Evidence for a conformational change in actin induced by fimbrin (N375) binding
- PMID: 9334343
- PMCID: PMC2139807
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.139.2.387
Evidence for a conformational change in actin induced by fimbrin (N375) binding
Abstract
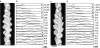
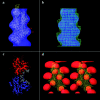
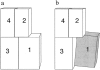
Fimbrin belongs to a superfamily of actin cross-linking proteins that share a conserved 27-kD actin-binding domain. This domain contains a tandem duplication of a sequence that is homologous to calponin. Calponin homology (CH) domains not only cross-link actin filaments into bundles and networks, but they also bind intermediate filaments and some signal transduction proteins to the actin cytoskeleton. This fundamental role of CH domains as a widely used actin-binding domain underlines the necessity to understand their structural interaction with actin. Using electron cryomicroscopy, we have determined the three-dimensional structure of F-actin and F-actin decorated with the NH2-terminal CH domains of fimbrin (N375). In a difference map between actin filaments and N375-decorated actin, one end of N375 is bound to a concave surface formed between actin subdomains 1 and 2 on two neighboring actin monomers. In addition, a fit of the atomic model for the actin filament to the maps reveals the actin residues that line, the binding surface. The binding of N375 changes actin, which we interpret as a movement of subdomain 1 away from the bound N375. This change in actin structure may affect its affinity for other actin-binding proteins and may be part of the regulation of the cytoskeleton itself. Difference maps between actin and actin decorated with other proteins provides a way to look for novel structural changes in actin.
Figures


Similar articles
-
An atomic model of fimbrin binding to F-actin and its implications for filament crosslinking and regulation.Nat Struct Biol. 1998 Sep;5(9):787-92. doi: 10.1038/1828. Nat Struct Biol. 1998. PMID: 9731773
-
The CH-domain of calponin does not determine the modes of calponin binding to F-actin.J Mol Biol. 2006 Jun 2;359(2):478-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.03.044. Epub 2006 Apr 3. J Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16626733
-
High-resolution cryo-EM structure of the F-actin-fimbrin/plastin ABD2 complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Feb 5;105(5):1494-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0708667105. Epub 2008 Jan 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18234857 Free PMC article.
-
Novel structural insights into F-actin-binding and novel functions of calponin homology domains.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008 Dec;18(6):702-8. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2008.10.003. Epub 2008 Nov 13. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008. PMID: 18952167 Review.
-
Location of the binding site of the mannose-specific lectin comitin on F-actin.J Mol Biol. 1998 Dec 18;284(5):1255-63. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.2294. J Mol Biol. 1998. PMID: 9878346 Review.
Cited by
-
The Dictyostelium discoideum FimA protein, unlike yeast and plant fimbrins, is regulated by calcium similar to mammalian plastins.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 27;13(1):16208. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42682-1. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37758724 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Range and Directional Allostery of Actin Filaments Plays Important Roles in Various Cellular Activities.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 1;21(9):3209. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093209. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32370032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Actin binding domain of filamin distinguishes posterior from anterior actin filaments in migrating Dictyostelium cells.Biophys Physicobiol. 2016 Dec 17;13:321-331. doi: 10.2142/biophysico.13.0_321. eCollection 2016. Biophys Physicobiol. 2016. PMID: 28409084 Free PMC article.
-
The Calcium-Dependent Switch Helix of L-Plastin Regulates Actin Bundling.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 1;7:40662. doi: 10.1038/srep40662. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28145401 Free PMC article.
-
Fascin- and α-Actinin-Bundled Networks Contain Intrinsic Structural Features that Drive Protein Sorting.Curr Biol. 2016 Oct 24;26(20):2697-2706. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2016.07.080. Epub 2016 Sep 22. Curr Biol. 2016. PMID: 27666967 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams AE, Botstein D, Drubin DG. Requirement of yeast fimbrin for actin organization and morphogenesis in vivo. Nature (Lond) 1991;354:404–408. - PubMed
-
- Anderson NL, Gemmell MA, Coussens PM, Murao S, Huberman E. Specific protein phosphorylation in human promyelocytic HL-60 leukemia cells susceptible or resistant to induction of cell differentiation by phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate. Cancer Res. 1985;45:4955–4962. - PubMed
-
- Bresnick AR, Janmey PA, Condeelis J. Evidence that a 27-residue sequence is the actin-binding site of ABP-120. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:12989–12993. - PubMed


