Abstract
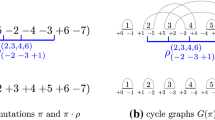
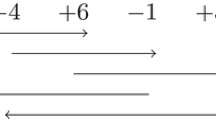
Sorting by Genome Rearrangements is a classic problem in Computational Biology. Several models have been considered so far, each of them defines how a genome is modeled (for example, permutations when assuming no duplicated genes, strings if duplicated genes are allowed, and/or use of signs on each element when gene orientation is known), and which rearrangements are allowed. Recently, a new problem, called Sorting by Multi-Cut Rearrangements, was proposed. It uses the k-Cut rearrangement which cuts a permutation (or a string) at \(k \ge 2\) places and rearranges the generated blocks to obtain a new permutation (or string) of same size. This new rearrangement may model chromoanagenesis, a phenomenon consisting of massive simultaneous rearrangements. Similarly as the Double-Cut-and-Join, this new rearrangement also generalizes several genome rearrangements such as reversals, transpositions, revrevs, transreversals, and block-interchanges. In this paper, we extend a previous work based on unsigned permutations and strings to signed permutations. We show the complexity of this problem for different values of k, that the approximation algorithm proposed for unsigned permutations with any value of k can be adapted to signed permutations, and a 1.5-approximation algorithm for the specific case \(k=4\).
This work was supported by the National Council of Technological and Scientific Development, CNPq (grants 425340/2016-3 and 202292/2020-7), the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior - Brasil (CAPES) - Finance Code 001, and the São Paulo Research Foundation, FAPESP (grants 2013/08293-7, 2015/11937-9, and 2019/27331-3).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alekseyev, M.A.: Multi-break rearrangements and breakpoint re-uses: from circular to linear genomes. J. Comput. Biol. 15(8), 1117–1131 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1089/cmb.2008.0080
Alekseyev, M.A., Pevzner, P.A.: Multi-break rearrangements and chromosomal evolution. Theor. Compu. Sci. 395(2–3), 193–202 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcs.2008.01.013
Alexandrino, A.O., Oliveira, A.R., Dias, U., Dias, Z.: On the complexity of some variations of sorting by transpositions. J. Univ. Comput. Sci. 26(9), 1076–1094 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3897/jucs.2020.057
Bafna, V., Pevzner, P.A.: Sorting by transpositions. SIAM J. Discrete Math. 11(2), 224–240 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1137/S089548019528280X
Bergeron, A.: A very elementary presentation of the Hannenhalli-Pevzner theory. Discrete Appl. Math. 146(2), 134–145 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dam.2004.04.010
Bulteau, L., Fertin, G., Jean, G., Komusiewicz, C.: Sorting by multi-cut rearrangements. Algorithms 14(6), 169 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/a14060169
Bulteau, L., Fertin, G., Rusu, I.: Sorting by transpositions is difficult. SIAM J. Discrete Math. 26(3), 1148–1180 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1137/110851390
Christie, D.A.: Sorting permutations by block-interchanges. Inf. Process. Lett. 60(4), 165–169 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-0190(96)00155-X
Elias, I., Hartman, T.: A 1.375-Approximation algorithm for sorting by transpositions. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 3(4), 369–379 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCBB.2006.44
Fertin, G., Labarre, A., Rusu, I., Tannier, É., Vialette, S.: Combinatorics Of Genome Rearrangements. Computational Molecular Biology, The MIT Press, London (2009). https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/9780262062824.001.0001
Hannenhalli, S., Pevzner, P.A.: Transforming cabbage into turnip: polynomial algorithm for sorting signed permutations by reversals. J. ACM 46(1), 1–27 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1145/300515.300516
Holland, A.J., Cleveland, D.W.: Chromoanagenesis and cancer: mechanisms and consequences of localized, complex chromosomal rearrangements. Nat. Med. 18(11), 1630–1638 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2988
Lin, G.H., Xue, G.: Signed genome rearrangement by reversals and transpositions: models and approximations. Theor. Comput. Sci. 259(1–2), 513–531 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3975(00)00038-4
Pellestor, F., Gatinois, V.: Chromoanagenesis: a piece of the macroevolution scenario. Mol. Cytogenet. 13(1), 1–9 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13039-020-0470-0
Yancopoulos, S., Attie, O., Friedberg, R.: Efficient sorting of genomic permutations by translocation. Inversion and block interchange. Bioinformatics 21(16), 3340–3346 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bti535
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Rodrigues Oliveira, A., Oliveira Alexandrino, A., Jean, G., Fertin, G., Dias, U., Dias, Z. (2022). Sorting by k-Cuts on Signed Permutations. In: Jin, L., Durand, D. (eds) Comparative Genomics. RECOMB-CG 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13234. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-06220-9_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-06220-9_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-06219-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-06220-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)