Abstract
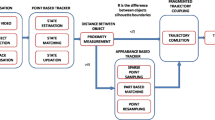
In multiple-object tracking, the lack in prior information limits the association performance. Furthermore, to improve tracking, dynamic models are needed in order to determine the settings of the estimation algorithm. In case of complex motions, the dynamic cannot be learned and the task of tracking becomes difficult. That is why online spatio-temporal motion estimation is of crucial importance. In this paper, we propose a new model for multiple target online tracking: the Energetic Normalized Mutual Information Model (ENMIM). ENMIM combines two algorithms: (i) Quadtree Normalized Mutual Information, QNMI, a recursive partitioning methodology involving a region motion extraction; (ii) an energy minimization approach for data association adapted to the constraint of lack in prior information about motion and based on geometric properties. ENMIM is able to handle typical problems such as large inter-frame displacements, unlearned motions and noisy images with low contrast. The main advantage of ENMIM is its parameterless and its capacity to handle noisy multi-modal images without exploiting any pre-processing step.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doucet, A., Godsill, S., Andrieu, C.: On sequential monte carlo sampling methods for bayesian filtering. Statistics and computing, 197–208 (2000)
Doucet, A., Gordon, N., de Freitas, J.: An introduction to sequential monte carlo methods. In: Sequential Monte Carlo Methods in Practice, Springer, New York (2001)
Kitagawa, G.: Monte carlo filter and smoother for non-gaussian nonlinear state space models. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 1–25 (1996)
Blake, A., Isard, M.: Active contours. Springer, Heidelberg (1998)
Isard, M., Blake, A.: Condensation - conditional density propagation for visual tracking. Int. J. Computer Vision (1998)
Rong, L., Bar-Shalom, Y.: Tracking in clutter with nearest neighbor filter: analysis and performance. IEEE transactions on aerospace and electronic systems (1996)
Vermaak, J., Godsill, S., Pérez, P.: Monte carlo filtering for multi-target tracking and data association. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems (2005)
Fortmann, T., Bar-Shalom, Y., Scheffe, M.: Sonar tracking of multiple targets using joint probabilistic data association. IEEE Journ. Oceanic Engineering (1983)
Viola, P.: Alignment by maximization of mutual information. Ph.D. thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Boston, MA, USA (1995)
Collignon, A.: Multi-modality medical image registration by maximization of mutual information. Ph.D. thesis, Catholic University of Leuven, Leuven Belgium (1998)
Knops, Z.F., Maintz, J., Viergever, M., Pluim, J.: Registration using segment intensity remapping and mutual information. In: Barillot, C., Haynor, D.R., Hellier, P. (eds.) MICCAI 2004. LNCS, vol. 3216, pp. 805–812. Springer, Heidelberg (2004)
North, B., Blake, A., Isard, M., Rittscher, J.: Learning and classification of complex dynamics. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (2000)
Abed, A.E., Dubuisson, S., Béréziat, D.: Comparison of statistical and shape-based approaches for non-rigid motion tracking with missing data using a particle filter. In: Blanc-Talon, J., Philips, W., Popescu, D., Scheunders, P. (eds.) ACIVS 2006. LNCS, vol. 4179, pp. 185–196. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
El Abed, A., Dubuisson, S., Béréziat, D. (2007). ENMIM: Energetic Normalized Mutual Information Model for Online Multiple Object Tracking with Unlearned Motions. In: Blanc-Talon, J., Philips, W., Popescu, D., Scheunders, P. (eds) Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems. ACIVS 2007. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4678. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74607-2_87
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74607-2_87
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-74606-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-74607-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)