DNA vaccine protection against SARS-CoV-2 in rhesus macaques
- PMID: 32434945
- PMCID: PMC7243363
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abc6284
DNA vaccine protection against SARS-CoV-2 in rhesus macaques
Abstract
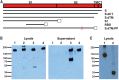
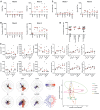
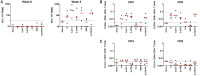
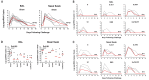
The global coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has made the development of a vaccine a top biomedical priority. In this study, we developed a series of DNA vaccine candidates expressing different forms of the SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein and evaluated them in 35 rhesus macaques. Vaccinated animals developed humoral and cellular immune responses, including neutralizing antibody titers at levels comparable to those found in convalescent humans and macaques infected with SARS-CoV-2. After vaccination, all animals were challenged with SARS-CoV-2, and the vaccine encoding the full-length S protein resulted in >3.1 and >3.7 log10 reductions in median viral loads in bronchoalveolar lavage and nasal mucosa, respectively, as compared with viral loads in sham controls. Vaccine-elicited neutralizing antibody titers correlated with protective efficacy, suggesting an immune correlate of protection. These data demonstrate vaccine protection against SARS-CoV-2 in nonhuman primates.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SARS-CoV-2 infection protects against rechallenge in rhesus macaques.Science. 2020 Aug 14;369(6505):812-817. doi: 10.1126/science.abc4776. Epub 2020 May 20. Science. 2020. PMID: 32434946 Free PMC article.
-
ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine prevents SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in rhesus macaques.Nature. 2020 Oct;586(7830):578-582. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2608-y. Epub 2020 Jul 30. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32731258 Free PMC article.
-
Single-shot Ad26 vaccine protects against SARS-CoV-2 in rhesus macaques.Nature. 2020 Oct;586(7830):583-588. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2607-z. Epub 2020 Jul 30. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32731257 Free PMC article.
-
Approaches and Challenges in SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Development.Cell Host Microbe. 2020 Sep 9;28(3):364-370. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2020.08.002. Epub 2020 Aug 10. Cell Host Microbe. 2020. PMID: 32798444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential adjuvants for the development of a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine based on experimental results from similar coronaviruses.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Sep;86:106717. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106717. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32585611 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ensemble modeling of SARS-CoV-2 immune dynamics in immunologically naïve rhesus macaques predicts that potent, early innate immune responses drive viral elimination.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 7;15:1426016. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1426016. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39575237 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and Immunogenicity Study of a Bivalent Vaccine for Combined Prophylaxis of COVID-19 and Influenza in Non-Human Primates.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Sep 26;12(10):1099. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12101099. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39460266 Free PMC article.
-
Navigating the Landscape of B Cell Mediated Immunity and Antibody Monitoring in SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Efficacy: Tools, Strategies and Clinical Trial Insights.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Sep 24;12(10):1089. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12101089. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39460256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Primary SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern infections elicit broad antibody Fc-mediated effector functions and memory B cell responses.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Aug 15;20(8):e1012453. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012453. eCollection 2024 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39146376 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of the HC009 mRNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 26;15:1416375. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1416375. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39131158 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu F., Zhao S., Yu B., Chen Y.-M., Wang W., Song Z.-G., Hu Y., Tao Z.-W., Tian J.-H., Pei Y.-Y., Yuan M.-L., Zhang Y.-L., Dai F.-H., Liu Y., Wang Q.-M., Zheng J.-J., Xu L., Holmes E. C., Zhang Y.-Z., A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 579, 265–269 (2020). 10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou P., Yang X.-L., Wang X.-G., Hu B., Zhang L., Zhang W., Si H.-R., Zhu Y., Li B., Huang C.-L., Chen H.-D., Chen J., Luo Y., Guo H., Jiang R.-D., Liu M.-Q., Chen Y., Shen X.-R., Wang X., Zheng X.-S., Zhao K., Chen Q.-J., Deng F., Liu L.-L., Yan B., Zhan F.-X., Wang Y.-Y., Xiao G.-F., Shi Z.-L., A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 579, 270–273 (2020). 10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Holshue M. L., DeBolt C., Lindquist S., Lofy K. H., Wiesman J., Bruce H., Spitters C., Ericson K., Wilkerson S., Tural A., Diaz G., Cohn A., Fox L., Patel A., Gerber S. I., Kim L., Tong S., Lu X., Lindstrom S., Pallansch M. A., Weldon W. C., Biggs H. M., Uyeki T. M., Pillai S. K.; Washington State 2019-nCoV Case Investigation Team , First Case of 2019 Novel Coronavirus in the United States. N. Engl. J. Med. 382, 929–936 (2020). 10.1056/NEJMoa2001191 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li Q., Guan X., Wu P., Wang X., Zhou L., Tong Y., Ren R., Leung K. S. M., Lau E. H. Y., Wong J. Y., Xing X., Xiang N., Wu Y., Li C., Chen Q., Li D., Liu T., Zhao J., Liu M., Tu W., Chen C., Jin L., Yang R., Wang Q., Zhou S., Wang R., Liu H., Luo Y., Liu Y., Shao G., Li H., Tao Z., Yang Y., Deng Z., Liu B., Ma Z., Zhang Y., Shi G., Lam T. T. Y., Wu J. T., Gao G. F., Cowling B. J., Yang B., Leung G. M., Feng Z., Early Transmission Dynamics in Wuhan, China, of Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 382, 1199–1207 (2020). 10.1056/NEJMoa2001316 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhu N., Zhang D., Wang W., Li X., Yang B., Song J., Zhao X., Huang B., Shi W., Lu R., Niu P., Zhan F., Ma X., Wang D., Xu W., Wu G., Gao G. F., Tan W.; China Novel Coronavirus Investigating and Research Team , A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 382, 727–733 (2020). 10.1056/NEJMoa2001017 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 AI007387/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI110700/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007151/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI139538/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI108197/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI126603/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI146779/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI121394/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI149644/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 OD024917/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI124377/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI100625/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI129797/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI132178/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI128751/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous


