
Add scatter plots and bubble charts in Numbers on iPad
To create any type of graph, you can add a graph to a sheet first, then select the table cells with the data you want to use. Or, you can select the data first, then create a graph that displays the data. Either way, when you change the data in the table, the graph updates automatically.
Tip: You can learn about different graph types in the Graph Basics template. With the spreadsheet manager in browse view, tap Choose a Template, then tap Charting Basics in the Basic template category. Tap the tabs near the top of the template (Column and Bar Graphs, Interactive Graph and so on) to view the different sheets — each sheet explains a different type of graph.
Intro to scatter graphs and bubble graphs
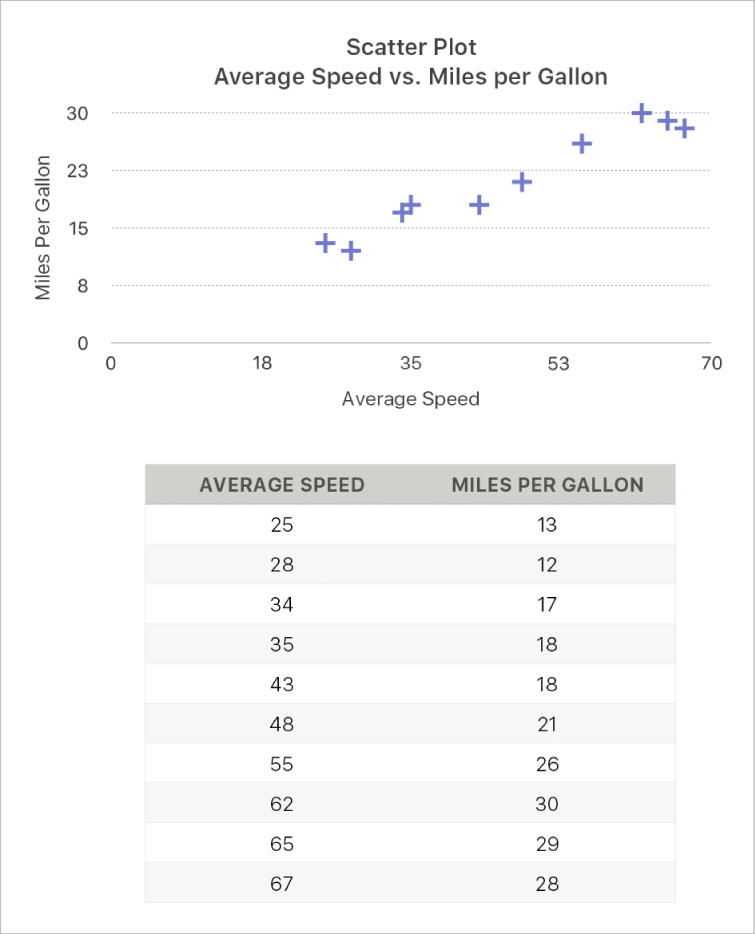
Scatter plots show relationships between two or more sets of data. They display data as points and require at least two columns (or rows) of data to plot values for a single data series. By default, each data series in a scatter plot shares the x-axis value and therefore, you need to add only one additional row or column to show another data series.
The scatter plot below shows the correlation between driving speed and mileage (litres per kilometre).
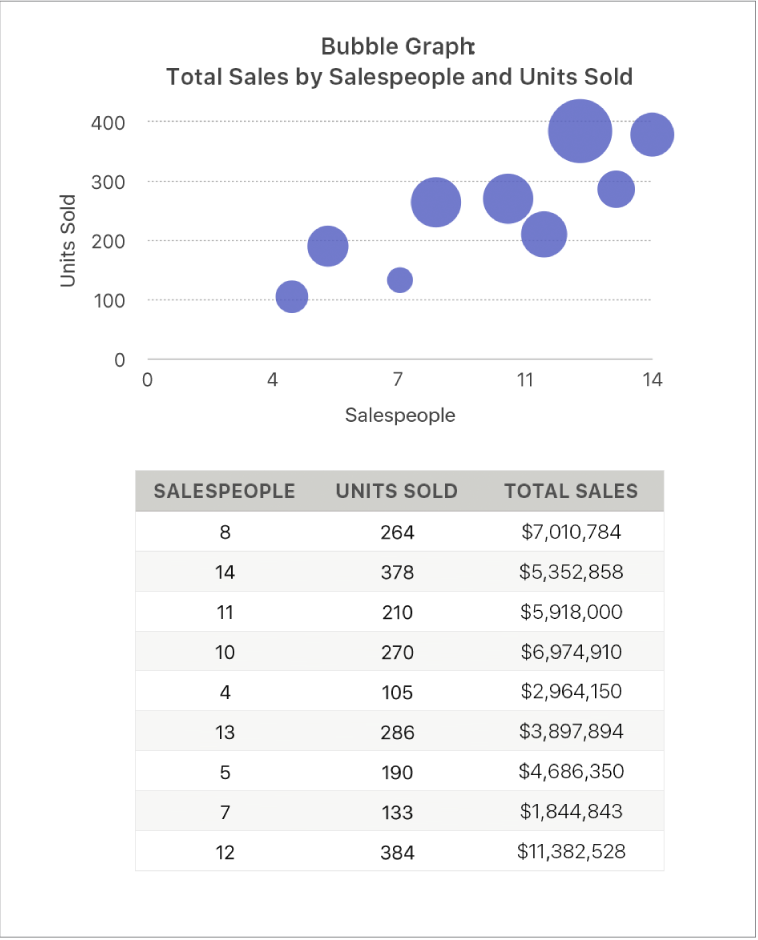
A bubble chart is a type of scatter plot in which the data are plotted as bubbles of varying sizes, rather than as points. Each data series in a bubble chart includes a third dimension that conveys the relationship between the compared values (x and y) and a size value (z). The size value determines the size of the bubble.
By default, each data series in a bubble chart shares the x-axis value, so you need to add only two additional rows or columns of data to show another data series. If you select to use independent x-axis values, you need to add three additional rows or columns (x, y and z) to show another data series.
The bubble chart below shows how the number of units sold (y) varies with the number of salespeople (x). The data is plotted as bubbles of varying sizes — the larger the bubble, the higher the total sales amount (z).
To create these graphs, you can add a graph to a sheet first, then select the table cells with the data you want to use. Or, you can select the cells first, then create a graph that displays the data. Either way, when you change the data in the table, the graph updates automatically.
If the data in your table is categorised, you can select a column to plot the results of a summary row calculation.
The topics below describe how to add a graph first, then select the data.
Create a scatter plot
Tap
 in the toolbar.
in the toolbar.Tap 2D or Interactive to see all the options; there are no 3D scatter plots.
Tap a scatter plot to add it.
Tap the graph, tap Edit References, then select the table rows or columns that have the data you want to use.
You can select rows or columns from one or more tables, including tables on different sheets. Do one of the following:
Select two columns or rows: The scatter plot, plots one data series. The first column selected determines the x-axis values, and the second column determines the y-axis values.
Select more than two columns or rows: The first column selected determines the x-axis values, each additional column selected creates a new series (and determines the y-axis values for that series).
If you want each scatter series to use a different column for the x-axis values, tap
 in the toolbar, then tap Don’t Share X Values.
in the toolbar, then tap Don’t Share X Values.Select only a single column or row: The scatter plot, plots the data similar to a line graph, with the values from the selected column along the y-axis.
Tap Done in the toolbar.
Create a bubble chart
Tap
 in the toolbar.
in the toolbar.Tap 2D or Interactive to see all the options; there are no 3D bubble charts.
Tap a bubble chart to add it.
Tap the graph, tap Edit References, then select the table rows or columns with the data you want to use.
You can select rows or columns from one or more tables, including tables on different sheets. Do one of the following:
To plot one data series: Select three columns. The first column selected determines the x-axis values, the second column determines the y-axis values and the third column determines the size of the bubble.
To plot more than one data series: Select sets of three columns. The bubble plot, plots each group of three columns as one data series. The first column selected determines the x-axis values, the second column determines the y-axis values and the third column determines the size of the bubble.
To have each bubble series share one column for the x-axis values, tap
 in the toolbar, then tap Share X Values. In this case, select sets of two columns for each additional data series.
in the toolbar, then tap Share X Values. In this case, select sets of two columns for each additional data series.To use data from a single column: Select the column. The bubble chart plots the data similar to a line graph, with the values from the selected column along the y-axis.
To change whether rows or columns are plotted as the data series, tap
 in the toolbar, then tap an option.
in the toolbar, then tap an option.Tap Done in the toolbar.
Share the x-axis for multiple values along the y-axis
Sharing the x-axis means plotting a single kind of value along the x-axis, while allowing for multiple kinds of values to be plotted along the y-axis. By default, the x-axis values are shared among multiple sets of y-axis values in some types of graphs.
Tap the graph, then tap Edit References.
Tap
 in the toolbar, then tap Share X Values.
in the toolbar, then tap Share X Values.Tap Done to return to the graph.
You can change the data reflected in the graph at any time. To learn how, see Modify graph data in Numbers on iPad.
