Pharmacological responsiveness of periodic limb movements in patients with restless legs syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36692194
- PMCID: PMC10071388
- DOI: 10.5664/jcsm.10440
Pharmacological responsiveness of periodic limb movements in patients with restless legs syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
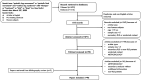
Study objectives: Periodic limb movements during sleep (PLMS) are a frequent finding in restless legs syndrome, but their impact on sleep is still debated, as well the indication for treatment. We systematically reviewed the available literature to describe which drug categories are effective in suppressing PLMS, assessing their efficacy through a meta-analysis, when this was possible.
Methods: The review protocol was preregistered on PROSPERO (CRD42021175848), and the systematic search was conducted on and EMBASE (last searched on March 2020). We included original human studies, which assessed PLMS modification on drug treatment with a full-night polysomnography, through surface electrodes on each tibialis anterior muscle. When at least 4 studies were available on the same drug or drug category, we performed a random-effect model meta-analysis.
Results: Dopamine agonists like pramipexole and ropinirole resulted the most effective, followed by l-dopa and other dopamine agonists. Alpha2delta ligands are moderately effective as well opioids, despite available data on these drugs are much more limited than those on dopaminergic agents. Valproate and carbamazepine did not show a significant effect on PLMS. Clonazepam showed contradictory results. Perampanel and dypiridamole showed promising but still insufficient data. The same applies to iron supplementation.
Conclusions: Dopaminergic agents are the most powerful suppressors of PLMS. However, most therapeutic trials in restless legs syndrome do not report objective polysomnographic findings, there is a lack of uniformity in presenting results on PLMS. Longitudinal polysomnographic interventional studies, using well-defined and unanimous scoring criteria and endpoints on PLMS are needed.
Citation: Riccardi S, Ferri R, Garbazza C, Miano S, Manconi M. Pharmacological responsiveness of periodic limb movements in patients with restless legs syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Sleep Med. 2023;19(4):811-822.
Keywords: nocturnal myoclonus; periodic limb movements during sleep; polysomnography; restless legs syndrome; tibialis anterior muscle; treatment.
© 2023 American Academy of Sleep Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have seen and approved this manuscript. The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Night-to-night variability of periodic leg movements during sleep in restless legs syndrome and periodic limb movement disorder: comparison between the periodicity index and the PLMS index.Sleep Med. 2013 Mar;14(3):293-6. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2012.08.014. Epub 2012 Oct 12. Sleep Med. 2013. PMID: 23068780 Clinical Trial.
-
L-Dopa improves Restless Legs Syndrome and periodic limb movements in sleep but not Attention-Deficit-Hyperactivity Disorder in a double-blind trial in children.Sleep Med. 2011 May;12(5):471-7. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2011.01.008. Epub 2011 Apr 3. Sleep Med. 2011. PMID: 21463967 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Ropinirole decreases periodic leg movements and improves sleep parameters in patients with restless legs syndrome.Sleep. 2004 Aug 1;27(5):907-14. doi: 10.1093/sleep/27.5.907. Sleep. 2004. PMID: 15453549 Clinical Trial.
-
[Restless legs syndrome and periodic limb movements in sleep: pathophysiology and treatment].Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2003 May-Jun;37(3):633-43. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2003. PMID: 14593758 Review. Polish.
-
Restless legs syndrome and periodic limb movements during sleep: diagnosis and treatment.Neurologist. 2007 Sep;13(5):294-301. doi: 10.1097/NRL.0b013e3181422589. Neurologist. 2007. PMID: 17848868 Review.
Cited by
-
Review of the role of the endogenous opioid and melanocortin systems in the restless legs syndrome.Brain. 2024 Jan 4;147(1):26-38. doi: 10.1093/brain/awad283. Brain. 2024. PMID: 37633259 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferri R , Fulda S , Allen RP , et al. International and European Restless Legs Syndrome Study Groups (IRLSSG and EURLSSG) . World Association of Sleep Medicine (WASM) 2016 standards for recording and scoring leg movements in polysomnograms developed by a joint task force from the International and the European Restless Legs Syndrome Study Groups (IRLSSG and EURLSSG) . Sleep Med. 2016. ; 26 : 86 – 95 . - PubMed
-
- Ambrosetto C , Lugaresi E , Coccagna G , Tassinari CA . Clinical and polygraphic remarks in the syndrome of restless legs . Riv Patol Nerv Ment. 1965. ; 86 ( 2 ): 244 – 252 . - PubMed
-
- Montplaisir J , Boucher S , Poirier G , Lavigne G , Lapierre O , Lespérance P . Clinical, polysomnographic, and genetic characteristics of restless legs syndrome: A study of 133 patients diagnosed with new standard criteria . Mov Disord. 1997. ; 12 ( 1 ): 61 – 65 . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical


