Abstract
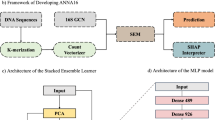
In bioinformatics analysis, the correct identification of an unknown sequence by subsequent matching with a known sequence is a crucial and critical initial step. One of the constantly evolving open and challenging areas of research is understanding the adaptation of microbiome communities derived from different environment as well as human gut. The critical component of such studies is to analyze 16s rRNA gene sequence and classify it to a corresponding taxonomy. Thus far recent literature discusses such sequence classification tasks being solved using many algorithms such as early methods of k-mer frequency matching, and assembly-based clustering or advanced methods of machine learning algorithms– for instance, random forests, naïve Bayesian techniques, and recently deep learning architectures. Our previous work focused on a comprehensive study of 16s rRNA gene classification by implementing simplistic singular neural models of Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). The outcome of this study demonstrated very promising classification results for family, genus and species taxonomic levels, prompting an immediate investigation into deep ensemble models for problem at hand. In this study, we attempt to classify 16s rRNA gene using deep ensemble models along with a hybrid model that emulates an ensemble in its early convolutional layers followed by a recurrent layer.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achtman, M.: A phylogenetic perspective on molecular epidemiology. In: Molecular Medical Microbiology, pp. 485–509. Academic Press (2002)
Ghosh, A., Mehta, A., Khan, A.M.: Metagenomic analysis and its applications. Encycl. Bioinf. Comput. Biol. 3, 184–193 (2019)
Qin, J., et al.: A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nat. 490(7418), 55–60 (2012)
Turnbaugh, P.J., Ley, R.E., Mahowald, M.A., Magrini, V., Mardis, E.R., Gordon, J.I.: An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 444(7122), 1027 (2006)
Turnbaugh, P.J., et al.: A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 457(7228), 480–484 (2009)
Karlsson, F.H., et al.: Symptomatic atherosclerosis is associated with an altered gut metagenome. Nat. Commun. 3(1), 1–8 (2012)
Janda, J.M., Abbott, S.L.: 16S rRNA gene sequencing for bacterial identification in the diagnostic laboratory: pluses, perils, and pitfalls. J. Clin. Microbiol. 45(9), 2761–2764 (2007)
Berg, J.M., Tymoczko, J.L., Stryer, L.: Biochemistry. Freeman, New York (2002)
Chakravorty, S., Helb, D., Burday, M., Connell, N., Alland, D.: A detailed analysis of 16S ribosomal RNA gene segments for the diagnosis of pathogenic bacteria. J. Microbiol. Methods 69(2), 330–339 (2007)
Woo, P.C.Y., Lau, S.K.P., Teng, J.L.L., Tse, H., Yuen, K.Y.: Then and now: use of 16S rDNA gene sequencing for bacterial identification and discovery of novel bacteria in clinical microbiology laboratories. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 14(10), 908–934 (2008)
Woese, C.R.: Bacterial evolution. Microbiol. Rev. 51(2), 221 (1987)
Fiannaca, A., et al.: Deep learning models for bacteria taxonomic classification of metagenomic data. BMC Bioinform. 19(7), 198 (2018)
Schloss, P.D., et al.: Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75(23), 7537–7541 (2009)
Wood, D.E., Salzberg, S.L.: Kraken: ultrafast metagenomic sequence classification using exact alignments. Genome Biol. 15(3), R46 (2014)
Wang, Q., Garrity, G.M., Tiedje, J.M., Cole, J.R.: Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73(16), 5261–5267 (2007)
La Rosa, M., Fiannaca, A., Rizzo, R., Urso, A.: Probabilistic topic modeling for the analysis and classification of genomic sequences. BMC Bioinform. 16(6), S2 (2015)
Zhang, A.B., Sikes, D.S., Muster, C., Li, S.Q.: Inferring species membership using DNA sequences with back-propagation neural networks. Syst. Biol. 57(2), 202–215 (2008)
LeCun, Y.: 1.1 Deep learning hardware: past, present, and future. In: 2019 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), pp. 12–19. IEEE, February 2019
Park, Y., Kellis, M.: Deep learning for regulatory genomics. Nat. Biotech. 33(8), 825 (2015)
Busia, A., et al.: A deep learning approach to pattern recognition for short DNA sequences. bioRxiv, 353474 (2019)
Desai, H.P., Parameshwaran, A.P., Sunderraman, R., Weeks, M.: Comparative study using neural networks for 16S ribosomal gene classification. J. Comput. Biol. 27(2), 248–258 (2020)
Laboratory for integrated bioinformatics, center for integrative medical sciences, RIKEN. GRD - Genomic-based 16S ribosomal RNA Database (2015)
Rokach, L.: Ensemble-based classifiers. Artif. Intell. Rev. 33(1–2), 1–39 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-009-9124-7
Prabhavalkar, R., Rao, K., Sainath, T.N., Li, B., Johnson, L., Jaitly, N.: A comparison of sequence-to-sequence models for speech recognition. In: Interspeech, pp. 939–943, August 2017
Venugopalan, S., Rohrbach, M., Donahue, J., Mooney, R., Darrell, T., Saenko, K.: Sequence to sequence-video to text. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4534–4542 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Desai, H.P., Parameshwaran, A.P., Sunderraman, R., Weeks, M. (2020). Deep Ensemble Models for 16S Ribosomal Gene Classification. In: Cai, Z., Mandoiu, I., Narasimhan, G., Skums, P., Guo, X. (eds) Bioinformatics Research and Applications. ISBRA 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12304. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-57821-3_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-57821-3_25
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-57820-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-57821-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)