Myopia, its prevalence, current therapeutic strategy and recent developments: A Review
- PMID: 35918918
- PMCID: PMC9672758
- DOI: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_2415_21
Myopia, its prevalence, current therapeutic strategy and recent developments: A Review
Abstract
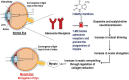
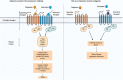
Myopia is a widespread and complex refractive error in which a person's ability to see distant objects clearly is impaired. Its prevalence rate is increasing worldwide, and as per WHO, it is projected to increase from 22% in 2000 to 52% by 2050. It is more prevalent in developed, industrial areas and affects individuals of all ages. There are a number of treatments available for the control of myopia, such as glasses, contact lenses, laser surgery, and pharmaceuticals agents. However, these treatments are less beneficial and have significant side effects. A novel molecule, 7-methylxanthine (7-MX), has been found to be a highly beneficial alternate in the treatment of myopia and excessive eye elongation. Many preclinical and clinical studies showed that 7-MX is effective for the treatment of myopia and is presently under phase II of clinical investigation. We have also investigated preclinical toxicity studies such as acute, sub-acute, sub-chronic, and chronic on rats. In these studies, 7-MX was found to be non-toxic as compared to other reported anti-myopic agents. Moreover, as an ideal drug, 7-MX is observed to have no or low toxicity, brain permeability, non-allergic, higher oral administration efficacy, and low treatment costs and thus qualifies for the long-term treatment of myopia. This review article on 7-MX as an alternative to myopia treatment will highlight recent findings from well-designed preclinical and clinical trials and propose a potential future therapy.
Keywords: 7-methylxanthine; myopia; prevalence; treatments.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
Comment in
-
Comment on: Myopia, its prevalence, current therapeutic strategy and recent developments: A review.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2023 Feb;71(2):672. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_2130_22. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 36727388 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Phakic intraocular lenses for the treatment of refractive errors: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009;9(14):1-120. Epub 2009 Oct 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009. PMID: 23074518 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment options for myopia.Optom Vis Sci. 2009 Jun;86(6):624-8. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0b013e3181a6a225. Optom Vis Sci. 2009. PMID: 19390466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Axial eye growth and refractive error development can be modified by exposing the peripheral retina to relative myopic or hyperopic defocus.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014 Sep 4;55(10):6765-73. doi: 10.1167/iovs.14-14524. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014. PMID: 25190657 Free PMC article.
-
Myopia control in children through refractive therapy gas permeable contact lenses: is it for real?Am J Ophthalmol. 2013 Dec;156(6):1076-1081.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2013.04.039. Am J Ophthalmol. 2013. PMID: 24238200 Review.
-
Sub-chronic and chronic toxicity evaluation of 7-methylxanthine: a new molecule for the treatment of myopia.Drug Chem Toxicol. 2022 May;45(3):1383-1394. doi: 10.1080/01480545.2020.1833904. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 33076712
Cited by
-
Prevalence of Myopia Among Schoolchildren and the Impact of Increased Screen Time: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2024 Aug 13;16(8):e66815. doi: 10.7759/cureus.66815. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39280371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence, sociodemographic risk factors, and coverage of myopia correction among adolescent students in the central region of Portugal.BMC Public Health. 2024 Sep 12;24(1):2490. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-19914-8. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39266991 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Acute Mental Stress on Choroidal Thickness.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Jul 5;11(7):684. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11070684. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061766 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of toric soft contact lenses for vision correction in patients with different degrees of astigmatism: a real-world study.Int J Ophthalmol. 2023 Nov 18;16(11):1845-1853. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2023.11.17. eCollection 2023. Int J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 38028513 Free PMC article.
-
Repeated Low-Level Red-Light Therapy for Controlling Onset and Progression of Myopia-a Review.Int J Med Sci. 2023 Sep 4;20(10):1363-1376. doi: 10.7150/ijms.85746. eCollection 2023. Int J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37786442 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pan CW, Ramamurthy D, Saw SM. Worldwide prevalence and risk factors for myopia. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2012;32:3–16. - PubMed
-
- Saw SM, Katz J, Schein OD, Chew SJ, Chan TK. Epidemiology of myopia. Epidemiol Rev. 1996;18:175–87. - PubMed
-
- Hosaka A. Population studies--myopia experience in Japan. Acta Ophthalmol. 1988;185:37–40. - PubMed
-
- Marzani D, Wallman J. Growth of the two layers of the chick sclera is modulated reciprocally by visual conditions. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1997;38:1726–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical