Abstract
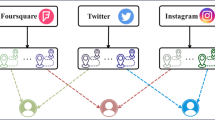
Identifying the geographic location of online social media users, also known as User Geolocation (UG), plays an essential part in many Internet application services. One main challenge is the scarcity of users’ public geographic information. To overcome it, most works focus on user geolocation prediction with posts and interactions on social media. However, they do not consider the distinction of variant social connections, which may impair the performance of the UG models. To address this issue, we propose a multi-view model, Heterogeneous graph Attention networks for user Geolocation (HAG), which introduces the attention mechanism to mine valuable cues in social networks and text contexts jointly. In the network module, we creatively apply a heterogeneous graph to model various social interactions and introduce a heterogeneous graph attention network to learn network structure information. In the text module, we propose a context attention network to extract geo-related text information. Extensive experiments conducted on three Twitter datasets show that HAG achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to strong baselines.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Backstrom, L., Sun, E., Marlow, C.A.: Find me if you can: improving geographical prediction with social and spatial proximity. In: WWW 2010 (2010)
Bahdanau, D., Cho, K., Bengio, Y.: Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. CoRR arXiv:1409.0473 (2015)
Bao, J., Zheng, Y., Wilkie, D., Mokbel, M.: Recommendations in location-based social networks: a survey. GeoInformatica 19, 525–565 (2015)
Blei, D.M., Ng, A., Jordan, M.I.: Latent Dirichlet allocation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 3, 993–1022 (2003)
Cheng, Z., Caverlee, J., Lee, K.: You are where you tweet: a content-based approach to geo-locating twitter users. In: Proceedings of the 19th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (2010)
Cheng, Z., Caverlee, J., Lee, K.: A content-driven framework for geolocating microblog users. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 4, 2:1–2:27 (2013)
Clevert, D.A., Unterthiner, T., Hochreiter, S.: Fast and accurate deep network learning by exponential linear units (ELUs). arXiv: Learning (2016)
Davis, C., Pappa, G., de Oliveira, D.R.R., de Lima Arcanjo, F.: Inferring the location of twitter messages based on user relationships. Trans. GIS 15, 735–751 (2011)
Ding, J., Gravano, L., Shivakumar, N.: Computing geographical scopes of web resources. In: VLDB (2000)
Do, T., Nguyen, D.M., Tsiligianni, E., Cornelis, B., Deligiannis, N.: Multiview deep learning for predicting twitter users’ location. arXiv:1712.08091 (2017)
Dong, Y., Hu, Z., Wang, K., Sun, Y., Tang, J.: Heterogeneous network representation learning. In: IJCAI (2020)
Eisenstein, J., O’Connor, B.T., Smith, N.A., Xing, E.: A latent variable model for geographic lexical variation. In: EMNLP (2010)
Han, B., Cook, P., Baldwin, T.: Geolocation prediction in social media data by finding location indicative words. In: COLING (2012)
Huang, B., Carley, K.M.: A hierarchical location prediction neural network for twitter user geolocation. arXiv:1910.12941 (2019)
Jones, K.: A statistical interpretation of term specificity and its application in retrieval. J. Doc. 60, 493–502 (2004)
McGee, J., Caverlee, J., Cheng, Z.: Location prediction in social media based on tie strength. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (2013)
Pedregosa, F., et al.: Scikit-learn: machine learning in python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 12, 2825–2830 (2011)
Pennington, J., Socher, R., Manning, C.D.: GloVe: global vectors for word representation. In: EMNLP (2014)
Rahimi, A., Cohn, T., Baldwin, T.: Twitter user geolocation using a unified text and network prediction model. arXiv:1506.08259 (2015)
Rahimi, A., Cohn, T., Baldwin, T.: A neural model for user geolocation and lexical dialectology. arXiv:1704.04008 (2017)
Rahimi, A., Cohn, T., Baldwin, T.: Semi-supervised user geolocation via graph convolutional networks. In: ACL (2018)
Roller, S., Speriosu, M., Rallapalli, S., Wing, B., Baldridge, J.: Supervised text-based geolocation using language models on an adaptive grid. In: EMNLP-CoNLL (2012)
Sakaki, T., Okazaki, M., Matsuo, Y.: Tweet analysis for real-time event detection and earthquake reporting system development. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 25, 919–931 (2013)
Schlichtkrull, M., Kipf, T.N., Bloem, P., van den Berg, R., Titov, I., Welling, M.: Modeling relational data with graph convolutional networks. In: Gangemi, A., et al. (eds.) ESWC 2018. LNCS, vol. 10843, pp. 593–607. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-93417-4_38
Sinnott, R.W.: Virtues of the haversine. Sky Telescope 68(2), 158–159 (1984)
Sun, Y., Han, J.: Mining heterogeneous information networks: a structural analysis approach. SIGKDD Explor. 14, 20–28 (2013)
Sun, Y., Han, J., Yan, X., Yu, P.S., Wu, T.: PathSim: meta path-based top-k similarity search in heterogeneous information networks. Proc. VLDB Endow. 4, 992–1003 (2011)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. arXiv:1706.03762 (2017)
Velickovic, P., Cucurull, G., Casanova, A., Romero, A., Lio’, P., Bengio, Y.: Graph attention networks. arXiv:1710.10903 (2018)
Wang, F., Lu, C.-T., Qu, Y., Yu, P.S.: Collective geographical embedding for geolocating social network users. In: Kim, J., Shim, K., Cao, L., Lee, J.-G., Lin, X., Moon, Y.-S. (eds.) PAKDD 2017. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 10234, pp. 599–611. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-57454-7_47
Wang, M., et al.: Deep graph library: a graph-centric, highly-performant package for graph neural networks. arXiv: Learning (2019)
Wang, X., et al.: Heterogeneous graph attention network. In: The World Wide Web Conference (2019)
Wing, B., Baldridge, J.: Simple supervised document geolocation with geodesic grids. In: ACL (2011)
Wing, B., Baldridge, J.: Hierarchical discriminative classification for text-based geolocation. In: EMNLP (2014)
Zhang, C., Song, D., Huang, C., Swami, A., Chawla, N.: Heterogeneous graph neural network. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (2019)
Zheng, C., Jiang, J.Y., Zhou, Y., Young, S., Wang, W.: Social media user geolocation via hybrid attention. In: Proceedings of the 43rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, X., Lin, F., Dong, D., Chen, W., Liu, B. (2021). Heterogeneous Graph Attention Network for User Geolocation. In: Pham, D.N., Theeramunkong, T., Governatori, G., Liu, F. (eds) PRICAI 2021: Trends in Artificial Intelligence. PRICAI 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13032. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-89363-7_33
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-89363-7_33
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-89362-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-89363-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)