The Tongue in Three Species of Lemurs: Flower and Nectar Feeding Adaptations
- PMID: 34679832
- PMCID: PMC8532830
- DOI: 10.3390/ani11102811
The Tongue in Three Species of Lemurs: Flower and Nectar Feeding Adaptations
Abstract
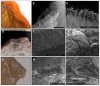
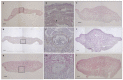
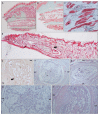
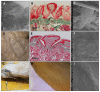
The mobility of the primate tongue allows for the manipulation of food, but, in addition, houses both general sensory afferents and special sensory end organs. Taste buds can be found across the tongue, but the ones found within the fungiform papillae on the anterior two thirds of the tongue are the first gustatory structures to come into contact with food, and are critical in making food ingestion decisions. Comparative studies of both the macro and micro anatomy in primates are sparse and incomplete, yet there is evidence that gustatory adaptation exists in several primate taxa. One is the distally feathered tongues observed in non-destructive nectar feeders, such as Eulemur rubriventer. We compare both the macro and micro anatomy of three lemurid species who died of natural causes in captivity. We included the following two non-destructive nectar feeders: Varecia variegata and Eulemur macaco, and the following destructive flower feeder: Lemur catta. Strepsirrhines and tarsiers are unique among primates, because they possess a sublingua, which is an anatomical structure that is located below the tongue. We include a microanatomical description of both the tongue and sublingua, which were accomplished using hematoxylin-eosin and Masson trichrome stains, and scanning electron microscopy. We found differences in the size, shape, and distribution of fungiform papillae, and differences in the morphology of conical papillae surrounding the circumvallate ones in all three species. Most notably, large distinct papillae were present at the tip of the tongue in nectar-feeding species. In addition, histological images of the ventro-apical portion of the tongue displayed that it houses an encapsulated structure, but only in Lemur catta case such structure presents cartilage inside. The presence of an encapsulated structure, coupled with the shared morphological traits associated with the sublingua and the tongue tip in Varecia variegata and Eulemur macaco, point to possible feeding adaptations that facilitate non-destructive flower feeding in these two lemurids.
Keywords: Chievitz; Eulemur macaco; Lemur catta; Madagascar; Varecia variegatta; coevolution; ecology; papillae; sublingua.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Differential patterns in flower feeding by Eulemur fulvus rufus and Eulemur rubriventer in Madagascar.Am J Primatol. 1992;28(3):191-203. doi: 10.1002/ajp.1350280304. Am J Primatol. 1992. PMID: 31941214
-
The red ruffed lemur, Varecia rubra (É. Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, 1812): a comparative morphology investigation of lingual papillae and connective tissue cores.Anat Sci Int. 2023 Mar;98(2):260-272. doi: 10.1007/s12565-022-00695-2. Epub 2022 Nov 15. Anat Sci Int. 2023. PMID: 36378423
-
Organ cultures of embryonic rat tongue support tongue and gustatory papilla morphogenesis in vitro without intact sensory ganglia.J Comp Neurol. 1997 Jan 20;377(3):324-40. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9861(19970120)377:3<324::aid-cne2>3.0.co;2-4. J Comp Neurol. 1997. PMID: 8989649
-
Comparative morphology of the primate tongue.Ann Anat. 2019 May;223:19-31. doi: 10.1016/j.aanat.2019.01.008. Epub 2019 Feb 6. Ann Anat. 2019. PMID: 30738175 Review.
-
Spacing patterns on tongue surface-gustatory papilla.Int J Dev Biol. 2004;48(2-3):157-61. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.15272380. Int J Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15272380 Review.
Cited by
-
Pollinator diversity benefits natural and agricultural ecosystems, environmental health, and human welfare.Plant Divers. 2022 Feb 3;44(5):429-435. doi: 10.1016/j.pld.2022.01.005. eCollection 2022 Sep. Plant Divers. 2022. PMID: 36187551 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jordano P. Coevolution in multispecific interactions among free-living species. Evol. Educ. Outreach. 2010;3:40–46. doi: 10.1007/s12052-009-0197-1. - DOI
-
- Thompson J.N. Four central points about coevolution. Evol. Educ. Outreach. 2010;3:7–13. doi: 10.1007/s12052-009-0200-x. - DOI
-
- Dew J.L., Wright P. Frugivory and seed dispersal by four species of primates in Madagascar’s eastern rain forest. Biotropica. 1998;30:425–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7429.1998.tb00076.x. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources


