Abstract
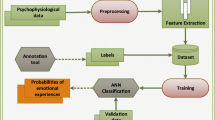
This paper examines the generality of features extracted from heart rate (HR) and skin conductance (SC) signals as predictors of self-reported player affect expressed as pairwise preferences. Artificial neural networks are trained to accurately map physiological features to expressed affect in two dissimilar and independent game surveys. The performance of the obtained affective models which are trained on one game is tested on the unseen physiological and self-reported data of the other game. Results in this early study suggest that there exist features of HR and SC such as average HR and one and two-step SC variation that are able to predict affective states across games of different genre and dissimilar game mechanics.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Picard, R.: Affective computing. The MIT press, Cambridge (2000)
Cacioppo, J., Tassinary, L., Berntson, G.: Psychophysiological science. In: Handbook of Psychophysiology, vol. 2, pp. 3–23 (2000)
Yannakakis, G., Martínez, H., Jhala, A.: Towards affective camera control in games. User Modeling and User-Adapted Interaction 20, 313–340 (2010), doi:10.1007/s11257-010-9078-0
Andreassi, J.: Psychophysiology: Human Behavior and Physiological Response (2000)
Cacioppo, J., Berntson, G., Larsen, J., Poehlmann, K., Ito, T., et al.: The psychophysiology of emotion. In: Handbook of Emotions, pp. 119–142 (1993)
Calvo, R., D’Mello, S.: Affect detection: An interdisciplinary review of models, methods, and their applications. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 18–37 (2010)
Rani, P., Liu, C., Sarkar, N., Vanman, E.: An empirical study of machine learning techniques for affect recognition in human–robot interaction. Pattern Analysis & Applications 9(1), 58–69 (2006)
Fernandez, R., Picard, R.: Signal processing for recognition of human frustration. In: Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 1998, vol. 6, pp. 3773–3776. IEEE, Los Alamitos (1998)
Gilleade, K., Dix, A., Allanson, J.: Affective videogames and modes of affective gaming: assist me, challenge me, emote me. In: Proc. DIGRA 2005 (2005)
Hudlicka, E.: Affective game engines: motivation and requirements. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Foundations of Digital Games, pp. 299–306. ACM, New York (2009)
Kivikangas, J., Ekman, I., Chanel, G., Jarvela, S., Salminen, M., Cowley, B., Henttonen, P., Ravaja, N.: Review on psychophysiological methods in game research. In: Proc. of 1st Nordic DiGRA
Fairclough, S.: Psychophysiological inference and physiological computer games. In: ACE Workshop-Brainplay, vol. 7 (2007)
Mandryk, R., Atkins, M.: A fuzzy physiological approach for continuously modeling emotion during interaction with play technologies. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies 65(4), 329–347 (2007)
Ravaja, N., Saari, T., Laarni, J., Kallinen, K., Salminen, M., Holopainen, J., Järvinen, A.: The psychophysiology of video gaming: Phasic emotional responses to game events. In: Proceedings of the DiGRA Conference Changing Views: Worlds in play
Rani, P., Sarkar, N., Liu, C.: Maintaining optimal challenge in computer games through real-time physiological feedback. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Human Computer Interaction, pp. 184–192 (2005)
Nacke, L., Lindley, C.: Flow and immersion in first-person shooters: measuring the player’s gameplay experience. In: Proceedings of the 2008 Conference on Future Play: Research, Play, Share, pp. 81–88. ACM, New York (2008)
Picard, R., Vyzas, E., Healey, J.: Toward machine emotional intelligence: Analysis of affective physiological state. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1175–1191 (2001)
Nasoz, F., Alvarez, K., Lisetti, C., Finkelstein, N.: Emotion recognition from physiological signals using wireless sensors for presence technologies. Cognition, Technology & Work 6(1), 4–14 (2004)
McQuiggan, S., Lee, S., Lester, J.: Early prediction of student frustration. In: Paiva, A.C.R., Prada, R., Picard, R.W. (eds.) ACII 2007. LNCS, vol. 4738, pp. 698–709. Springer, Heidelberg (2007)
Yannakakis, G.N., Hallam, J., Lund, H.H.: Entertainment capture through heart rate activity in physical interactive playgrounds. User Modeling and User-Adapted Interaction 18(1), 207–243 (2008)
Yannakakis, G.N., Hallam, J.: Entertainment Modeling through Physiology in Physical Play. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies 66, 741–755 (2008)
Tognetti, S., Garbarino, M., Bonanno, A., Matteucci, M., Bonarini, A.: Enjoyment recognition from physiological data in a car racing game. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Affective Interaction in Natural Environments, pp. 3–8. ACM, New York (2010)
Tognetti, S., Garbarino, M., Bonarini, A., Matteucci, M.: Modeling enjoyment preference from physiological responses in a car racing game. In: 2010 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Games (CIG), pp. 321–328. IEEE, Los Alamitos (2010)
Martínez, H.P., Yannakakis, G.N.: Genetic search feature selection for affective modeling: a case study on reported preferences. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Affective Interaction in Natural Environments, pp. 15–20. ACM, New York (2010)
Fürnkranz, J., Hüllermeier, E.: Preference learning. Künstliche Intelligenz 19(1), 60–61 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Perez Martínez, H., Garbarino, M., Yannakakis, G.N. (2011). Generic Physiological Features as Predictors of Player Experience. In: D’Mello, S., Graesser, A., Schuller, B., Martin, JC. (eds) Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction. ACII 2011. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 6974. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-24600-5_30
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-24600-5_30
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-24599-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-24600-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)