Effect of Ghrelin on the Cardiovascular System
- PMID: 36009817
- PMCID: PMC9405061
- DOI: 10.3390/biology11081190
Effect of Ghrelin on the Cardiovascular System
Abstract
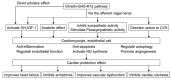
Ghrelin, an n-octanoyl-modified 28-amino-acid-peptide, was first discovered in the human and rat stomach as an endogenous ligand for the growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHS-R). Ghrelin-GHS-R1a signaling regulates feeding behavior and energy balance, promotes vascular activity and angiogenesis, improves arrhythmia and heart failure, and also protects against cardiovascular disease by suppressing cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction. Ghrelin's cardiovascular protective effects are mediated by the suppression of sympathetic activity; activation of parasympathetic activity; alleviation of vascular endothelial dysfunction; and regulation of inflammation, apoptosis, and autophagy. The physiological functions of ghrelin should be clarified to determine its pharmacological potential as a cardiovascular medication.
Keywords: GHS-R; cardiovascular system; des-acyl ghrelin; ghrelin; growth hormone; sympathetic activity.
Conflict of interest statement
H.H. received financial support from Tosoh Bioscience.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Research progress of ghrelin on cardiovascular disease.Biosci Rep. 2021 Jan 29;41(1):BSR20203387. doi: 10.1042/BSR20203387. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33427286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physiological significance of ghrelin in the cardiovascular system.Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2019;95(8):459-467. doi: 10.2183/pjab.95.032. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31611501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Des-acyl ghrelin induces food intake by a mechanism independent of the growth hormone secretagogue receptor.Endocrinology. 2006 May;147(5):2306-14. doi: 10.1210/en.2005-1357. Epub 2006 Feb 16. Endocrinology. 2006. PMID: 16484324
-
Ghrelin's Orexigenic Effect Is Modulated via a Serotonin 2C Receptor Interaction.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015 Jul 15;6(7):1186-97. doi: 10.1021/cn500318q. Epub 2015 Mar 10. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25727097
-
Ghrelin: more than a natural GH secretagogue and/or an orexigenic factor.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2005 Jan;62(1):1-17. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2004.02160.x. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2005. PMID: 15638864 Review.
Cited by
-
Ghrelin is essential for lowering blood pressure during torpor.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Oct 10;15:1487028. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1487028. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39449746 Free PMC article.
-
N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide Correlates with Ghrelin and Acyl-Ghrelin in Pre-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 23;25(11):5696. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115696. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38891884 Free PMC article.
-
Growth hormone releasing peptide-6 (GHRP-6) prevents doxorubicin-induced myocardial and extra-myocardial damages by activating prosurvival mechanisms.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 30;15:1402138. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1402138. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38873418 Free PMC article.
-
Ghrelin and glucagon-like peptide-1 according to body adiposity and glucose homeostasis.Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2023 May 12;67(4):e000611. doi: 10.20945/2359-3997000000611. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2023. PMID: 37252699 Free PMC article.
-
Gut Molecules in Cardiometabolic Diseases: The Mechanisms behind the Story.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 8;24(4):3385. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043385. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834796 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Date Y., Kojima M., Hosoda H., Sawaguchi A., Mondal M.S., Suganuma T., Matsukura S., Kangawa K., Nakazato M. Ghrelin, a novel growth hormone-releasing acylated peptide, is synthesized in a distinct endocrine cell type in the gastrointestinal tracts of rats and humans. Endocrinology. 2000;141:4255–4261. doi: 10.1210/endo.141.11.7757. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources


