Abstract
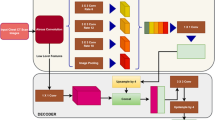
Accurate segmentation of lungs and clavicles on chest radiographs plays a pivotal role in screening, diagnosis, treatment planning, and prognosis of many chest diseases. Although a number of solutions have been proposed, both segmentation tasks remain challenging. In this paper, we propose an ensemble of deep segmentation models (enDeepSeg) that combines the U-Net and DeepLabv3+ to address this challenge. We first extract image patches to train the U-Net and DeepLabv3+ model, respectively, and then use the weighted sum of the segmentation probability maps produced by both models to determine the label of each pixel. The weight of each model is adaptively estimated according to its error rate on the validation set. We evaluated the proposed enDeepSeg model on the Japanese Society of Radiological Technology (JSRT) database and achieved an average Jaccard similarity coefficient (JSC) of 0.961 and 0.883 in the segmentation of lungs and clavicles, respectively, which are higher than those obtained by ten lung segmentation and six clavicle segmentation algorithms. Our results suggest that the enDeepSeg model is able to segment lungs and clavicles on chest radiographs with the state-of-the-art accuracy.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ruuskanen, O., Lahti, E., Jennings, L.C., et al.: Viral pneumonia. Lancet 377, 1264–1275 (2011)
Seghers, D., Loeckx, D., Maes, F., et al.: Minimal shape and intensity cost path segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 26, 1115–1129 (2007)
Shao, Y., Gao, Y., Guo, Y., et al.: Hierarchical lung field segmentation with joint shape and appearance sparse learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 33, 1761–1780 (2014)
Candemir, S., Jaeger, S., Palaniappan, K., et al.: Lung segmentation in chest radiographs using anatomical atlases with nonrigid registration. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 33, 577–590 (2014)
Ibragimov, B., Likar, B., Pernu, F., et al.: Accurate landmark-based segmentation by incorporating landmark misdetections. In: IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2016), pp. 1072–1075 (2016)
Ginneken, B.V., Stegmann, M.B., Loog, M.: Segmentation of anatomical structures in chest radiographs using supervised methods: a comparative study on a public database. Med. Image Anal. 10, 19–40 (2006)
Novikov, A.A., Lenis, D., Major, D., et al.: Fully convolutional architectures for multi-class segmentation in chest radiographs. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 37, 1865–1876 (2018)
Dai, W., Dong, N., Wang, Z., Liang, X., Zhang, H., Xing, E.P.: SCAN: structure correcting adversarial network for organ segmentation in chest X-rays. In: Stoyanov, D., et al. (eds.) DLMIA/ML-CDS -2018. LNCS, vol. 11045, pp. 263–273. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00889-5_30
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, William M., Frangi, Alejandro F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Chen, L.C., Zhu, Y., Papandreou, G., et al.: Encoderdecoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.02611 (2018)
Shiraishi, J., Katsuragawa, S., Ikezoe, J., et al.: Development of a digital image database for chest radiographs with and without a lung nodule: receiver operating characteristic analysis of radiologists’ detection of pulmonary nodules. Am. J. Roentgenol. 174, 71–74 (2000)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556 (2014)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., et al.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 770–778 (2016)
Hastie, T., Rosset, S., Zhu, J., et al.: Multi-class adaboost. Stat. Interface 2(3), 349–360 (2009)
Acknowledgement
This work was supported in part by the Science and Technology Innovation Committee of Shenzhen Municipality, China, under Grants JCYJ20180306171334997, in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 61771397, in part by Synergy Innovation Foundation of the University and Enterprise for Graduate Students in Northwestern Polytechnical University under Grants XQ201911, and in part by the Project for Graduate Innovation team of Northwestern Polytechnical University. We appreciate the efforts devoted to collect and share the JSRT database and SCR database for comparing interactive and (semi)-automatic algorithms for the segmentation of lungs and clavicles on chest radiographs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, J., Xia, Y., Zhang, Y. (2020). An Ensemble of Deep Neural Networks for Segmentation of Lung and Clavicle on Chest Radiographs. In: Zheng, Y., Williams, B., Chen, K. (eds) Medical Image Understanding and Analysis. MIUA 2019. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1065. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-39343-4_38
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-39343-4_38
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-39342-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-39343-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)