p46, a novel natural killer cell-specific surface molecule that mediates cell activation
- PMID: 9314561
- PMCID: PMC2211712
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.186.7.1129
p46, a novel natural killer cell-specific surface molecule that mediates cell activation
Abstract
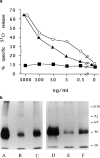
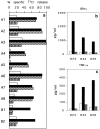
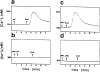
Limited information is available on the surface molecules that are involved in natural killer (NK) cell triggering. In this study, we selected the BAB281 monoclonal antibody (mAb) on the basis of its ability to trigger NK-mediated target cell lysis. BAB281 identified a novel NK cell-specific surface molecule of 46 kD (p46) that is expressed by all resting or activated NK cells. Importantly, unlike the NK cell antigens identified so far, the expression of p46 was strictly confined to NK cells. Upon mAb-mediated cross-linking, p46 molecules induced strong cell triggering leading to [Ca2+]i increases, lymphokine production, and cytolytic activity both in resting NK cells and NK cell clones. The p46-mediated induction of Ca2+ increases or triggering of cytolytic activity was downregulated by the simultaneous engagement of inhibitory receptors including p58, p70, and CD94/NKG2A. Both the unique cellular distribution and functional capability of p46 molecules suggest a possible role in the mechanisms of non-major histocompatibility complex-restricted cytolysis mediated by human NK cells.
Figures







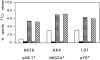
Similar articles
-
Existence of both inhibitory (p58) and activatory (p50) receptors for HLA-C molecules in human natural killer cells.J Exp Med. 1995 Sep 1;182(3):875-84. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.3.875. J Exp Med. 1995. PMID: 7650491 Free PMC article.
-
HLA-G recognition by human natural killer cells. Involvement of CD94 both as inhibitory and as activating receptor complex.Eur J Immunol. 1997 Aug;27(8):1875-80. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830270809. Eur J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9295021
-
Expression of p58.2 or CD94/NKG2A inhibitory receptors in an NK-like cell line, YTINDY, leads to HLA Class I-mediated inhibition of cytotoxicity in the p58.2- but not the CD94/NKG2A-expressing transfectant.Cell Immunol. 2002 Sep;219(1):57-70. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(02)00578-6. Cell Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12473268
-
Activating receptors and coreceptors involved in human natural killer cell-mediated cytolysis.Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:197-223. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.197. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11244035 Review.
-
Natural killer cell-mediated recognition of human trophoblast.Semin Cancer Biol. 1999 Feb;9(1):13-8. doi: 10.1006/scbi.1998.0108. Semin Cancer Biol. 1999. PMID: 10092546 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive snapshots of natural killer cells functions, signaling, molecular mechanisms and clinical utilization.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Nov 8;9(1):302. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-02005-w. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39511139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bulk and single-cell transcriptomics identify gene signatures of stem cell-derived NK cell donors with superior cytolytic activity.Mol Ther Oncol. 2024 Sep 2;32(4):200870. doi: 10.1016/j.omton.2024.200870. eCollection 2024 Dec 19. Mol Ther Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39346765 Free PMC article.
-
Natural killer cells in cancer immunotherapy.MedComm (2020). 2024 Jun 15;5(7):e626. doi: 10.1002/mco2.626. eCollection 2024 Jul. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 38882209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chimeric Antigen Cytotoxic Receptors for In Vivo Engineering of Tumor-Targeting NK Cells.Immunohorizons. 2024 Jan 1;8(1):97-105. doi: 10.4049/immunohorizons.2300099. Immunohorizons. 2024. PMID: 38240638 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal profiling reveals site-specific adaptation and tissue residency hallmarks of γδ T cells across organs in mice.Nat Immunol. 2024 Feb;25(2):343-356. doi: 10.1038/s41590-023-01710-y. Epub 2024 Jan 4. Nat Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38177282 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Herberman RB, Nunn ME, Lavrin DH. Natural cytotoxic reactivity of mouse lymphoid cells against syngeneic and allogeneic tumours. I. Distribution of reactivity and specificity. Int J Cancer. 1976;16:216–229. - PubMed
-
- Liao NS, Bix M, Zijstra M, Jaenisch R, Raulet D. MHC class I deficiency: susceptibility to natural killer (NK) cells and impaired NK activity. Science (Wash DC) 1991;253:199–202. - PubMed
-
- Karre K. An unexpected petition for pardon. Curr Biol. 1992;2:613–616. - PubMed
-
- Moretta L, Ciccone E, Mingari MC, Biassoni R, Moretta A. Human NK cells: origin, clonality, specificity and receptors. Adv Immunol. 1994;55:341–380. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous


