
File system formats available in Disk Utility
You can format a disk or volume using one of the following file system formats.
Apple File System (APFS)
Apple File System (APFS), the default file system for Mac computers with solid state drives, features strong encryption, space sharing, snapshots, fast directory sizing, and improved file system fundamentals. While APFS is optimized for the Flash/SSD storage used in recent Mac computers, it can also be used with older systems with traditional hard disk drives (HDD) and external, direct-attached storage. macOS High Sierra supports APFS for both bootable and data volumes.
APFS allocates disk space within a container on demand. The disk’s free space is shared and can be allocated to any of the individual volumes as needed. If desired, you can specify reserve and quota sizes for each volume. Each volume uses only part of the overall container, so the available space is the total size of the container, minus the size of all volumes in the container.
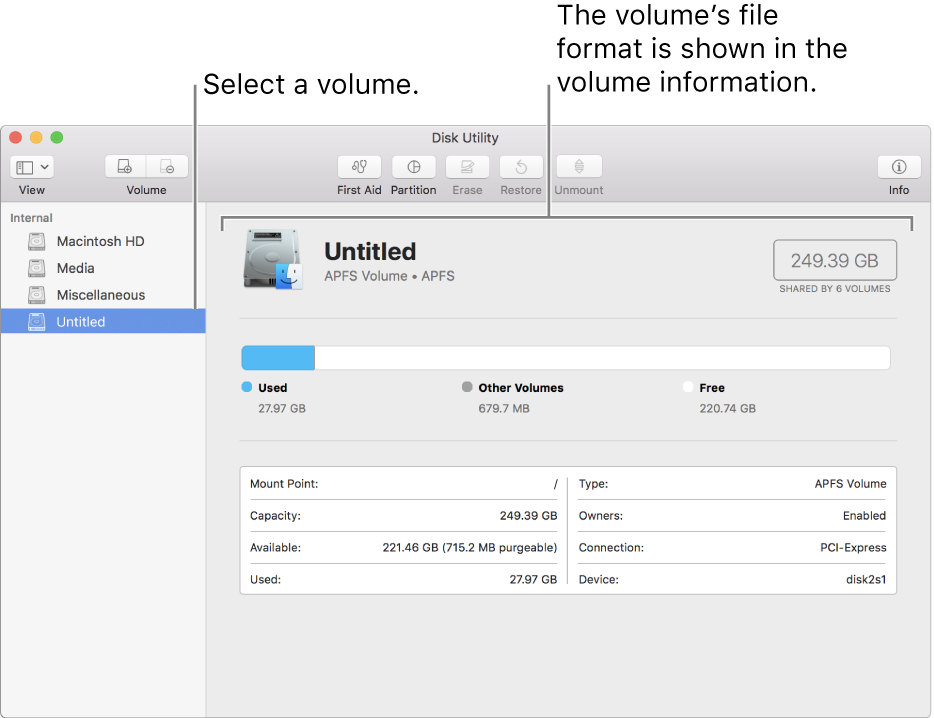
Each volume within an APFS container can have its own APFS format—APFS, APFS (Encrypted), APFS (Case-sensitive), or APFS (Case-sensitive, Encrypted).
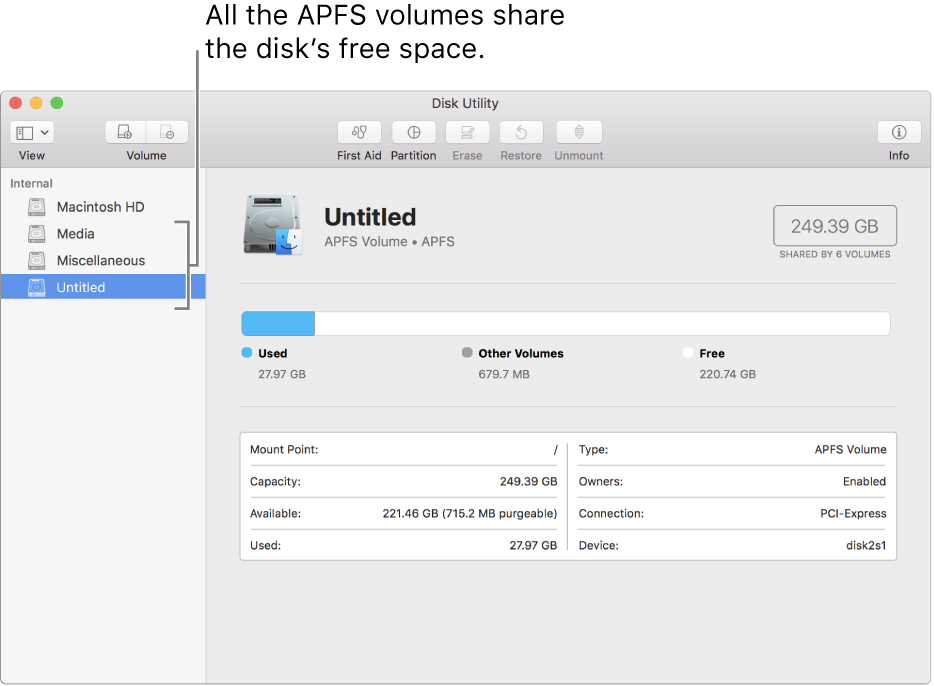
You can easily add a volume to an APFS container.
Mac OS Extended, MS-DOS (FAT), and ExFAT
Volumes can also be formatted as Mac OS Extended (the file system that comes with macOS Sierra and earlier), MS-DOS (FAT), or ExFAT.
The device must contain at least one volume that contains data. For instructions, see Add a volume to a device formatted as Mac OS Extended, MS-DOS (FAT), or ExFAT. If a volume formatted as Mac OS Extended doesn’t have enough space available, you can enlarge it.
