Low dialysate sodium levels for chronic haemodialysis
- PMID: 30646428
- PMCID: PMC6353061
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011204.pub2
Low dialysate sodium levels for chronic haemodialysis
Update in
-
Low dialysate sodium levels for chronic haemodialysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 5;11(11):CD011204. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011204.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39498822
Abstract
Background: Cardiovascular (CV) disease is the leading cause of death in dialysis patients, and strongly associated with fluid overload and hypertension. It is plausible that low dialysate [Na+] may decrease total body sodium content, thereby reducing fluid overload and hypertension, and ultimately reducing CV morbidity and mortality.
Objectives: This review evaluated harms and benefits of using a low (< 138 mM) dialysate [Na+] for maintenance haemodialysis (HD) patients.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Kidney and Transplant Register of Studies up to 7 August 2018 through contact with the Information Specialist using search terms relevant to this review. Studies in the Register are identified through searches of CENTRAL, MEDLINE, and EMBASE, conference proceedings, the International Clinical Trials Register (ICTRP) Search Portal and ClinicalTrials.gov.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs), both parallel and cross-over, of low (< 138 mM) versus neutral (138 to 140 mM) or high (> 140 mM) dialysate [Na+] for maintenance HD patients were included.
Data collection and analysis: Two investigators independently screened studies for inclusion and extracted data. Statistical analyses were performed using random effects models, and results expressed as risk ratios (RR) for dichotomous outcomes, and mean differences (MD) or standardised MD (SMD) for continuous outcomes, with 95% confidence intervals (CI). Confidence in the evidence was assessed using GRADE.
Main results: We included 12 studies randomising 310 patients, with data available for 266 patients after dropout. All but one study evaluated a fixed concentration of low dialysate [Na+], and one profiled dialysate [Na+]. Three studies were parallel group, and the remaining nine cross-over. Of the latter, only two used a washout between intervention and control periods. Most studies were short-term with a median (interquartile range) follow-up of 3 (3, 8.5) weeks. Two were of a single HD session, and two of a single week's HD. Half of the studies were conducted prior to 2000, and five reported use of obsolete HD practices. Risks of bias in the included studies were often high or unclear, lowering confidence in the results.Compared to neutral or high dialysate [Na+], low dialysate [Na+] had the following effects on "efficacy" endpoints: reduced interdialytic weight gain (10 studies: MD -0.35 kg, 95% CI -0.18 to -0.51; high certainty evidence); probably reduced predialysis mean arterial blood pressure (BP) (4 studies: MD -3.58 mmHg, 95% CI -5.46 to -1.69; moderate certainty evidence); probably reduced postdialysis mean arterial BP (MAP) (4 studies: MD -3.26 mmHg, 95% CI -1.70 to -4.82; moderate certainty evidence); probably reduced predialysis serum [Na+] (7 studies: MD -1.69 mM, 95% CI -2.36 to -1.02; moderate certainty evidence); may have reduced antihypertensive medication (2 studies: SMD -0.67 SD, 95% CI -1.07 to -0.28; low certainty evidence). Compared to neutral or high dialysate [Na+], low dialysate [Na+] had the following effects on "safety" endpoints: probably increased intradialytic hypotension events (9 studies: RR 1.56, 95% 1.17 to 2.07; moderate certainty evidence); probably increased intradialytic cramps (6 studies: RR 1.77, 95% 1.15 to 2.73; moderate certainty evidence).Compared to neutral or high dialysate [Na+], low dialysate [Na+] may make little or no difference to: intradialytic BP (2 studies: MD for systolic BP -3.99 mmHg, 95% CI -17.96 to 9.99; diastolic BP 1.33 mmHg, 95% CI -6.29 to 8.95; low certainty evidence); interdialytic BP (2 studies:, MD for systolic BP 0.17 mmHg, 95% CI -5.42 to 5.08; diastolic BP -2.00 mmHg, 95% CI -4.84 to 0.84; low certainty evidence); dietary salt intake (2 studies: MD -0.21g/d, 95% CI -0.48 to 0.06; low certainty evidence).Due to very low quality of evidence, it is uncertain whether low dialysate [Na+] changed extracellular fluid status, venous tone, arterial vascular resistance, left ventricular mass or volumes, thirst or fatigue. Studies did not examine cardiovascular or all-cause mortality, cardiovascular events, or hospitalisation.
Authors' conclusions: It is likely that low dialysate [Na+] reduces intradialytic weight gain and BP, which are effects directionally associated with improved outcomes. However, the intervention probably also increases intradialytic hypotension and reduces serum [Na+], effects that are associated with increased mortality risk. The effect of the intervention on overall patient health and well-being is unknown. Further evidence is needed in the form of longer-term studies in contemporary settings, evaluating end-organ effects in small-scale mechanistic studies using optimal methods, and clinical outcomes in large-scale multicentre RCTs.
Conflict of interest statement
JD: None known
AV: None known
MM: is currently employed by Baxter Healthcare as the Director of Medical Affairs Asia‐Pacific, Renal Therapeutic Area
Figures
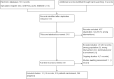

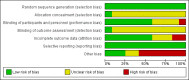
Similar articles
-
Low dialysate sodium levels for chronic haemodialysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 5;11(11):CD011204. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011204.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39498822
-
Calcium channel blockers for people with chronic kidney disease requiring dialysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 1;10(10):CD011064. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011064.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33000470 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of low dialysate sodium levels for patients with maintenance haemodialysis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Surg. 2020 Jul;79:332-339. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.05.027. Epub 2020 May 21. Int J Surg. 2020. PMID: 32447003
-
Home versus in-centre haemodialysis for people with kidney failure.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Apr 8;4(4):CD009535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38588450 Review.
-
Antihypertensive treatment for kidney transplant recipients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Jul 31;7(7):CD003598. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003598.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39082471 Review.
Cited by
-
Low dialysate sodium levels for chronic haemodialysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 5;11(11):CD011204. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011204.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39498822
-
The effect of different dialysate sodium concentrations on ambulatory blood pressure in hemodialysis patients: a prospective interventional study.Clin Kidney J. 2024 Feb 21;17(8):sfae041. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfae041. eCollection 2024 Aug. Clin Kidney J. 2024. PMID: 39135940 Free PMC article.
-
Modification of Dialysate Na+ Concentration but not Ultrafiltration or Dialysis Treatment Time Affects Tissue Na+ Deposition in Patients on Hemodialysis.Kidney Int Rep. 2024 Feb 9;9(5):1310-1320. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2024.02.002. eCollection 2024 May. Kidney Int Rep. 2024. PMID: 38707813 Free PMC article.
-
Interdialytic weight gain and low dialysate sodium concentration in patients on chronic hemodialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2024 Jul;56(7):2313-2323. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-03972-3. Epub 2024 Mar 6. Int Urol Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38446246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dialysate Sodium Lowering in Maintenance Hemodialysis: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2024 Jun 1;19(6):712-722. doi: 10.2215/CJN.0000000000000431. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38349776 Clinical Trial.
References
References to studies included in this review
Akdag 2015 {published data only}
Beduschi 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Beduschi GC, Telini LS, Caramori JC, Martin LC, Barretti P. Effect of dialysate sodium reduction on body water volume, blood pressure, and inflammatory markers in hemodialysis patients‐‐a prospective randomized controlled study. Renal Failure 2013;35(5):742‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Boquin 1977 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Boquin E, Parnell S, Grondin G, Wollard C, Leonard D, Michaels R, et al. Crossover study of the effects of different dialysate sodium concentrations in large surface area, short‐term dialysis. Proceedings of the Clinical Dialysis & Transplant Forum 1977;7:48‐52. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chambers 2002 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Chambers G, Hoenich NA. Is stepwise profiling of ultrafiltration and sodium beneficial to the elderly patient receiving haemodialysis therapy? [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2002;13(September, Program & Abstracts):580a. [CENTRAL: CN‐00444738]
Daugirdas 1985 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Daugirdas JT, Al‐Kudsi RR, Ing TS, Norusis MJ. A double‐blind evaluation of sodium gradient hemodialysis. American Journal of Nephrology 1985;5(3):163‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Henrich 1982 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Henrich WL, Woodard TD, McPhaul JJ Jr. The chronic efficacy and safety of high sodium dialysate: double‐blind, crossover study. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 1982;2(3):349‐53. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Liu 2016 {published data only}
-
- Liu J, Sun F, Ma LJ, Shen Y, Mei X, Zhou YL. Increasing dialysis sodium removal on arterial stiffness and left ventricular hypertrophy in hemodialysis patients. Journal of Renal Nutrition 2016;26(1):38‐44. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
MATCH‐NA 2015 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Inrig JK, Molina C, D'Silva K, Kim C, Buren P, Allen JD, et al. Effect of low versus high dialysate sodium concentration on blood pressure and endothelial‐derived vasoregulators during hemodialysis: a randomized crossover study. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2015;65(3):464‐73. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ogden 1978 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Ogden DA. A double blind crossover comparison of high and low sodium dialysis. Proceedings of the Clinical Dialysis & Transplant Forum 1978;8:157‐65. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Ogden DA, Cohen IM. High and low sodium hemodialysis ‐ a twelve week double blind crossover comparison [abstract]. Kidney International 1979;16(6):895.
Quereda 1988 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Quereda C, Orofino L, Marcen R, Lamas S, Sabater J, Ortuno J. Contribution of membrane and dialysate to the incidence of hemodialysis (HD)‐induced symptomatic hypotension (SH) [abstract]. 10th International Congress of Nephrology; 1987 Jul 26‐31; London, UK. 1987:167.
-
- Quereda C, Orofino L, Marcen R, Sabater J, Matesanz R, Ortuno J. Influence of dialysate and membrane biocompatibility on hemodynamic stability in hemodialysis. International Journal of Artificial Organs 1988;11(4):259‐64. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Quereda C, Orofino L, Marcen R, Sabater J, Ortuno J. Combined use of low temperature and high sodium dialysate improves symptomatic hypotension (SH) in hemodialysis (HD) [abstract]. 24th Annual Congress. EDTA‐ERA; 1987 Oct 25‐29; West Berlin, Germany. 1987:132.
Suckling 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Suckling RJ, Swift PA, He FJ, Markandu ND, Macgregor GA. Altering plasma sodium concentration rapidly changes blood pressure during haemodialysis. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2013;28(8):2181‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Van Kuijk 1996 {published data only}
-
- Kuijk WH, Wirtz JJ, Grave W, Heer F, Menheere PP, Hooff JP, et al. Vascular reactivity during combined ultrafiltration‐haemodialysis: influence of dialysate sodium. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 1996;11(2):323‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Acchiardo 1975 {published data only}
-
- Acchiardo SR, Skoutaski VA, Hatch FE. Management of muscle cramps in hemodialysis patients. Controlled prospective study. Proceedings of the Clinical Dialysis & Transplant Forum 1975;5:6‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
AIMS 2011 {published data only}
-
- Locatelli F, Stefoni S, Petitclerc T, Coli L. HFR‐Acquilibrium International Multicentric Study (AIMS): focus on intradialytic cardiovascular stability [abstract no: LB‐PO3148]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2011;22(Abstracts):3B.
-
- Locatelli F, Stefoni S, Petitclerc T, Coli L, Filippo S, Andrulli S, et al. Effect of a plasma sodium biofeedback system applied to HFR on the intradialytic cardiovascular stability. Results from a randomized controlled study. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2012;27(10):3935‐42. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Bachtiar 2005 {published data only}
-
- Bachtiar NS, Khairuddin K, Hoenich N, Hussain R, Tan SY. Management of hypertension in patients on chronic haemodialysis: modulation of dialysate sodium compared to adjustment of dry weight as determined by bioimpedance analysis [abstract no: W‐PO40028]. Nephrology 2005;10(Suppl):A286‐7.
Barre 1988 {published data only}
-
- Barre PE, Brunelle G, Gascon‐Barr M. A randomized double blind trial of dialysate sodiums of 145 mEq/L, 150 mEq/L, and 155 mEq/L. ASAIO Transactions 1988;34(3):338‐41. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
CARNIDIAL 2012 {published data only}
-
- Mercadal L, Coudert M, Vassault A, Pieroni L, Debure A, Ouziala M, et al. L‐carnitine treatment in incident hemodialysis patients: the multicenter, randomized, double‐blinded, placebo‐controlled CARNIDIAL trial. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology: CJASN 2012;7(11):1836‐42. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Coli 2000 {published data only}
-
- Coli L, Dalmastri V, Pascalis A, Isola E, Magelli C, Magnani G, et al. Modulating dialysate sodium and ultrafiltration: various profiles and their clinical effectiveness [abstract]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2000;15(9):219. [CENTRAL: CN‐00460570]
De Nicola 2000 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Nicola L, Bellizzi V, Minutolo R, Cioffi M, Giannattasio P, Terracciano V, et al. Effect of dialysate sodium concentration on interdialytic increase of potassium. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2000;11(12):2337‐43. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
de Vries 1990 {published data only}
-
- Vries PM, Kouw PM, Olthof CG, Solf A, Schuenemann B, Oe LP, et al. The influence of dialysate sodium and variable ultrafiltration on fluid balance during hemodialysis. ASAIO Transactions 1990;36(4):821‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ebrahimi 2017 {published data only}
-
- Ebrahimi H, Safavi M, Saeidi MH, Emamian MH. Effects of sodium concentration and dialysate temperature changes on blood pressure in hemodialysis patients: a randomized, triple‐blind crossover clinical trial. Therapeutic Apheresis & Dialysis 2017;21(2):117‐25. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ekart 2015 {published data only}
-
- Ekart R, Volgemut Z, Bevc S, Stropnik‐Galuf T, Hojs R. Effect of different dialysate sodium concentration on blood pressure in hemodialysis patients: a randomized study [abstract no: PP.11.03]. Journal of Hypertension 2015;33(Suppl 1):e224‐5. [EMBASE: 71935304]
Enia 1998 {published data only}
-
- Enia G, Panuccio V, Parlongo S, Crucitti S, Biondo A, Pustorino D, et al. Hypotensive effect of ultra‐low sodium dialysate in CAPD patients: a double‐blind, randomized, crossover study [abstract no: T271]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1998;9(Program & Abstracts):282A. [CENTRAL: CN‐00445236]
Ficociello 2012 {published data only}
-
- Ficociello LH, Usvyat L, Ginsberg N, Moore S, Pacelli L, Taylor P, et al. Alignment of dialysate sodium to serum sodium in dialysis patients with serum sodium <137 mmol/L [abstract]. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2012;59(4):A35. [EMBASE: 71074694]
HEMATOL 2013 {published data only}
-
- Du Cheyron D, Terzi N, Seguin A, Valette X, Prevost F, Ramakers M, et al. Use of online blood volume and blood temperature monitoring during haemodialysis in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury: a single‐centre randomized controlled trial. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2013;28(2):430‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Henrich 1983 {published data only}
-
- Henrich WL, Woodard TD, Meyer BD, Chappell TR, Rubin LJ. High sodium bicarbonate and acetate hemodialysis: double‐blind crossover comparison of hemodynamic and ventilatory effects. Kidney International 1983;24(2):240‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lambie 2005 {published data only}
-
- Lambie SH, McIntyre CW. Use of an on‐line conductivity monitoring to study individually set dialysate sodium concentrations: a randomised controlled study [abstract no: SU‐FC253]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2003;14(Nov):55A‐6A.
-
- Lambie SH, Taal MW, Fluck RJ, McIntyre CW. Online conductivity monitoring: validation and usefulness in a clinical trial of reduced dialysate conductivity. ASAIO Journal 2005;51(1):70‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Levin 1996 {published data only}
-
- Levin A, Carlisle EF, Ansell J, Goldstein MB. Double blind crossover trial (DBCT) of ramped hypertonic sodium dialysis (RHTD): beneficial effects for specific clinical problems [abstract]. Kidney International 1990;37(1):306. [CENTRAL: CN‐00626025]
-
- Levin A, Goldstein MB. The benefits and side effects of ramped hypertonic sodium dialysis. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1996;7(2):242‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Macon 1995 {published data only}
-
- Macon EJ, Campbell OC. A randomized comparison between sodium modeling and slow dialysis in the prevention of the dialysis disequilibrium syndrome (DES) [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1995;6(3):547. [CENTRAL: CN‐00484936]
Mahiout 1987 {published data only}
-
- Mahiout A, Ludat K, Gahl GM, Schultze G. Effect of sodium dialysate concentration on beta2 microglobulin during haemodialysis [abstract]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 1987;2(5):448. [CENTRAL: CN‐00260334]
Meira 2010 {published data only}
-
- Meira FS, Figueiredo AE, Zemiarcki J, Pacheco J, Poli‐de‐Figueiredo CE, d'Avila DO. Two variable sodium profiles and adverse effects during hemodialysis: a randomized crossover study. Therapeutic Apheresis & Dialysis 2010;14(3):328‐33. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Moret 2006 {published data only}
-
- Moret K, Aalten J, Wall Blake W, Gerlag P, Beerenhout C, Sande F, et al. The effect of sodium profiling and feedback technologies on plasma conductivity and ionic mass balance: a study in hypotension‐prone dialysis patients. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2006;21(1):138‐44. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
NCT01015313 {unpublished data only}
-
- Kotanko P, Levin N. Effects of intensified sodium management in hemodialysis patients. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01015313 (first received 18 November 2009).
NCT01168947 {unpublished data only}
-
- Kotanko P. Effect of sodium concentration of priming and rinsing fluids on weight gain. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01168947 (first received 23 July 2010).
NCT01766882 {unpublished data only}
-
- Saran R. Volume, sodium and blood pressure management in HD (VSBP). www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01766882 (first received 11 January 2013).
Oliver 2001 {published data only}
-
- Oliver A, Wright M, Matson A, King N, Woodrow G, Dye L, et al. The effect of low sodium dialysis on fluid consumption and thirst scores in haemodialysis patients with high and low baseline interdialytic weight gain [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2001;12(Program & Abstracts):273A. [CENTRAL: CN‐00447029]
Oliver 2001a {published data only}
-
- Oliver MJ, Edwards LJ, Churchill DN. Impact of sodium and ultrafiltration profiling on hemodialysis‐related symptoms. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2001;12(1):151‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Oliver MJ, Edwards LJ, Churchill DN. Randomized study of the effect of sodium profiled dialysis with blood volume monitoring on dialysis related symptoms [abstract no:A0989]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1999;10(Program & Abstracts):194A.
Robberechts 2013 {published data only}
-
- Robberechts T, Allamani M, Marmitte N, Ingelgem D, Niepen P. The effect of hyponatremic versus isonatremic dialysate in patients with intradialytic hypertension [abstract]. Acta Clinica Belgica 2013;68(6):460. [EMBASE: 71520514]
-
- Robberechts T, Allamani M, Niepen P. The effect of hyponatremic versus isonatremic dialysate in patients with intradialytic hypertension [abstract]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2015;30(Suppl 3):iii241‐2. [EMBASE: 72206929]
Sandy 1996 {published data only}
-
- Sandy D, Kozlowski L, Bednarz D, Heyka R, Paganini E. A stratified prospective randomized cross‐over comparison of variable (VNA) vs fixed (FNA) sodium dialysate during ICU ARF IHD therapy [abstract no: A1379]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1996;7(9):1525.
Sang 1997 {published data only}
-
- Sang GL, Kovithavongs C, Ulan R, Kjellstrand CM. Sodium ramping in hemodialysis: a study of beneficial and adverse effects. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 1997;29(5):669‐77. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Selby 2007 {published data only}
-
- Selby N, Taal M, McIntyre C. Reduction of dialysate sodium concentration using conventional HD or prescribed end dialysis plasma conductivity (Diacontrol©) [abstract no: SP678]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2006;21(Suppl 4):iv244.
-
- Selby NM, Taal MW, McIntyre CW. Comparison of progressive conductivity reduction with Diacontrol and standard dialysis. ASAIO Journal 2007;53(2):194‐200. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Selby NM, Taal MW, McIntyre CW. Reduction of dialysate sodium concentration using conventional HD or prescribed end plasma conductivity (Diacontrol©) [abstract no: SA‐PO1140]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2006;17(Abstracts):813A.
References to studies awaiting assessment
ISRCTN71215609 {published data only}
-
- ISRCTN71215609. Study into achievement of isonatric haemodialysis by individual tailoring of dialysate sodium according to ionic mass balance derived from online conductance monitoring. www.controlled‐trials.com/ISRCTN71215609 (first received 30 September 2005).
References to ongoing studies
NCT00724633 {unpublished data only}
-
- Suri R, Lindsay R, Rehman F. Effect of lowering the dialysate sodium on blood pressure in hemodialysis patients. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00724633 (first received 29 July 2008).
NCT02145260 {unpublished data only}
-
- McCausland F, Waikar S. Trial of dialysate sodium in chronic hospitalized hemodialysis patients. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02145260 (first received 22 May 2014).
RESOLVE 2016 {unpublished data only}
-
- Jardine M. Randomised evaluation of sodium dialysate levels on vascular events (RESOLVE). www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02823821 (first received 6 July 2016).
SoLID 2013 {published data only}
-
- Dunlop JL, Vandal AC, Zoysa JR, Gabriel RS, Haloob IA, Hood CJ, et al. Rationale and design of the Sodium Lowering In Dialysate (SoLID) trial: a randomised controlled trial of low versus standard dialysate sodium concentration during hemodialysis for regression of left ventricular mass. BMC Nephrology 2013;14:149. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dunlop JL, Vandal AC, Zoysa JR, Gabriel RS, Haloob IA, Hood CJ, et al. Update: Rationale and design of the Sodium Lowering In Dialysate (SoLID) trial: a randomised controlled trial of low versus standard dialysate sodium concentration during hemodialysis for regression of left ventricular mass. BMC Nephrology 2015;16:120. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Marshall MR, Vandal AC, Dunlop JL, Zoysa JR, Haloob IA, Hood CJ, et al. The sodium lowering in dialysate (SoLID) trial: a randomized controlled trial of low versus standard dialysate sodium concentration (DNa) during hemodialysis (HD) for regression of left ventricular (LV) mass [abstract no: HI‐OR04]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2016;27(Abstract Suppl):1B.
Additional references
Agarwal 2003
-
- Argarwal R. Systolic hypertension in hemodialysis patients.[Erratum appears in Semin Dial. 2003 Jul‐Aug;16(4):334]. Seminars in Dialysis 2003;16(3):208‐13. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Altman 2003
Amro 2014
-
- Amro A, Waldum B, Dammen T, Miaskowski C, Os I. Symptom clusters in patients on dialysis and their association with quality‐of‐life outcomes. Journal of Renal Care 2014;40(1):23‐33. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Basile 2015
-
- Basile C, Pisano A, Lisi P, Rossi L, Lomonte C, Bolignano D. High versus low dialysate sodium concentration in chronic haemodialysis patients: a systematic review of 23 studies. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2015;31(4):1‐16. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Basri 2002
-
- Basri NA, Shaheen FA. Visual loss in uremic patients on dialysis: a case report and review of literature. Saudi Journal of Kidney Disease & Transplantation 2002;13(1):45‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Boon 2004
-
- Boon D, Montfrans GA, Koopman MG, Krediet RT, Bos WJ. Blood pressure response to uncomplicated hemodialysis: the importance of changes in stroke volume. Nephron 2004;96(3):c82‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bos 2000
-
- Bos WJ, Bruin S, Olden RW, Keur I, Wesseling KH, Westerhof N, et al. Cardiac and hemodynamic effects of hemodialysis and ultrafiltration. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2000;35(5):819‐26. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Braunwald 1965
-
- Braunwald E, Plauth WH Jr, Morrow AG. A method for the detection and quantification of impaired sodium excretion. Results of an oral sodium tolerance test in normal subjects and in patients with heart disease. Circulation 1965;32:223‐31. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Burton 2009
Cabrera 2015
Caplin 2011
-
- Caplin B, Kumar S, Davenport A. Patients' perspective of haemodialysis‐associated symptoms. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2011;26(8):2656‐63. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chang 2011
Charra 2004
-
- Charra B, Chazot C, Jean G, Hurot JM, Terrat JC, Vanel T, et al. Role of sodium in dialysis. Minerva Urologica e Nefrologica 2004;56(3):205‐13. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chertow 2010
Cybulsky 1985
-
- Cybulsky AV, Matni A, Hollomby DJ. Effects of high sodium dialysate during maintenance hemodialysis. Nephron 1985;41(1):57‐61. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Davenport 2008
-
- Davenport A. Potential adverse effects of replacing high volume hemofiltration exchanges on electrolyte balance and acid‐base status using the current commercially available replacement solutions in patients with acute renal failure. International Journal of Artificial Organs 2008;31(1):3‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Davies 2016 [pers comm]
-
- Davies E. (Kidney Research UK). re: Future priorities for renal research: survey report: a report on the findings from a patient survey exercise assessing kidney patients' views on research priorities. Letter to: E Davies (Kidney Research UK) 2016.
Descombes 2014
-
- Descombes E, Fellay B, Riedo E, Hemett OM, Magnin, J‐L, Fellay G. Comparison of sodium conductivity prescription and dialysate sodium concentration with three different hemodialysis (HD) monitors: not all the monitors are equal [abstract no: P71]. Swiss Med Weekly 2014;144(Suppl 208):31S. [EMBASE: 71713933]
Dheenan 2001
-
- Dheenan S, Henrich WL. Preventing dialysis hypotension: a comparison of usual protective maneuvers. Kidney International 2001;59(3):1175‐81. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Dubin 2011
Dunlop 2012
-
- Marshall MR, Dunlop JL. Are dialysate sodium levels too high?. Seminars in Dialysis 2012;25(3):277‐83. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ekbal 2016
-
- Ekbal NJ, Consalus A, Persaud J, Davenport A. Reliability of delivered dialysate sodium concentration. Hemodialysis International 2016;20(Suppl 1):S2‐6. [EMBASE: 612346884] - PubMed
Eknoyan 2002
-
- Eknoyan G, Beck GJ, Cheung AK, Daugirdas JT, Greene T, Kusek JW, et al. Effect of dialysis dose and membrane flux in maintenance hemodialysis. New England Journal of Medicine 2002;347(25):2010‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Eldehni 2012
-
- Eldehni MT, Mcintyre CW. Are there neurological consequences of recurrent intradialytic hypotension?. Seminars in Dialysis 2012;25(3):253‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Eldehni 2015
Fischbach 1988
-
- Fischbach M, Tarral E, Geisert J. Sequential hypertonic haemodialysis in children. Pediatric Nephrology 1988;2(4):442‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Flanigan 1998
-
- Flanigan MJ. Sodium flux and dialysate sodium in hemodialysis. Seminars in Dialysis 1998;11(5):298‐304. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1525-139X.1998.tb00372.x] - DOI
Flanigan 2008
-
- Flanigan MJ. How should dialysis fluid be individualized for the chronic hemodialysis patient? Sodium. Seminars in Dialysis 2008;21(3):226‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Flythe 2015
Gotch 1990
-
- Gotch F, Evans M, Metzner K, Westphal D, Polaschegg H. An on‐line monitor of dialyzer Na and K flux in hemodialysis. ASAIO Transactions 1990;36(3):M359‐61. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
GRADE 2008
Grassi 2002
-
- Grassi G, Dell'Oro R, Seravalle G, Foglia G, Trevano FQ, Mancia G. Short‐ and long‐term neuroadrenergic effects of moderate dietary sodium restriction in essential hypertension. Circulation 2002;106(15):1957‐61. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gul 2016
-
- Gul A, Miskulin DC, Paine SS, Narsipur SS, Arbeit LA, Harford AM, et al. Comparison of prescribed and measured dialysate sodium: a quality improvement project. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2016;67(3):439‐45. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hecking 2011
-
- Hecking M, Kainz A, Horl WH, Herkner H, Sunder‐Plassmann G. Sodium setpoint and sodium gradient: influence on plasma sodium change and weight gain. American Journal of Nephrology 2011;33(1):39‐48. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hecking 2012
Hecking 2015
-
- Hecking M, Rayner H, Port FK. More evidence needed before lower dialysate sodium concentrations can be recommended. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2015;65(3):519‐20. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hecking 2017
-
- Hecking M, Wong MM, Port FK, Robinson BM, McCullough KP. Regional differences in the associations between prescribed dialysate sodium concentration and interdialytic weight gain in the dialysis outcomes and practice patterns study. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2017;70(3):450‐1. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Heerspink 2009
-
- Heerspink HJ, Ninomiya T, Zoungas S, Zeeuw D, Grobbee DE, Jardine MJ, et al. Effect of lowering blood pressure on cardiovascular events and mortality in patients on dialysis: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet 2009;373(9668):1009‐15. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JP, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hollenberg 1972
-
- Hollenberg NK, Adams DF, Solomon HS, Abrams HL, Merrill JP. What mediates the renal vascular response to a salt load in normal man?. Journal of Applied Physiology 1972;33(4):491‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hollenberg 1980
-
- Hollenberg NK. Set point for sodium homeostasis: surfeit, deficit, and their implications. Kidney International 1980;17(4):423‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hoorn 2013
-
- Hoorn EJ, Zietse R. Hyponatremia and mortality: moving beyond associations. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2013;62(1):139‐49. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
K/DOQI Workgroup 2005
-
- K/DOQI Workgroup. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for cardiovascular disease in dialysis patients. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2005;45(4 Suppl 3):S1‐153. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kalantar‐Zadeh 2009
Keen 2007
-
- Keen ML, Gotch FA. The association of the sodium "setpoint" to interdialytic weight gain and blood pressure in hemodialysis patients. International Journal of Artificial Organs 2007;30(11):971‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kimura 1984
-
- Kimura G, Gotch FA. Serum sodium concentration and body fluid distribution during interdialysis: importance of sodium to fluid intake ratio in hemodialysis patients. International Journal of Artificial Organs 1984;7(6):331‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kotanko 2015
Kyriazis 2002
-
- Kyriazis J, Glotsos J, Bilirakis L, Smirnioudis N, Tripolitou M, Georgiakodis F, et al. Dialysate calcium profiling during hemodialysis: use and clinical implication. Kidney International 2002;61(1):276‐87. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Locatelli 1984
-
- Locatelli F, Ponti R, Pedrini L, Costanzo R, Filippo S, Marai P, et al. Sodium kinetics across dialysis membranes. Nephron 1984;38(3):174‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lomonte 2011
-
- Lomonte C, Basile C. Do not forget to individualize dialysate sodium prescription. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2011;26(4):1126‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
London 2001
-
- London GM, Pannier B, Guerin AP, Blacher J, Marchais SJ, Darne B, et al. Alterations of left ventricular hypertrophy in and survival of patients receiving hemodialysis: follow‐up of an interventional study. Journal of American Society of Nephrology 2001;12(12):2759‐67. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mandai 2013
Manlucu 2010
-
- Manlucu J, Gallo K, Heidenheim PA, Lindsay RM. Lowering postdialysis plasma sodium (conductivity) to increase sodium removal in volume‐expanded hemodialysis patients: a pilot study using a biofeedback software system. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2010;56(1):69‐76. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Marshall 2012
-
- Marshall MR, Dunlop JL. Are dialysate sodium levels too high?. Seminars in Dialysis 2012;25(3):277‐83. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Marshall 2017
-
- Marshall MR, Chan CT. The evolution of home HD ‐ meeting modern patient needs. Contributions to Nephrology 2017;189:36‐45. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Matsuoka 1990
-
- Matsuoka H, Kimura G, Sanai T, Kojima S, Kawano Y, Imanishi M, et al. Normalization of increased sodium sensitivity by maintenance hemodialysis. American Journal of Hypertension 1990;3(8 Pt 1):628‐31. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mc Causland 2012
McIntyre 2008
-
- McIntyre CW, Burton JO, Selby NM, Leccisotti L, Korsheed S, Baker CS, et al. Hemodialysis‐induced cardiac dysfunction is associated with an acute reduction in global and segmental myocardial blood flow. Clinical Journal of The American Society of Nephrology: CJASN 2008;3(1):19‐26. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
McIntyre 2011
McIntyre 2014
-
- McIntyre CW, Odudu A. Hemodialysis‐associated cardiomyopathy: a newly defined disease entity. Seminars in Dialysis 2014;27(2):87‐97. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Movilli 2013
-
- Movilli E, Camerini C, Gaggia P, Zubani R, Feller P, Poiatti P, et al. Role of dialysis sodium gradient on intradialytic hypertension: an observational study. American Journal of Nephrology 2013;38(5):413‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Munoz Mendoza 2011
-
- Munoz Mendoza J, Bayes LY, Sun S, Doss S, Schiller B. Effect of lowering dialysate sodium concentration on interdialytic weight gain and blood pressure in patients undergoing thrice‐weekly in‐center nocturnal hemodialysis: a quality improvement study. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2011;58(6):956‐63. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Oberleithner 2007
Oliver 2001b
-
- Oliver MJ, Edwards LJ, Churchill DN. Impact of sodium and ultrafiltration profiling on hemodialysis‐related symptoms. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2001;12(1):151‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ozkahya 2002
-
- Ozkahya M, Toz H, Ozerkan F, Duman S, Ok E, Basci A, Mees EJ. Impact of volume control on left ventricular hypertrophy in dialysis patients. Journal of Nephrology 2002;15(6):655‐60. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Peixoto 2010
-
- Peixoto AJ, Gowda N, Parikh CR, Santos SF. Long‐term stability of serum sodium in hemodialysis patients. Blood Purification 2010;29(3):264‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Peixoto 2011
-
- Peixoto AJ, Santos SF. How should the predialysis plasma sodium level be interpreted in hemodialysis patients?. Seminars in Dialysis 2011;24(4):409‐11. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Penne 2011
-
- Penne EL, Sergeyeva O. Sodium gradient: a tool to individualize dialysate sodium prescription in chronic hemodialysis patients?. Blood Purification 2011;31(1‐3):86‐91. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Polaschegg 1985
-
- Polaschegg HD, Husar D (inventors), Fresenius AG (assignee). Apparatus with regulated mixing of the dialysis solution. US patent 4508622. Patent date 02.04.85. Priority DE21.06.82 3223051 International classification B01D13/00. www.patents.justia.com/patent/4508622 (date accessed 7 November 2018).
Port 1973
-
- Port FK, Johnson WJ, Klass DW. Prevention of dialysis disequilibrium syndrome by use of high sodium concentration in the dialysate. Kidney International 1973;3(5):327‐33. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Poulikakos 2014
Ragon 1985
-
- Ragon A, Reynier JP, Murisasco A, Elsen R, Leblond G. Dialysate sodium control during modeling in hemodialysis. Artificial Organs 1985;9(1):63‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rahman 1999
-
- Rahman M, Dixit A, Donley V, Gupta S, Hanslik T, Lacson E, et al. Factors associated with inadequate blood pressure control in hypertensive hemodialysis patients. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 1999;33(3):498‐506. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Raimann 2009
-
- Raimann J, Liu L, Ulloa D, Kotanko P, Levin NW. Consequences of overhydration and the need for dry weight assessment. Contributions to Nephrology 2009;161:99‐107. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Raimann 2018
Rocco 2011
Rodrigues Telini 2013
-
- Rodrigues Telini LS, Carvalho Beduschi G, Caramori JC, Castro JH, Martin LC, Barretti P. Effect of dietary sodium restriction on body water, blood pressure, and inflammation in hemodialysis patients: a prospective randomized controlled study. International Urology & Nephrology 2014;46(1):91‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sands 2014
-
- Sands JJ, Usvyat LA, Sullivan T, Segal JH, Zabetakis P, Kotanko P, et al. Intradialytic hypotension: frequency, sources of variation and correlation with clinical outcome. Hemodialysis International 2014;18(2):415‐22. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Santos 2008
Santos 2010
-
- Santos SF, Peixoto AJ. Sodium balance in maintenance hemodialysis. Seminars in Dialysis 2010;23(6):549‐55. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Schipper 2011
-
- Schipper K, Abma TA. Coping, family and mastery: top priorities for social science research by patients with chronic kidney disease. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2011;26(10):3189‐95. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Schreiber 2001
-
- Schrieber MJ Jr. Clinical case‐based approach to understanding intradialytic hypotension. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2001;38(4 Suppl 4):S37‐47. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Schünemann 2011a
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JP, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 11: Presenting results and 'Summary of findings' tables. In: Higgins JP, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Schünemann 2011b
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JP, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JP, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Selby 2007a
-
- Selby NM, McIntyre CW. The acute cardiac effects of dialysis. Seminars in Dialysis 2007;20(3):220‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Shepherd 1987
-
- Shepherd R, Farleigh CA, Atkinson C, Pryor JS. Effects of haemodialysis on taste and thirst. Appetite 1987;9(2):79‐88. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sherman 2011
-
- Sherman RA, Kapoian T. Intradialytic hypotension strikes again. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2011;22(8):1396‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Shoji 2004
-
- Shoji T, Tsubakihara Y, Fujii M, Imai E. Hemodialysis‐associated hypotension as an independent risk factor for two‐year mortality in hemodialysis patients. Kidney International 2004;66(3):1212‐20. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Song 2002
-
- Song JH, Lee SW, Suh CK, Kim MJ. Time‐averaged concentration of dialysate sodium relates with sodium load and interdialytic weight gain during sodium‐profiling hemodialysis.[Erratum appears in Am J Kidney Dis 2002 Dec;40(6):1357]. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2002;40(2):291‐301. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Song 2005
-
- Song JH, Park GH, Lee SY, Lee SW, Lee SW, Kim MJ. Effect of sodium balance and the combination of ultrafiltration profile during sodium profiling hemodialysis on the maintenance of the quality of dialysis and sodium and fluid balances. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2005;16(1):237‐46. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Stefansson 2014
Stewart 1972
-
- Stewart WK, Fleming LW, Manuel MA. Muscle cramps during maintenance haemodialysis. Lancet 1972;1(7759):1049‐51. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Stiller 2001
-
- Stiller S, Bonnie‐Schorn E, Grassmann A, Uhlenbusch‐Korwer I, Mann H. A critical review of sodium profiling for hemodialysis. Seminars in Dialysis 2001;14(5):337‐47. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Stragier 2018
-
- Stragier A, Lopot F, Svara F, Polakovic V. Fallacies and pitfalls of dialysis sodium prescription and control. Blood Purification 2018;46(1):27‐33. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Strauss 1958
-
- Strauss MB, Lamdin E, Smith WP, Bleifer DJ. Surfeit and deficit of sodium; a kinetic concept of sodium excretion. A.M.A. Archives of Internal Medicine 1958;102(4):527‐536. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sukhanov 2011
Swart 2011
-
- Swart RM, Hoorn EJ, Betjes MG, Zietse R. Hyponatremia and inflammation: the emerging role of interleukin‐6 in osmoregulation. Nephron. Physiology 2011;118(2):45‐51. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Taratufolo 2001
-
- Taratufolo A, Egidi S, Grassotti A, Pedulla F, Satriani M, Galeotti P, et al. Clinical impact of residual renal function on patients starting dialysis treatment. Edtna‐Erca Journal 2001;27(2):75‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Thein 2007
-
- Thein H, Haloob I, Marshall MR. Associations of a facility level decrease in dialysate sodium concentration with blood pressure and interdialytic weight gain. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2007;22(9):2630‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Tisler 2003
-
- Tisler A, Akocsi K, Borbas B, Fazakas L, Ferenczi S, Gorogh S, et al. The effect of frequent or occasional dialysis‐associated hypotension on survival of patients on maintenance haemodialysis. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2003;18(12):2601‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Titze 2008
-
- Titze J. Water‐free Na+ retention: interaction with hypertension and tissue hydration. Blood Purification 2008;26(1):95‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Titze 2009
-
- Titze J. Water‐free sodium accumulation. Seminars in Dialysis 2009;23(3):253‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Van Stone 1982
-
- Stone JC, Bauer J, Carey J. The effect of dialysate sodium concentration on body fluid compartment volume, plasma renin activity and plasma aldosterone concentration in chronic hemodialysis patients. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 1982;2(1):58‐64. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Waikar 2009
Waikar 2011
Weiner 2014
-
- Weiner DE, Brunelli SM, Hunt A, Schiller B, Glassock R, Maddux FW, et al. Improving clinical outcomes among hemodialysis patients: a proposal for a "volume first" approach from the chief medical officers of US dialysis providers. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2014;64(5):685‐95. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wells 2004
-
- Wells M, Foroozan R. Transient visual loss may anticipate occipital infarction from hemodialysis. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2004;43(5):e29‐33. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wilkinson 1977
-
- Wilkinson R, Barber SG, Robson V. Cramps, thirst and hypertension in hemodialysis patients ‐‐ the influence of dialyzate sodium concentration. Clinical Nephrology 1977;7(3):101‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wong 2017
-
- Wong MM, McCullough KP, Bieber BA, Bommer J, Hecking M, Levin NW, et al. Interdialytic weight gain: trends, predictors, and associated outcomes in the International Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS). American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2017;69(3):367‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Zazgornik 1997
-
- Zazgornik J, Biesenbach G, Forstenlehner M, Stummvoll K. Profile of antihypertensive drugs in hypertensive patients on renal replacement therapy (RRT). Clinical Nephrology 1997;48(6):337‐40. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Zhang 2014
Zhou 2014
-
- Zhou YL, Liu J, Ma L, Sun F, Shen Y, Huang J, et al. Impact of dry weight determined by calf bioimpedance ratio on carotid stiffness and left ventricular hypertrophy in hemodialysis patients. Artificial Organs 2014;38(4):327‐34. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical


