Abstract
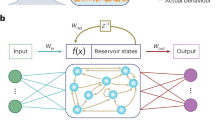
As we approach the physical limits of CMOS technology, advances in materials science and nanotechnology are making available a variety of unconventional computing substrates that can potentially replace top-down-designed silicon-based computing devices. Inherent stochasticity in the fabrication process and nanometer scale of these substrates inevitably lead to design variations, defects, faults, and noise in the resulting devices. A key challenge is how to harness such devices to perform robust computation. We propose reservoir computing as a solution. In reservoir computing, computation takes place by translating the dynamics of an excited medium, called a reservoir, into a desired output. This approach eliminates the need for external control and redundancy, and the programming is done using a closed-form regression problem on the output, which also allows concurrent programming using a single device. Using a theoretical model, we show that both regular and irregular reservoirs are intrinsically robust to structural noise as they perform computation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haselman, M., Hauck, S.: The future of integrated circuits: A survey of nanoelectronics. Proceedings of the IEEE 98(1), 11–38 (2010)
Chen, Y., Jung, G.Y., Ohlberg, D.A.A., Li, X., Stewart, D.R., Jeppesen, J.O., Nielsen, K.A., Stoddart, J.F., Williams, R.S.: Nanoscale molecular-switch crossbar circuits. Nanotechnology 14(4), 462 (2003)
Snider, G.: Computing with hysteretic resistor crossbars. Appl. Phys. A 80, 1165–1172 (2005)
Xu, P., Jeon, S.H., Chen, H.T., Luo, H., Zou, G., Jia, Q., Marian, T.C., Williams, D.J., Zhang, B., Han, X., Wang, H.L.: Facile synthesis and electrical properties of silver wires through chemical reduction by polyaniline. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 114(50), 22147–22154 (2010)
Stieg, A.Z., Avizienis, A.V., Sillin, H.O., Martin-Olmos, C., Aono, M., Gimzewski, J.K.: Emergent criticality in complex Turing B-type atomic switch networks. Advanced Materials 24(2), 286–293 (2012)
Semiconductor Industry Association: International technology roadmap for semiconductors, ITRS (2011), http://www.itrs.net/Links/2011ITRS/
Schmid, A., Leblebici, Y.: A modular approach for reliable nanoelectronic and very-deep submicron circuit design based on analog neural network principles. In: Proc. IEEE-NANO, pp. 647–650 (2003)
Žaloudek, L., Sekanina, L.: Cellular automata-based systems with fault-tolerance. Natural Computing 11(4), 673–685 (2012)
Tran, A.H., Yanushkevich, S., Lyshevski, S., Shmerko, V.: Design of neuromorphic logic networks and fault-tolerant computing. In: Proc. IEEE-NANO, pp. 457–462 (2011)
Zhang, W., Wu, N.J.: CMOL-based cellular neural networks and parallel processor for future image processing. In: Proc. IEEE-NANO, pp. 737–740 (2008)
Lawson, J.W., Wolpert, D.H.: Adaptive programming of unconventional nano-architectures. Journal of Computational and Theoretical Nanoscience 3(2), 272–279 (2006)
Anghel, M., Teuscher, C., Wang, H.L.: Adaptive learning in random linear nanoscale networks. In: Proc. IEEE-NANO, pp. 445–450 (2011)
Lukoševičius, M., Jaeger, H., Schrauwen, B.: Reservoir computing trends. KI - Künstliche Intelligenz 26(4), 365–371 (2012)
Hermans, M., Schrauwen, B.: Recurrent kernel machines: Computing with infinite echo state networks. Neural Computation 24(1), 104–133 (2011)
Lukoševičius, M., Jaeger, H.: Reservoir computing approaches to recurrent neural network training. Computer Science Review 3(3), 127–149 (2009)
Verstraeten, D., Schrauwen, B., D’Haene, M., Stroobandt, D.: An experimental unification of reservoir computing methods. Neural Networks 20(3), 391–403 (2007)
Maass, W., Natschläger, T., Markram, H.: Real-time computing without stable states: a new framework for neural computation based on perturbations. Neural computation 14(11), 2531–2560 (2002)
Jaeger, H.: The “echo state” approach to analysing and training recurrent neural networks. Technical Report GMD Rep. 148, St. Augustin. German National Research Center for Information Technology (2001)
Wyffels, F., Schrauwen, B.: A comparative study of reservoir computing strategies for ly time series prediction. Neurocomputing 73(10-12), 1958–1964 (2010)
Jaeger, H., Haas, H.: Harnessing nonlinearity: Predicting chaotic systems and saving energy in wireless communication. Science 304(5667), 78–80 (2004)
Paquot, Y., Duport, F., Smerieri, A., Dambre, J., Schrauwen, B., Haelterman, M., Massar, S.: Optoelectronic reservoir computing. Scientific Reports 2 (2012)
Jaeger, H.: Adaptive nonlinear system identification with echo state networks. In: NIPS, pp. 593–600 (2002)
Dasgupta, S., Wörgötter, F., Manoonpong, P.: Information theoretic self-organised adaptation in reservoirs for temporal memory tasks. In: Jayne, C., Yue, S., Iliadis, L. (eds.) EANN 2012. CCIS, vol. 311, pp. 31–40. Springer, Heidelberg (2012)
Jaeger, H.: Short term memory in echo state networks. Technical Report GMD Report 152. GMD-Forschungszentrum Informationstechnik (2002)
Jaeger, H.: Tutorial on training recurrent neural networks, covering BPPT, RTRL, EKF and the “echo state network” approach. Technical Report GMD Report 159. German National Research Center for Information Technology, St. Augustin-Germany (2002)
Penrose, R.: A generalized inverse for matrices. Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society 51, 406–413 (1955)
Rodan, A., Tiňo, P.: Minimum complexity echo state network. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 22, 131–144 (2011)
Atiya, A., Parlos, A.: New results on recurrent network training: Unifying the algorithms and accelerating convergence. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 11, 697–709 (2000)
Erdös, P., Rényi, A.: On random graphs. Publ. Math. Debrecen 6, 290–297 (1959)
Sarangi, S., Greskamp, B., Teodorescu, R., Nakano, J., Tiwari, A., Torrellas, J.: VARIUS: A model of process variation and resulting timing errors for microarchitects. IEEE Transactions on Semiconductor Manufacturing 21(1), 3–13 (2008)
Terabe, K., Hasegawa, T., Nakayama, T., Aono, M.: Quantized conductance atomic switch. Nature 433(7021), 47–50 (2005)
Sillin, H.O., Aguilera, R., Shieh, H.H., Avizienis, A.V., Aono, M., Stieg, A.Z., Gimzewski, J.K.: A theoretical and experimental study of neuromorphic atomic switch networks for reservoir computing. Nanotechnology 24(38), 384004 (2013)
Ozturk, M.C., Xu, D., Príncipe, J.C.: Analysis and design of echo state networks. Neural Computation 19(1), 111–138 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Goudarzi, A., Lakin, M.R., Stefanovic, D. (2014). Reservoir Computing Approach to Robust Computation Using Unreliable Nanoscale Networks. In: Ibarra, O., Kari, L., Kopecki, S. (eds) Unconventional Computation and Natural Computation. UCNC 2014. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 8553. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-08123-6_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-08123-6_14
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-08122-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-08123-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)