Abstract
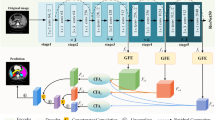
The fully convolutional networks (FCNs) have been widely applied in numerous medical image segmentation tasks. However, tissue regions usually have large variations of shape and scale, so the ability of neural networks to learn multi-scale features is important to the segmentation performance. In this paper, we improve the network for multi-scale feature fusion, in the medical image segmentation by introducing two feature fusion modules: i) global attention multi-scale feature fusion module (GMF); ii) local dense multi-scale feature fusion module (LMF). GMF aims to use global context information to guide the recalibration of low-level features from both spatial and channel aspects, so as to enhance the utilization of effective multi-scale features and suppress the noise of low-level features. LMF adopts bottom-up top-down structure to capture context information, to generate semantic features, and to fuse feature information at different scales. LMF can integrate local dense multi-scale context features layer by layer in the network, thus improving the ability of network to encode interdependent relationships among boundary pixels. Based on the above two modules, we propose a novel medical image segmentation framework (GLF-Net). We evaluated the proposed network and modules on challenging brain tumor segmentation and pancreas segmentation datasets, and very competitive performance has been achieved.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
References
Qin, Y., et al.: Autofocus layer for semantic segmentation. In: Frangi, A.F., Schnabel, J.A., Davatzikos, C., Alberola-López, C., Fichtinger, G. (eds.) MICCAI 2018. LNCS, vol. 11072, pp. 603–611. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00931-1_69
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Wang, H., Gu, R., Li, Z.: Automated segmentation of intervertebral disc using fully dilated separable deep neural networks. In: Zheng, G., Belavy, D., Cai, Y., Li, S. (eds.) CSI 2018. LNCS, vol. 11397, pp. 66–76. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-13736-6_6
Yu, C., Wang, J., Peng, C., Gao, C., Yu, G., Sang, N.: Learning a discriminative feature network for semantic segmentation. In: CVPR, pp. 1857–1866 (2018)
Roy, A.G., Navab, N., Wachinger, C.: Concurrent spatial and channel ‘squeeze & excitation’ in fully convolutional networks. In: Frangi, A.F., Schnabel, J.A., Davatzikos, C., Alberola-López, C., Fichtinger, G. (eds.) MICCAI 2018. LNCS, vol. 11070, pp. 421–429. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00928-1_48
Farabet, C., Couprie, C., Najman, L., LeCun, Y.: Learning hierarchical features for scene labeling. IEEE Trans. PAMI 35(8), 1915–1929 (2013)
Zhao, H., Shi, J., Qi, X., Wang, X., Jia, J.: Pyramid scene parsing network. In: CVPR, pp. 2881–2890 (2017)
Oktay, O., Schlemper, J., Folgoc, L.L., Lee, M., Heinrich, M.: Attention U-Net: learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.03999 (2018)
Wu, Y., He, K.: Group normalization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.08494 (2018)
Menze, B.H., Jakab, A., Bauer, S., et al.: The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (BRATS). IEEE TMI 34(10), 1993–2024 (2015)
Bakas, S., Akbari, H., Sotiras, A., Bilello, M., Rozycki, M., Kirby, J.S., et al.: Advancing The Cancer Genome Atlas glioma MRI collections with expert segmentation labels and radiomic features. Nature Sci. Data 4, 170117 (2017)
Bakas, S., et al.: Identifying the best machine learning algorithms for brain tumor segmentation, progression assessment, and overall survival prediction in the BRATS Challenge. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.02629 (2018)
Bakas, S., et al.: Segmentation labels and radiomic features for the pre-operative scans of the TCGA-GBM collection. The Cancer Imaging Archive (2017)
Bakas, S., et al.: Segmentation labels and radiomic features for the pre-operative scans of the TCGA-LGG collection. The Cancer Imaging Archive (2017)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: CVPR, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, H., Wang, G., Liu, Z., Zhang, S. (2020). Global and Local Multi-scale Feature Fusion Enhancement for Brain Tumor Segmentation and Pancreas Segmentation. In: Crimi, A., Bakas, S. (eds) Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. BrainLes 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11992. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-46640-4_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-46640-4_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-46639-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-46640-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)