Randomized trial of intermittent intraputamenal glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 30808022
- PMCID: PMC6391602
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awz023
Randomized trial of intermittent intraputamenal glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
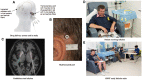
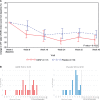
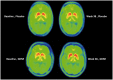
We investigated the effects of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) in Parkinson's disease, using intermittent intraputamenal convection-enhanced delivery via a skull-mounted transcutaneous port as a novel administration paradigm to potentially afford putamen-wide therapeutic delivery. This was a single-centre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Patients were 35-75 years old, had motor symptoms for 5 or more years, and presented with moderate disease severity in the OFF state [Hoehn and Yahr stage 2-3 and Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale motor score (part III) (UPDRS-III) between 25 and 45] and motor fluctuations. Drug delivery devices were implanted and putamenal volume coverage was required to exceed a predefined threshold at a test infusion prior to randomization. Six pilot stage patients (randomization 2:1) and 35 primary stage patients (randomization 1:1) received bilateral intraputamenal infusions of GDNF (120 µg per putamen) or placebo every 4 weeks for 40 weeks. Efficacy analyses were based on the intention-to-treat principle and included all patients randomized. The primary outcome was the percentage change from baseline to Week 40 in the OFF state (UPDRS-III). The primary analysis was limited to primary stage patients, while further analyses included all patients from both study stages. The mean OFF state UPDRS motor score decreased by 17.3 ± 17.6% in the active group and 11.8 ± 15.8% in the placebo group (least squares mean difference: -4.9%, 95% CI: -16.9, 7.1, P = 0.41). Secondary endpoints did not show significant differences between the groups either. A post hoc analysis found nine (43%) patients in the active group but no placebo patients with a large clinically important motor improvement (≥10 points) in the OFF state (P = 0.0008). 18F-DOPA PET imaging demonstrated a significantly increased uptake throughout the putamen only in the active group, ranging from 25% (left anterior putamen; P = 0.0009) to 100% (both posterior putamina; P < 0.0001). GDNF appeared to be well tolerated and safe, and no drug-related serious adverse events were reported. The study did not meet its primary endpoint. 18F-DOPA imaging, however, suggested that intermittent convection-enhanced delivery of GDNF produced a putamen-wide tissue engagement effect, overcoming prior delivery limitations. Potential reasons for not proving clinical benefit at 40 weeks are discussed.
Keywords: GDNF; Parkinson’s disease; convection-enhanced delivery; glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor; neurorestoration.
© The Author(s) (2019). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Figures
Comment in
-
BMP5/7 protect dopaminergic neurons in an α-synuclein mouse model of Parkinson's disease.Brain. 2021 Mar 3;144(2):e15. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa368. Brain. 2021. PMID: 33253359 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Growth differentiation factor 5 exerts neuroprotection in an α-synuclein rat model of Parkinson's disease.Brain. 2021 Mar 3;144(2):e14. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa367. Brain. 2021. PMID: 33253375 No abstract available.
-
Reply: Growth differentiation factor 5 exerts neuroprotection in an α-synuclein rat model of Parkinson's disease and BMP5/7 protect dopaminergic neurons in an α-synuclein mouse model of Parkinson's disease.Brain. 2021 Mar 3;144(2):e16. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa369. Brain. 2021. PMID: 33257974 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Extended Treatment with Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Parkinson's Disease.J Parkinsons Dis. 2019;9(2):301-313. doi: 10.3233/JPD-191576. J Parkinsons Dis. 2019. PMID: 30829619 Free PMC article.
-
Randomized controlled trial of intraputamenal glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor infusion in Parkinson disease.Ann Neurol. 2006 Mar;59(3):459-66. doi: 10.1002/ana.20737. Ann Neurol. 2006. PMID: 16429411 Clinical Trial.
-
Unilateral intraputamenal glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in patients with Parkinson disease: response to 1 year of treatment and 1 year of withdrawal.J Neurosurg. 2007 Apr;106(4):614-20. doi: 10.3171/jns.2007.106.4.614. J Neurosurg. 2007. PMID: 17432712 Clinical Trial.
-
GDNF delivery for Parkinson's disease.Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2007;97(Pt 2):135-54. doi: 10.1007/978-3-211-33081-4_16. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2007. PMID: 17691299 Review.
-
Unraveling the role of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in the treatment of Parkinson's disease.Neurol Sci. 2024 Apr;45(4):1409-1418. doi: 10.1007/s10072-023-07253-2. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Neurol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38082050 Review.
Cited by
-
Growth Factors and Their Application in the Therapy of Hereditary Neurodegenerative Diseases.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 20;12(8):1906. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081906. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent progress in the applications of presynaptic dopaminergic positron emission tomography imaging in parkinsonism.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Jan 1;20(1):93-106. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.391180. Epub 2023 Dec 21. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 38767479 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Prodromal Parkinson Disease: We May Be Able to But Should We?Neurology. 2024 Jun 11;102(11):e209394. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000209394. Epub 2024 May 17. Neurology. 2024. PMID: 38759130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic modifiers of synucleinopathies-lessons from experimental models.Oxf Open Neurosci. 2023 Mar 9;2:kvad001. doi: 10.1093/oons/kvad001. eCollection 2023. Oxf Open Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38596238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dopaminergic Cell Replacement for Parkinson's Disease: Addressing the Intracranial Delivery Hurdle.J Parkinsons Dis. 2024;14(3):415-435. doi: 10.3233/JPD-230328. J Parkinsons Dis. 2024. PMID: 38457149 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Airaksinen MS, Saarma M. The GDNF family: signalling, biological functions and therapeutic value. Nat Rev Neurosci 2002; 3: 383–94. - PubMed
-
- Allen SJ, Watson JJ, Shoemark DK, Barua NU, Patel NK. GDNF, NGF and BDNF as therapeutic options for neurodegeneration. Pharmacol Ther 2013; 138: 155–75. - PubMed
-
- Aoi M, Date I, Tomita S, Ohmoto T. The effect of intrastriatal single injection of GDNF on the nigrostriatal dopaminergic system in hemiparkinsonian rats: behavioral and histological studies using two different dosages. Neurosci Res 2000; 36: 319–25. - PubMed
-
- Barua NU, Hopkins K, Woolley M, O’Sullivan S, Harrison R, Edwards RJ, et al.A novel implantable catheter system with transcutaneous port for intermittent convection-enhanced delivery of carboplatin for recurrent glioblastoma. Drug Deliv 2016; 23: 167–73. - PubMed
-
- Barua NU, Woolley M, Bienemann AS, Johnson DE, Lewis O, Wyatt MJ, et al.Intermittent convection-enhanced delivery to the brain through a novel transcutaneous bone-anchored port. J Neurosci Methods 2013; 214: 223–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical


