Abstract
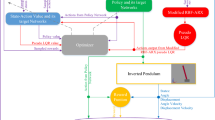
Reinforcement learning is a class of model-free learning control method that can solve Markov decision problems. But it has some problems in applications, especially in MDPs of continuous state spaces. In this paper, based on the vague neural networks, we propose a Q-learning algorithm which is comprehensively considering the reward and punishment of the environment. Simulation results in cart-pole balancing problem illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Horikawa, S., Furuhashi, T., Uchikawa, Y.: On fuzzy modeling using fuzzy neural network with the back-propagation algorithm. IEEE Trans. NN-3(5), 801–806 (1992)
Gau, W.L., Buehrer, D.J.: Vague sets [J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems,Man,and Cybernetics 23(2), 610–614 (1993)
Bustince, H., Burillo, P.: Vague sets are intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 79(1), 403–405 (1996)
Chen, S.M.: Fuzzy system reliability analysis based on vague set theory. In: 1997 IEEE International Conference on Computational Cybernetics and Simulation, vol. 2, pp. 1650–1655 (1997)
Zheng, Y., Luo, S., Lv, Z.: The negative effect on the control of inverted pendulum caused by the limit cycle in reinforcement learning. In: ICNN&B 2005, pp. 772–775 (2005)
Onat, A.: Q-learning with recurrent Neural Networks as a Controller for the Inverted Pendulum Problem. In: The Fifth International Conference on Neural Information Processing, October 21-23, pp. 837–840 (1998)
Anderson, C.W.: Learning to control an inverted pendulum using neural networks. IEEE Control System Magazine 9(3), 31–37 (1989)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhao, Y., Luo, S., Wang, L., Ma, A., Fang, R. (2006). Vague Neural Network Based Reinforcement Learning Control System for Inverted Pendulum. In: King, I., Wang, J., Chan, LW., Wang, D. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4234. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11893295_76
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11893295_76
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-46484-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-46485-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)