Efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of the DNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (ZyCoV-D): the interim efficacy results of a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in India
- PMID: 35367003
- PMCID: PMC8970574
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00151-9
Efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of the DNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (ZyCoV-D): the interim efficacy results of a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in India
Abstract
Background: ZyCoV-D, a DNA-based vaccine, showed promising safety and immunogenicity in a phase 1/2 trial. We now report the interim efficacy results of phase 3 clinical trial with ZyCoV-D vaccine in India.
Methods: We conducted an interim analysis of a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial at 49 centres in India. Healthy participants aged at least 12 years were enrolled and randomly assigned (1:1) to receive either ZyCov-D vaccine (Cadila Healthcare; 2 mg per dose) or placebo. An interactive web response system was used for randomisation (blocks of four) of participants as well as to enrol those aged 60 years and older with or without comorbid conditions, and those aged 12-17 years. It was also used to identify 600 participants for immunogenicity (blocks of six). Participants, investigators, and outcome assessors were masked to treatment assignment. Three doses of vaccine or placebo were administered intradermally via a needle-free injection system 28 days apart. The primary outcome was the number of participants with first occurrence of symptomatic RT-PCR-positive COVID-19 28 days after the third dose, until the targeted number of cases (interim analysis n=79, full analysis n=158) have been achieved. The analysis was done in the per-protocol population, which consisted of all participants with negative baseline SARS-CoV-2 status who received three doses of vaccine or placebo. Assessment of safety and tolerability was based on the safety population, which consisted of all enrolled participants who were known to have received at least one dose of study vaccine or placebo. This trial is registered with Clinical Trial Registry India, CTRI/2021/01/030416, and is ongoing.
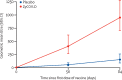
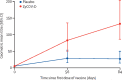
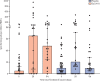
Findings: Between Jan 16, and June 23, 2021 (data cutoff), 33 194 individuals were screened, of whom 5241 did not meet screening criteria and 27 703 were enrolled and randomly assigned to receive ZyCoV-D (n=13 851) or placebo (n=13 852). Per-protocol, 81 cases were eligible and included in efficacy analysis (20 of 12 350 in the ZyCoV-D group and 61 of 12 320 in placebo group). The ZyCoV-D vaccine efficacy was found to be 66·6% (95% CI 47·6-80·7). The occurrence of solicited adverse events was similar between the treatment groups (623 [4·49%] in the ZyCoV-D group vs 620 [4·47%] in the placebo group). There were two deaths (one in each group) reported at the data cutoff, neither of which was considered related to the study treatments.
Interpretation: In this interim analysis, ZyCoV-D vaccine was found to be efficacious, safe, and immunogenic in a phase 3 trial.
Funding: National Biopharma Mission, Department of Biotechnology, Government of India and Cadila Healthcare, Ahmedabad, Gujarat India.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests JS, AD, KK, and TMCR are employees of Cadila Healthcare. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
DNA vaccines join the fight against COVID-19.Lancet. 2022 Apr 2;399(10332):1281-1282. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00524-4. Lancet. 2022. PMID: 35366995 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (inactivated, Vero cell): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Apr 13;22(1):276. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05180-1. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33849629 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy, safety, and lot-to-lot immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (BBV152): interim results of a randomised, double-blind, controlled, phase 3 trial.Lancet. 2021 Dec 11;398(10317):2173-2184. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02000-6. Epub 2021 Nov 11. Lancet. 2021. PMID: 34774196 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and immunogenicity of a recombinant tandem-repeat dimeric RBD-based protein subunit vaccine (ZF2001) against COVID-19 in adults: two randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1 and 2 trials.Lancet Infect Dis. 2021 Aug;21(8):1107-1119. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00127-4. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Lancet Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33773111 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and immunogenicity of CpG 1018 and aluminium hydroxide-adjuvanted SARS-CoV-2 S-2P protein vaccine MVC-COV1901: interim results of a large-scale, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial in Taiwan.Lancet Respir Med. 2021 Dec;9(12):1396-1406. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00402-1. Epub 2021 Oct 13. Lancet Respir Med. 2021. PMID: 34655522 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and immunogenicity of a protein subunit COVID-19 vaccine (ZF2001) in healthy children and adolescents aged 3-17 years in China: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1 trial and an open-label, non-randomised, non-inferiority, phase 2 trial.Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2023 Apr;7(4):269-279. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(22)00376-5. Epub 2023 Feb 17. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2023. PMID: 36803632 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
New insights for the development of efficient DNA vaccines.Microb Biotechnol. 2024 Nov;17(11):e70053. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.70053. Microb Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39545748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advanced technologies for the development of infectious disease vaccines.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024 Oct 21. doi: 10.1038/s41573-024-01041-z. Online ahead of print. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 39433939 Review.
-
Molecular targets and strategies in the development of nucleic acid cancer vaccines: from shared to personalized antigens.J Biomed Sci. 2024 Oct 9;31(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s12929-024-01082-x. J Biomed Sci. 2024. PMID: 39379923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19: vaccination, therapeutics and a review of the science and public health.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024 Jul 17;86(9):5343-5353. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000002374. eCollection 2024 Sep. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39239001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vaccines for Respiratory Viruses-COVID and Beyond.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Aug 22;12(8):936. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12080936. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204059 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO WHO Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19. March 11, 2020. https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-genera...
-
- Mammen MP, Jr, Tebas P, Agnes J, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of INO-4800 DNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2: a preliminary report of a randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled, phase 2 clinical trial in adults at high risk of viral exposure. medRxiv. 2021 doi: 10.1101/2021.05.07.21256652. published online May 7. (preprint). - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous


