Peripheral inflammation and blood-brain barrier disruption: effects and mechanisms
- PMID: 33381913
- PMCID: PMC7804893
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.13569
Peripheral inflammation and blood-brain barrier disruption: effects and mechanisms
Abstract
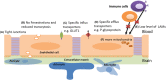
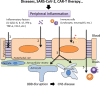
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is an important physiological barrier that separates the central nervous system (CNS) from the peripheral circulation, which contains inflammatory mediators and immune cells. The BBB regulates cellular and molecular exchange between the blood vessels and brain parenchyma. Normal functioning of the BBB is crucial for the homeostasis and proper function of the brain. It has been demonstrated that peripheral inflammation can disrupt the BBB by various pathways, resulting in different CNS diseases. Recently, clinical research also showed CNS complications following SARS-CoV-2 infection and chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy, which both lead to a cytokine storm in the circulation. Therefore, elucidation of the mechanisms underlying the BBB disruption induced by peripheral inflammation will provide an important basis for protecting the CNS in the context of exacerbated peripheral inflammatory diseases. In the present review, we first summarize the physiological properties of the BBB that makes the CNS an immune-privileged organ. We then discuss the relevance of peripheral inflammation-induced BBB disruption to various CNS diseases. Finally, we elaborate various factors and mechanisms of peripheral inflammation that disrupt the BBB.
Keywords: blood-brain barrier; central nervous system; inflammation; inflammatory factors; molecular mechanism.
© 2020 The Authors. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neuropathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019: neuroinflammation and blood brain barrier disruption are critical pathophysiological processes that contribute to the clinical symptoms of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Inflammopharmacology. 2021 Aug;29(4):939-963. doi: 10.1007/s10787-021-00806-x. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Inflammopharmacology. 2021. PMID: 33822324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipopolysaccharide-induced blood-brain barrier disruption: roles of cyclooxygenase, oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and elements of the neurovascular unit.J Neuroinflammation. 2015 Nov 25;12:223. doi: 10.1186/s12974-015-0434-1. J Neuroinflammation. 2015. PMID: 26608623 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory Regulation of CNS Barriers After Traumatic Brain Injury: A Tale Directed by Interleukin-1.Front Immunol. 2021 May 21;12:688254. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.688254. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34093593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral Infection of the Central Nervous System and Neuroinflammation Precede Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption during Japanese Encephalitis Virus Infection.J Virol. 2015 May;89(10):5602-14. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00143-15. Epub 2015 Mar 11. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25762733 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel In Vitro Mouse Model to Study Mycobacterium tuberculosis Dissemination Across Brain Vessels: A Combination Granuloma and Blood-Brain Barrier Mouse Model.Curr Protoc Immunol. 2020 Sep;130(1):e101. doi: 10.1002/cpim.101. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32716613 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
IP-10 acts early in CV-A16 infection to induce BBB destruction and promote virus entry into the CNS by increasing TNF-α expression.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 4;15:1374447. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1374447. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39559356 Free PMC article.
-
Glioblastoma cells alter brain endothelial cell homeostasis and tight junction protein expression in vitro.J Neurooncol. 2024 Nov 13. doi: 10.1007/s11060-024-04870-5. Online ahead of print. J Neurooncol. 2024. PMID: 39538037
-
In Vitro Assessment of the Neuroprotective Effects of Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) Polyphenols Against Tau Phosphorylation, Neuroinflammation, and Oxidative Stress.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 28;16(21):3667. doi: 10.3390/nu16213667. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39519499 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-brain barrier permeability increases with the differentiation of glioblastoma cells in vitro.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2024 Nov 1;21(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s12987-024-00590-0. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2024. PMID: 39487455 Free PMC article.
-
The Gut-Brain Axis and Neuroinflammation in Traumatic Brain Injury.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Oct 28. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04585-8. Online ahead of print. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39466574 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81771293/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- JCYJ20170413165705083/Science and Technology Innovation Commission of Shenzhen Municipality
- JCYJ20200109114608075/Science and Technology Innovation Commission of Shenzhen Municipality
- SGLH20180625142404672/Science and Technology Innovation Commission of Shenzhen Municipality
- 172644KYSB20200045/International collaboration project of Chinese Academy of Sciences
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous


