First observation of direct methane emission to the atmosphere from the subglacial domain of the Greenland Ice Sheet
- PMID: 30413774
- PMCID: PMC6226494
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-35054-7
First observation of direct methane emission to the atmosphere from the subglacial domain of the Greenland Ice Sheet
Abstract
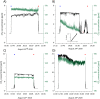
During a 2016 field expedition to the West Greenland Ice Sheet, a striking observation of significantly elevated CH4 concentrations of up to 15 times the background atmospheric concentration were measured directly in the air expelled with meltwater at a subglacial discharge point from the Greenland Ice Sheet. The range of hourly subglacial CH4 flux rate through the discharge point was estimated to be 3.1 to 134 g CH4 hr-1. These measurements are the first observations of direct emissions of CH4 from the subglacial environment under the Greenlandic Ice Sheet to the atmosphere and indicate a novel emission pathway of CH4 that is currently a non-quantified component of the Arctic CH4 budget.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Greenland melt drives continuous export of methane from the ice-sheet bed.Nature. 2019 Jan;565(7737):73-77. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0800-0. Epub 2019 Jan 2. Nature. 2019. PMID: 30602750
-
Characteristics of methane and carbon dioxide in ice caves at a high-mountain glacier of China.Sci Total Environ. 2024 Oct 10;946:174074. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.174074. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Sci Total Environ. 2024. PMID: 38909794
-
Recharge of a subglacial lake by surface meltwater in northeast Greenland.Nature. 2015 Feb 12;518(7538):223-7. doi: 10.1038/nature14116. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Nature. 2015. PMID: 25607355
-
Advances in modelling subglacial lakes and their interaction with the Antarctic ice sheet.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2016 Jan 28;374(2059):20140296. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2014.0296. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2016. PMID: 26667909 Review.
-
Technologies for retrieving sediment cores in Antarctic subglacial settings.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2016 Jan 28;374(2059):20150056. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2015.0056. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2016. PMID: 26667918 Review.
Cited by
-
CH4 emissions from runoff water of Alaskan mountain glaciers.Sci Rep. 2024 May 9;14(1):10558. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56608-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38724590 Free PMC article.
-
Large mercury release from the Greenland Ice Sheet invalidated.Sci Adv. 2024 Jan 26;10(4):eadi7760. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adi7760. Epub 2024 Jan 26. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38277451 Free PMC article.
-
Catchment characteristics and seasonality control the composition of microbial assemblages exported from three outlet glaciers of the Greenland Ice Sheet.Front Microbiol. 2022 Nov 29;13:1035197. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1035197. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36523833 Free PMC article.
-
Ice sheets matter for the global carbon cycle.Nat Commun. 2019 Aug 15;10(1):3567. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11394-4. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31417076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methane beneath Greenland's ice sheet is being released.Nature. 2019 Jan;565(7737):31-32. doi: 10.1038/d41586-018-07762-7. Nature. 2019. PMID: 30602742 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wadham JL, Tranter M, Tulaczyk S, Sharp M. Subglacial methanogenesis: A potential climatic amplifier? Global Biogeochem. Cycles. 2008;22:n/a–n/a. doi: 10.1029/2007GB002951. - DOI
-
- Walter Anthony KM, Anthony P, Grosse G, Chanton J. Geologic methane seeps along boundaries of Arctic permafrost thaw and melting glaciers. Nat. Geosci. 2012;5:419–426. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1480. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources


