Abstract
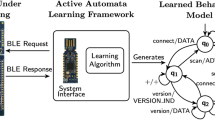
Near-Field Communication (NFC) is a widely adopted standard for embedded low-power devices in very close proximity. In order to ensure a correct system, it has to comply to the ISO/IEC 14443 standard. This paper concentrates on the low-level part of the protocol (ISO/IEC 14443-3) and presents a method and a practical implementation that complements traditional conformance testing. We infer a Mealy state machine of the system-under-test using active automata learning. This automaton is checked for bisimulation with a specification automaton modelled after the standard, which provides a strong verdict of conformance or non-conformance. As a by-product, we share some observations of the performance of different learning algorithms and calibrations in the specific setting of ISO/IEC 14443-3, which is the difficulty to learn models of system that a) consist of two very similar structures and b) very frequently give no answer (i.e. a timeout as an output).
This research received funding within the ECSEL Joint Undertaking (JU) under grant agreement No. 876038 (project InSecTT) and from the program “ICT of the Future” of the Austrian Research Promotion Agency (FFG) and the Austrian Ministry for Transport, Innovation and Technology under grant agreement No. 880852 (project LEARNTWINS). The JU receives support from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme and Austria, Sweden, Spain, Italy, France, Portugal, Ireland, Finland, Slovenia, Poland, Netherlands, Turkey. The document reflects only the author’s view and the Commission is not responsible for any use that may be made of the information it contains.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarts, F., De Ruiter, J., Poll, E.: Formal models of bank cards for free. In: 2013 IEEE Sixth International Conference on Software Testing, Verification and Validation Workshops, pp. 461–468 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSTW.2013.60
Aceto, L., Ingolfsdottir, A., Srba, J.: The algorithmics of bisimilarity. In: Advanced Topics in Bisimulation and Coinduction, pp. 100–172. Cambridge University Press (2011)
Angluin, D.: Learning regular sets from queries and counterexamples. Inf. Comput. 75(2), 87–106 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1016/0890-5401(87)90052-6
Baier, C., Katoen, J.P.: Principles of Model Checking. MIT Press, Cambridge (2008)
Bunte, O., et al.: The mCRL2 toolset for analysing concurrent systems. In: Vojnar, T., Zhang, L. (eds.) TACAS 2019. LNCS, vol. 11428, pp. 21–39. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-17465-1_2
Chen, Y.F., Hong, C.D., Lin, A.W., Rümmer, P.: Learning to prove safety over parameterised concurrent systems. In: 2017 Formal Methods in Computer Aided Design (FMCAD), pp. 76–83 (2017). https://doi.org/10.23919/FMCAD.2017.8102244
Garcia, F.D., de Koning Gans, G., Verdult, R.: Tutorial: proxmark, the swiss army knife for RFID security research: tutorial at 8th workshop on RFID security and privacy (RFIDSEC 2012). Technical report, Radboud University Nijmegen, ICIS, Nijmegen (2012)
Hancke, G.: Practical attacks on proximity identification systems. In: 2006 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (S &P 2006), pp. 6 pp.-333 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/SP.2006.30
Hong, C.-D., Lin, A.W., Majumdar, R., Rümmer, P.: Probabilistic bisimulation for parameterized systems. In: Dillig, I., Tasiran, S. (eds.) CAV 2019. LNCS, vol. 11561, pp. 455–474. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-25540-4_27
International Organization for Standardization: Cards and security devices for personal identification - Contactless proximity objects - Part 3: Initialization and anticollision. ISO/IEC Standard “14443-3”. International Organization for Standardization (2018)
International Organization for Standardization: Cards and security devices for personal identification - Contactless proximity objects - Part 4: Transmission protocol. ISO/IEC Standard “14443-4”. International Organization for Standardization (2018)
Isberner, M., Howar, F., Steffen, B.: The TTT algorithm: a redundancy-free approach to active automata learning. In: Bonakdarpour, B., Smolka, S.A. (eds.) RV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8734, pp. 307–322. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-11164-3_26
Isberner, M., Howar, F., Steffen, B.: The open-source LearnLib. In: Kroening, D., Păsăreanu, C.S. (eds.) CAV 2015. LNCS, vol. 9206, pp. 487–495. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-21690-4_32
Issovits, W., Hutter, M.: Weaknesses of the ISO/IEC 14443 protocol regarding relay attacks. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on RFID-Technologies and Applications, pp. 335–342 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/RFID-TA.2011.6068658
Jacobs, B., Silva, A.: Automata learning: a categorical perspective. In: van Breugel, F., Kashefi, E., Palamidessi, C., Rutten, J. (eds.) Horizons of the Mind. A Tribute to Prakash Panangaden. LNCS, vol. 8464, pp. 384–406. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-06880-0_20
Jansen, D.N., Groote, J.F., Keiren, J.J.A., Wijs, A.: An O(m log n) algorithm for branching bisimilarity on labelled transition systems. In: TACAS 2020. LNCS, vol. 12079, pp. 3–20. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-45237-7_1
Kearns, M.J., Vazirani, U.: An Introduction to Computational Learning Theory. MIT Press, Cambridge (1994)
Maass, M., Müller, U., Schons, T., Wegemer, D., Schulz, M.: NFCGate: an NFC relay application for Android. In: Proceedings of the 8th ACM Conference on Security & Privacy in Wireless and Mobile Networks, WiSec 2015, pp. 1–2. Association for Computing Machinery, New York (2015). https://doi.org/10.1145/2766498.2774984
McCulloch, W.S., Pitts, W.: A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull. Math. Biophys. 5(4), 115–133 (1943). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02478259
Mealy, G.H.: A method for synthesizing sequential circuits. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 34(5), 1045–1079 (1955). https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1538-7305.1955.tb03788.x
Merten, M., Howar, F., Steffen, B., Margaria, T.: Automata learning with on-the-fly direct hypothesis construction. In: Hähnle, R., Knoop, J., Margaria, T., Schreiner, D., Steffen, B. (eds.) ISoLA 2011. CCIS, pp. 248–260. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-34781-8_19
Moore, E.F.: Gedanken-experiments on sequential machines. In: Automata Studies, AM-34, vol. 34, pp. 129–154. Princeton University Press (1956). https://doi.org/10.1515/9781400882618-006
Neider, D., Smetsers, R., Vaandrager, F., Kuppens, H.: Benchmarks for automata learning and conformance testing. In: Margaria, T., Graf, S., Larsen, K.G. (eds.) Models, Mindsets, Meta: The What, the How, and the Why Not? LNCS, vol. 11200, pp. 390–416. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-22348-9_23
Peled, D., Vardi, M.Y., Yannakakis, M.: Black box checking. In: Wu, J., Chanson, S.T., Gao, Q. (eds.) Formal Methods for Protocol Engineering and Distributed Systems. IAICT, vol. 28, pp. 225–240. Springer, Boston, MA (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-35578-8_13
Rivest, R.L., Schapire, R.E.: Inference of finite automata using homing sequences. Inf. Comput. 103(2), 299–347 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1006/inco.1993.1021
Shahbaz, M., Groz, R.: Inferring mealy machines. In: Cavalcanti, A., Dams, D.R. (eds.) FM 2009. LNCS, vol. 5850, pp. 207–222. Springer, Heidelberg (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-05089-3_14
Smeenk, W., Moerman, J., Vaandrager, F., Jansen, D.N.: Applying automata learning to embedded control software. In: Butler, M., Conchon, S., Zaïdi, F. (eds.) ICFEM 2015. LNCS, vol. 9407, pp. 67–83. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-25423-4_5
Tappler, M., Aichernig, B.K., Bloem, R.: Model-based testing IoT communication via active automata learning. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Software Testing, Verification and Validation (ICST), pp. 276–287 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICST.2017.32
Vaandrager, F.: Model learning. Commun. ACM 60(2), 86–95 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1145/2967606
Vila, J., Rodríguez, R.J.: Practical experiences on NFC relay attacks with android. In: Mangard, S., Schaumont, P. (eds.) RFIDSec 2015. LNCS, vol. 9440, pp. 87–103. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24837-0_6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Marksteiner, S., Sirjani, M., Sjödin, M. (2024). Using Automata Learning for Compliance Evaluation of Communication Protocols on an NFC Handshake Example. In: Kofroň, J., Margaria, T., Seceleanu, C. (eds) Engineering of Computer-Based Systems. ECBS 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14390. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-49252-5_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-49252-5_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-49251-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-49252-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)