the interferometers. While we show that some interferometric implementations are robust (against simple attacks), our main finding is that several other implementations used in QKD experiments are totally insecure.
This result is somewhat surprising since although we assume ideal devices and an underlying protocol which is proven secure (e.g., the Bennett-Brassard QKD), the realization is insecure. Our novel attack demonstrates the risks of using practical realizations without performing an extensive security analysis of the specific setup in use.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharonov, Y., Bergmann, P.G., Lebowitz, J.L.: Time symmetry in the quantum process of measurement. Phys. Rev. 134(6B), B1410–B1416 (1964)
Aharonov, Y., Vaidman, L.: Properties of a quantum system during the time interval between two measurements. Physical Review A 41(1), 11–20 (1990)
Ben-Or, M., Horodecki, M., Leung, D.W., Mayers, D., Oppenheim, J.: The Universal Composable Security of Quantum Key Distribution. In: Kilian, J. (ed.) TCC 2005. LNCS, vol. 3378, pp. 386–406. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Bennett, C.H.: Quantum cryptography using any two nonorthogonal states. Physical Review Letters 68(21), 3121–3124 (1992)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum Cryptography: Public key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, pp. 175–179 (December 1984)
Biham, E., Boyer, M., Boykin, P.O., Mor, T., Roychowdhury, V.P.: A proof of the security of quantum key distribution. J. Cryptology 19(4), 381–439 (2006)
Biham, E., Huttner, B., Mor, T.: Quantum cryptographic network based on quantum memories. Physical Review A 54(4), 2651–2658 (1996)
Bonfrate, G., Harlow, M., Ford, C., Maxwell, G., Townsend, P.: Asymmetric mach-zehnder germano-silicate channel waveguide interferometers for quantum cryptography systems. Electronics Letters 37(13), 846–847 (2001)
Boyer, M., Kenigsberg, D., Mor, T.: Quantum Key Distribution with Classical Bob. Physical Review Letters 99(14), 140501 (2007)
Boyer, M., Gelles, R., Kenigsberg, D., Mor, T.: Semiquantum key distribution. Physical Review A 79(3), 032341 (2009)
Boyer, M., Gelles, R., Mor, T.: Attacks on Fixed Apparatus Quantum Key Distribution Schemes. In: Dediu, A.-H., Martín-Vide, C., Truthe, B. (eds.) TPNC 2012. LNCS, pp. 97–107. Springer, Heidelberg (2012)
Boykin, P.O., Roychowdhury, V.P.: Information vs. disturbance in dimension d. Quantum Info. Comput. 5(4), 396–412 (2005)
Brassard, G., Lütkenhaus, N., Mor, T., Sanders, B.C.: Limitations on practical quantum cryptography. Physical Review Letters 85(6), 1330–1333 (2000)
Bruß, D.: Optimal Eavesdropping in Quantum Cryptography with Six States. Physical Review Letters 81, 3018–3021 (1998)
Dusek, M., Lütkenhaus, N., Hendrych, M.: Chapter 5 quantum cryptography. In: Wolf, E. (ed.) Progress in Optics, vol. 49, pp. 381–454. Elsevier (2006)
Elliott, C., Pearson, D., Troxel, G.: Quantum cryptography in practice. In: SIGCOMM 2003, pp. 227–238 (2003)
Fuchs, C.A., Gisin, N., Griffiths, R.B., Niu, C.S., Peres, A.: Optimal eavesdropping in quantum cryptography. i. information bound and optimal strategy. Physical Review A 56(2), 1163–1172 (1997)
Fuchs, C.A., Peres, A.: Quantum-state disturbance versus information gain: Uncertainty relations for quantum information. Physical Review A 53(4), 2038–2045 (1996)
Gelles, R., Mor, T.: On the security of interferometric quantum key distribution (2011), (full version) arXiv:1110.6573
Gisin, N., Ribordy, G., Tittel, W., Zbinden, H.: Quantum cryptography. Reviews of Modern Physics 74(1), 145–195 (2002)
Gobby, C., Yuan, Z.L., Shields, A.J.: Quantum key distribution over 122 km of standard telecom fiber. Applied Physics Letters 84(19), 3762–3764 (2004)
Gottesman, D., Lo, H.-K., Lütkenhaus, N., Preskill, J.: Security of quantum key distribution with imperfect devices. Quantum Information and Computation 5, 325–360 (2004)
Hughes, R.J., Luther, G.G., Morgan, G.L., Simmons, C.: Quantum cryptography over 14km of installed optical fiber. In: Rochester Conference on Coherence and Quantum Optics, pp. 7–10 (June 1995)
Inamori, H., Lütkenhaus, N., Mayers, D.: Unconditional security of practical quantum key distribution. European Physical Journal D 41, 599–627 (2007)
Inoue, K., Waks, E., Yamamoto, Y.: Differential phase shift quantum key distribution. Physical Review Letters 89(3), 037902 (2002)
Jaeger, G., Sergienko, A.: Entangled states in quantum key distribution. In: AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 810(1), pp. 161–167 (2006)
Lütkenhaus, N.: Security against individual attacks for realistic quantum key distribution. Physical Review A 61(5), 052304 (2000)
Makarov, V., Hjelme, D.R.: Faked states attack on quantum cryptosystems. Journal of Modern Optics 52, 691–705 (2005)
Makarov, V., Anisimov, A., Skaar, J.: Effects of detector efficiency mismatch on security of quantum cryptosystems. Physical Review A 74, 022313 (2006)
Marøy, Ø., Lydersen, L., Skaar, J.: Security of quantum key distribution with arbitrary individual imperfections. Physical Review A 82, 032337 (2010)
Mayers, D.: Unconditional security in quantum cryptography. J. ACM 48(3), 351–406 (2001)
Mayers, D., Yao, A.: Quantum cryptography with imperfect apparatus. In: FOCS 1998, p. 503 (1998)
Muller, A., Herzog, T., Huttner, B., Tittel, W., Zbinden, H., Gisin, N.: “Plug and play” systems for quantum cryptography. Applied Physics Letters 70(7), 793–795 (1997)
Nambu, Y., Hatanaka, T., Nakamura, K.: Planar lightwave circuits for quantum cryptographic systems. Arxiv:quant-ph/0307074 (2003)
Nambu, Y., Hatanaka, T., Nakamura, K.: BB84 quantum key distribution system based on silica-based planar lightwave circuits. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics 43(8B), L1109–L1110 (2004)
Nambu, Y., Yoshino, K., Tomita, A.: Quantum encoder and decoder for practical quantum key distribution using a planar lightwave circuit. Journal of Modern Optics 55(12), 1953–1970 (2008)
Nazarathy, M., Tselniker, I., Regev, Y., Orenstein, M., Katz, M.: Integrated-optical realizations of quantum key distribution over maximally unbiased bases. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics 12(4), 897–913 (2006)
Nazarathy, M.: Quantum key distribution over a fiber-optic channel by means of pulse position modulation. Opt. Lett. 30(12), 1533–1535 (2005)
Renner, R.: Security of Quantum Key Distribution. Ph.D. thesis, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Zurich (2005)
Shor, P.W., Preskill, J.: Simple proof of security of the BB84 quantum key distribution protocol. Physical Review Letters 85(2), 441–444 (2000)
Stucki, D., Gisin, N., Guinnard, O., Ribordy, G., Zbinden, H.: Quantum key distribution over 67 km with a plug&play system. New Journal of Physics 4, 41 (2002)
Takesue, H., Diamanti, E., Honjo, T., Langrock, C., Fejer, M.M., Inoue, K., Yamamoto, Y.: Differential phase shift quantum key distribution experiment over 105km fibre. New Journal of Physics 7, 232 (2005)
Takesue, H., Honjo, T., Kamada, H.: Differential phase shift quantum key distribution using 1.3-μm up-conversion detectors. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics 45, 5757 (2006)
Townsend, P.D.: Secure key distribution system based on quantum cryptography. Electronics Letters 30, 809–811 (1994)
Waks, E., Takesue, H., Yamamoto, Y.: Security of differential-phase-shift quantum key distribution against individual attacks. Physical Review A (Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics) 73(1), 012344 (2006)
Walton, Z.D., Abouraddy, A.F., Sergienko, A.V., Saleh, B.E.A., Teich, M.C.: Decoherence-free subspaces in quantum key distribution. Physical Review Letters 91(8), 087901 (2003)
Yoshino, K., Fujiwara, M., Tanaka, A., Takahashi, S., Nambu, Y., Tomita, A., Miki, S., Yamashita, T., Wang, Z., Sasaki, M., Tajima, A.: High-speed wavelength-division multiplexing quantum key distribution system. Opt. Lett. 37(2), 223–225 (2012)
Zou, X., Qiu, D., Li, L., Wu, L., Li, L.: Semiquantum-key distribution using less than four quantum states. Physical Review A 79(5), 052312 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gelles, R., Mor, T. (2012). On the Security of Interferometric Quantum Key Distribution. In: Dediu, AH., Martín-Vide, C., Truthe, B. (eds) Theory and Practice of Natural Computing. TPNC 2012. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 7505. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33860-1_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33860-1_12
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-33859-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-33860-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)