Cosmic string detection with tree-based machine learning
Abstract
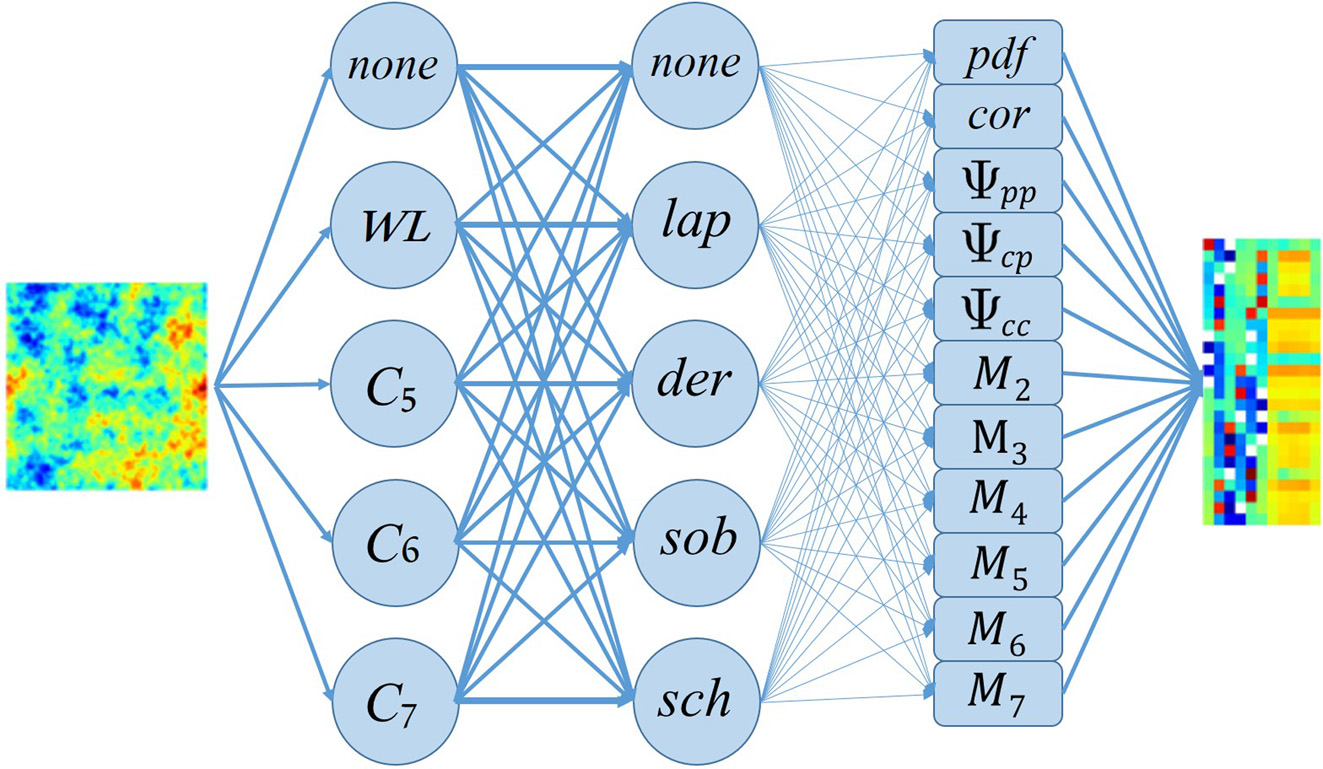
We explore the use of random forest and gradient boosting, two powerful tree-based machine learning algorithms, for the detection of cosmic strings in maps of the cosmic microwave background (CMB), through their unique Gott-Kaiser-Stebbins effect on the temperature anisotropies. The information in the maps is compressed into feature vectors before being passed to the learning units. The feature vectors contain various statistical measures of the processed CMB maps that boost cosmic string detectability. Our proposed classifiers, after training, give results similar to or better than claimed detectability levels from other methods for string tension, Gμ. They can make 3σ detection of strings with Gμ ≳ 2.1 × 10-10 for noise-free, 0.9'-resolution CMB observations. The minimum detectable tension increases to Gμ ≳ 3.0 × 10-8 for a more realistic, CMB S4-like (II) strategy, improving over previous results.
- Publication:
-
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
- Pub Date:
- July 2018
- DOI:
- 10.1093/mnras/sty1055
- arXiv:
- arXiv:1801.04140
- Bibcode:
- 2018MNRAS.478.1132V
- Keywords:
-
- methods: data analysis;
- observational;
- statistical;
- cosmic background radiation;
- Astrophysics - Cosmology and Nongalactic Astrophysics;
- Astrophysics - Instrumentation and Methods for Astrophysics;
- Physics - Data Analysis;
- Statistics and Probability;
- Statistics - Machine Learning
- E-Print:
- 7 pages, 3 figures, 2 tables, Comments are welcome