Abstract
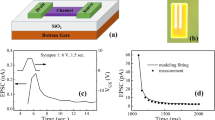
This paper uses the results of the characterization of amorphous semiconductor thin film transistors (TFTs) with a split gate and the quasi-permanent memory structure referred to as silicon oxide nitride semiconductor (SONOS) gates, to model spiking neural circuits with Hebbian learning ability. MOSFETs using organic (tris 8-hydroxyquinolinate aluminum (Alq3), copper phthalocyanine (CuPc)) and inorganic (ZnO) amorphous materials can be fabricated with split gates, which will provide multiple synaptic inputs. A simple Hebbian learning circuit is added to charge and discharge the SONOS device. The primary result of this work is the demonstration of the practicality of using SONOS amorphous organic TFTs with multiple gates and imbedded Hebbian learning capability in spiking neuron analog circuits. The use of these elements allows for the design and fabrication of high-density 3-dimensional circuits that can achieve the interconnect density of biological neural systems.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang, C., Kwack, Y., Kim, S.H., An, T.K., Hong, K., Nama, S., Park, M., Choi, W.S., Park, C.E.: Ambipolar thin-film transistors and an inverter based on pentacene/self-assembled monolayer modified ZnO hybrid structures for balanced hole and electron mobilities. Organic Electronics 12, 411–418 (2011)
Kitamura, M., Imada, T., Arakawa, Y.: Organic Transistor Circuits for Application to Organic Light-Emitting-Diode Displays Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 42, 2483–2487 (2003); Part 1, No. 4B. The Japan Society of Applied Physics (April 2003)
Sakanoue, T., Yahiro, M., Adachi, C., Takimiya, K., Toshimitsu, A.: Electrical characteristics of single-component ambipolar Organic field-effect transistors and effects of air exposure on them. J. Appl. Phys. 103, 094509 (2008)
van Schaijk, R., van Duuren, M., Mei, W.Y., van der Jeugd, K., Rothschild, A., Demand, M.: Oxide-Nitride-Oxide Layer Optimization for Reliable Embedded SONOS Memories. Microelectronic Engineering 72, 395–398 (2004)
Libsch, F.R., White, M.H.: Charge Transport and Storage of Low Programming Voltage SONOS/MONOS memory devices. Solid State Electronics 33(1), 105–126 (1990)
White, M.H., Yang, Y., Purwar, A., French, M.L.: A low voltage SONOS nonvolatile semiconductor memory technology. IEEE Trans. Comp., Packag., Manufact. Technol. A 20, 190–195 (1997)
Shlimak, I., Friedland, K.-J., Kravchenko, S.V., Ginodman, V., Butenko, A., Klapwijk, T.M.: Longitudinal resistivity in the quantum Hall effect regime in a split-gate Si MOSFET with variable electron density. Phys. Stat. Sol. 5(3), 839–841 (2008)
Akiya, M., Nakashima, S.: Novel Split-Gate MOSFET. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices ED-32(3) (1985)
van Schaik, A.: Building blocks for electronic spiking neural networks. Neural Networks 14, 617–628 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wood, R., Bruce, I., Mascher, P. (2012). Modeling of Spiking Analog Neural Circuits with Hebbian Learning, Using Amorphous Semiconductor Thin Film Transistors with Silicon Oxide Nitride Semiconductor Split Gates. In: Villa, A.E.P., Duch, W., Érdi, P., Masulli, F., Palm, G. (eds) Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning – ICANN 2012. ICANN 2012. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 7552. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33269-2_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33269-2_12
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-33268-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-33269-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)