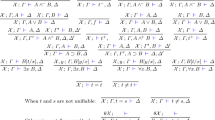Abstract
Quite recently Brass/Dix have introduced the semantics D-WFS for general disjunctive logic programs. The interesting feature of this approach is that it is both semantically and proof-theoretically founded. Any program Φ is associated a normal form res(Φ), called the residual program, by a non-trivial bottom-up construction using least fixpoints of two monotonic operators.
We show in this paper, that the original calculus, consisting of some simple transformations, has a very strong and appealing property: it is confluent. This means that all the transformations can be applied in any order: if we arrive at an irreducible program (no more transformation is applicable) then this is already the unique normal form. No proper subset of the calculus has this property.
We also give an equivalent characterization of D-WPS in terms of iterated minimal model reasoning. This construction is a generalization of a description of the wellfounded semantics: we introduce a very simple and neat construction of a sequence D i that eventually stops and represents the set of derivable disjunctions.
Both characterizations open the way for efficient implementations. The first because the ordering of the transformations does not matter, the second because special methods from Circumscription might be useful.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. R. Apt and Roland N. Bol. Logic Programming and Negation: A Survey. Journal of Logic Programming, 19–20:9–71, 1994.
Stefan Brass and Jürgen Dix. Computing Disjunctive Stable Semantics based on Clark's Completed Database. In Proc. of the 6th GI-Workshop “Grundlagen von Datenbanken”, Bad Helmstedt, September 1994, pages 30–34, 1994.
Stefan Brass and Jürgen Dix. A disjunctive semantics based on unfolding and bottom-up evaluation. In Bernd Wolfinger, editor, Innovationen bei Rechen-und Kommunikationssystemen, (IFIP '94-Congress, Workshop FG2: Disjunctive Logic Programming and Disjunctive Databases), pages 83–91, Berlin, 1994. Springer.
Stefan Brass and Jürgen Dix. A General Approach to Bottom-Up Computation of Disjunctive Semantics. In J. Dix, L. Pereira, and T. Przymusinski, editors, Nonmonotonic Extensions of Logic Programming, LNAI 927, pages 127–155. Springer, Berlin, 1995.
Stefan Brass and Jürgen Dix. Characterizations of the Stable Semantics by Partial Evaluation. In A. Nerode, W. Marek, and M. Truszczyński, editors, Logic Programming and Non-Monotonic Reasoning, Proceedings of the Third International Conference, LNCS 928, pages 85–98, Berlin, June 1995. Springer.
Stefan Brass and Jürgen Dix. Disjunctive Semantics based upon Partial and Bottom-Up Evaluation, In Leon Sterling, editor, Proceedings of the 12th Int. Conf. on Logic Programming, Tokyo, pages 199–213. MIT Press, June 1995.
Nicole Bidoit and Richard Hull. Positivism vs. minimalism in deductive databases. In Proc. of the 5th ACM Symp. on Principles of Database Systems (PODS'86), pages 123–132, 1986.
C. Baral, J. Lobo, and J. Minker. Generalized Disjunctive Well-founded Semantics for Logic Programs: Declarative Semantics. In Z.W. Ras, M. Zemankova, and M.L Emrich, editors, Proceedings of the 5th Int. Symp. on Methodologies for Intelligent Systems, Knoxville, TN, October 1990, pages 465–473. North-Holland, 1990.
C. Baral, J. Lobo, and J. Minker. WF3: A Semantics for Negation in Normal Disjunctive Logic Programs. In Z.W. Ras and M. Zemankova, editors, Methodologies for Intelligent Systems, LNAI 542, pages 459–468, Berlin, 1991. Springer.
K. L. Clark. Negation as Failure. In H. Gallaire and J. Minker, editors, Logic and Data-Bases, pages 293–322. Plenum, New York, 1978.
Jürgen Dix. A Classification-Theory of Semantics of Normal Logic Programs: II. Weak Properties. Fundamenta Informaticae, XXII(3):257–288, 1995.
Jürgen Dix. Semantics of Logic Programs: Their Intuitions and Formal Properties. An Overview. In Andre Fuhrmann and Hans Rott, editors, Logic, Action and Information — Essays on Logic in Philosophy and Artificial Intelligence, pages 241–327. DeGruyter, 1995.
Michael Gelfond and Vladimir Lifschitz. Classical Negation in Logic Programs and Disjunctive Databases. New Generation Computing, 9:365–387, 1991. (Extended abstract appeared in: Logic Programs with Classical Negation. Proceedings of the 7-th International Logic Programming Conference, Jerusalem, pages 579–597, 1990. MIT Press.).
Jorge Lobo, Jack Minker, and Arcot Rajasekar. Foundations of Disjunctive Logic Programming. MIT-Press, 1992.
Jack Minker. On indefinite databases and the closed world assumption. In Proceedings of the 6th Conference on Automated Deduction, New York, pages 292–308, Berlin, 1982. Springer.
Jack Minker. An Overview of Nonmonotonic Reasoning and Logic Programming. Journal of Logic Programming, Special Issue, 17, 1993.
Teodor Przymusinski. Stable Semantics for Disjunctive Programs. New Generation Computing Journal, 9:401–424, 1991. (Extended abstract appeared in: Extended stable semantics for normal and disjunctive logic programs. Proceedings of the 7-th International Logic Programming Conference, Jerusalem, pages 459–477, 1990. MIT Press, Cambridge, Mass.).
Teodor Przymusinski. Stationary Semantics for Normal and Disjunctive Logic Programs. In C. Delobel, M. Kifer, and Y. Masunaga, editors, DOOD '91, Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference, Berlin, December 1991. Muenchen, Springer. LNCS 566.
Teodor Przymusinski. Static Semantics For Normal and Disjunctive Logic Programs. Annals of Mathematics and Artificial Intelligence, Special Issue on Disjunctive Programs, 1995. to appear.
Arcot Rajasekar, Jorge Lobo, and Jack Minker. Weak Generalized Closed World Assumption. Journal of Automated Reasoning, 5:293–307, 1989.
Kenneth A. Ross. The well-founded semantics for disjunctive logic programs. In Proceedings of the first International Conference on Deductive and Object Oriented Databases, Kyoto, Japan, pages 1–22, 1989.
Kenneth A. Ross and Rodney A. Topor. Inferring negative Information from disjunctive Databases. Journal of Automated Reasoning, 4:397–424, 1988.
Chiaki Sakama and Hirohisa Seki. Partial Deduction of Disjunctive Logic Programs: A Declarative Approach. In Logic Program Synthesis and Transformation — Meta Programming in Logic, LNCS 883, pages 170–182, Berlin, 1995. Springer.
Allen van Gelder, Kenneth A. Ross, and John S. Schlipf. The well-founded semantics for general logic programs. Journal of the ACM, 38:620–650, 1991.
Jia-Huai You and Li-Yan Yuan. A three-valued semantics for deductive databases and logic programs. Journal of Computer and System Sciences, 49(2):334–361, 1994.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1996 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Brass, S., Dix, J. (1996). Characterizing D-WFS: Confluence and iterated GCWA. In: Alferes, J.J., Pereira, L.M., Orlowska, E. (eds) Logics in Artificial Intelligence. JELIA 1996. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 1126. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-61630-6_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-61630-6_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-61630-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-70643-4
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive