Early evolution of beetles regulated by the end-Permian deforestation
- PMID: 34747694
- PMCID: PMC8585485
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.72692
Early evolution of beetles regulated by the end-Permian deforestation
Abstract
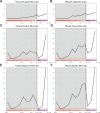
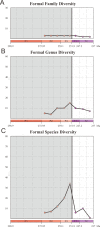
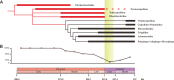
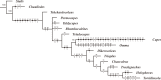
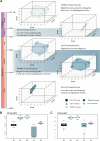
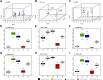
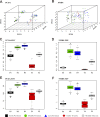
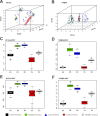
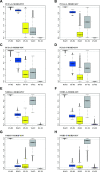
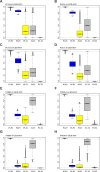
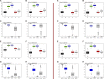
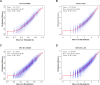
The end-Permian mass extinction (EPME) led to a severe terrestrial ecosystem collapse. However, the ecological response of insects-the most diverse group of organisms on Earth-to the EPME remains poorly understood. Here, we analyse beetle evolutionary history based on taxonomic diversity, morphological disparity, phylogeny, and ecological shifts from the Early Permian to Middle Triassic, using a comprehensive new dataset. Permian beetles were dominated by xylophagous stem groups with high diversity and disparity, which probably played an underappreciated role in the Permian carbon cycle. Our suite of analyses shows that Permian xylophagous beetles suffered a severe extinction during the EPME largely due to the collapse of forest ecosystems, resulting in an Early Triassic gap of xylophagous beetles. New xylophagous beetles appeared widely in the early Middle Triassic, which is consistent with the restoration of forest ecosystems. Our results highlight the ecological significance of insects in deep-time terrestrial ecosystems.
Keywords: beetle; carbon cycle; deforestation; disparity; diversity; evolutionary biology; extinction; none.
© 2021, Zhao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
XZ, YY, MC, EY, JC, EJ, XZ, BW No competing interests declared
Figures


Similar articles
-
Whirling in the late Permian: ancestral Gyrinidae show early radiation of beetles before Permian-Triassic mass extinction.BMC Evol Biol. 2018 Mar 16;18(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12862-018-1139-8. BMC Evol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29548278 Free PMC article.
-
The stability and collapse of marine ecosystems during the Permian-Triassic mass extinction.Curr Biol. 2023 Mar 27;33(6):1059-1070.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2023.02.007. Epub 2023 Feb 24. Curr Biol. 2023. PMID: 36841237
-
Species richness and disparity of parareptiles across the end-Permian mass extinction.Proc Biol Sci. 2019 Mar 27;286(1899):20182572. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2018.2572. Proc Biol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30890099 Free PMC article.
-
Permian-Triassic Osteichthyes (bony fishes): diversity dynamics and body size evolution.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2016 Feb;91(1):106-47. doi: 10.1111/brv.12161. Epub 2014 Nov 27. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2016. PMID: 25431138 Review.
-
Rapid turnover of top predators in African terrestrial faunas around the Permian-Triassic mass extinction.Curr Biol. 2023 Jun 5;33(11):2283-2290.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2023.04.007. Epub 2023 May 22. Curr Biol. 2023. PMID: 37220743 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic analysis and control of a rice-pest system under transcritical bifurcations.PeerJ. 2023 Oct 10;11:e16083. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16083. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37842048 Free PMC article.
-
Disparification and extinction trade-offs shaped the evolution of Permian to Jurassic Odonata.iScience. 2023 Jul 21;26(8):107420. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107420. eCollection 2023 Aug 18. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37583549 Free PMC article.
-
Taxonomic and carbon metabolic diversification of Bathyarchaeia during its coevolution history with early Earth surface environment.Sci Adv. 2023 Jul 7;9(27):eadf5069. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adf5069. Epub 2023 Jul 5. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37406125 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benton MJ, Newell AJ. Impacts of global warming on Permo-Triassic terrestrial ecosystems. Gondwana Research. 2014;25:1308–1337. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.12.010. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous


