Interleukin-24 (IL24) Is Suppressed by PAX3-FOXO1 and Is a Novel Therapy for Rhabdomyosarcoma
- PMID: 30190424
- PMCID: PMC6279487
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-0118
Interleukin-24 (IL24) Is Suppressed by PAX3-FOXO1 and Is a Novel Therapy for Rhabdomyosarcoma
Abstract
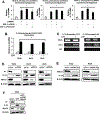
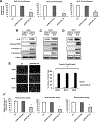
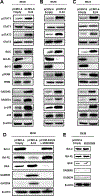
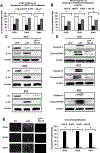
Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma (ARMS) patients have a poor prognosis, and this is primarily due to overexpression of the oncogenic fusion protein PAX3-FOXO1. Results of RNA-sequencing studies show that PAX3-FOXO1 represses expression of interleukin-24 (IL24), and these two genes are inversely expressed in patient tumors. PAX3-FOXO1 also regulates histone deacetylase 5 (HDAC5) in ARMS cells, and results of RNA interference studies confirmed that PAX3-FOXO1-mediated repression of IL24 is HDAC5-dependent. Knockdown of PAX3-FOXO1 decreases ARMS cell proliferation, survival, and migration, and we also observed similar responses in cells after overexpression of IL24, consistent with results reported for this tumor suppressor-like cytokine in other solid tumors. We also observed in double knockdown studies that the inhibition of ARMS cell proliferation, survival, and migration after knockdown of PAX3-FOXO1 was significantly (>75%) reversed by knockdown of IL24. Adenoviral-expressed IL24 was directly injected into ARMS tumors in athymic nude mice, and this resulted in decreased tumor growth and weight. Because adenoviral IL24 has already successfully undergone phase I in clinical trials, this represents an alternative approach (alone and/or combination) for treating ARMS patients who currently undergo cytotoxic drug therapies.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Reduced B7-H3 expression by PAX3-FOXO1 knockdown inhibits cellular motility and promotes myogenic differentiation in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 22;11(1):18802. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-98322-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34552155 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of MST/Hippo Signaling in a Genetically Engineered Mouse Model of Fusion-Positive Rhabdomyosarcoma Accelerates Tumorigenesis.Cancer Res. 2018 Oct 1;78(19):5513-5520. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-3912. Epub 2018 Aug 9. Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30093562 Free PMC article.
-
The HDAC3-SMARCA4-miR-27a axis promotes expression of the PAX3:FOXO1 fusion oncogene in rhabdomyosarcoma.Sci Signal. 2018 Nov 20;11(557):eaau7632. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aau7632. Sci Signal. 2018. PMID: 30459282 Free PMC article.
-
A call to ARMS: targeting the PAX3-FOXO1 gene in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2013 May;17(5):607-23. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2013.772136. Epub 2013 Feb 25. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2013. PMID: 23432728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic value of PAX3/7-FOXO1 fusion status in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma: Systematic review and meta-analysis.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2015 Oct;96(1):46-53. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2015.04.012. Epub 2015 May 14. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2015. PMID: 26008753 Review.
Cited by
-
The epigenetic regulatory effect of histone acetylation and deacetylation on skeletal muscle metabolism-a review.Front Physiol. 2023 Dec 8;14:1267456. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1267456. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 38148899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flavonoids kaempferol and quercetin are nuclear receptor 4A1 (NR4A1, Nur77) ligands and inhibit rhabdomyosarcoma cell and tumor growth.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Dec 14;40(1):392. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02199-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34906197 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear receptor 4A1 (NR4A1) antagonists target paraspeckle component 1 (PSPC1) in cancer cells.Mol Carcinog. 2022 Jan;61(1):73-84. doi: 10.1002/mc.23362. Epub 2021 Oct 26. Mol Carcinog. 2022. PMID: 34699643 Free PMC article.
-
Retargeting of NK-92 Cells against High-Risk Rhabdomyosarcomas by Means of an ERBB2 (HER2/Neu)-Specific Chimeric Antigen Receptor.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 22;13(6):1443. doi: 10.3390/cancers13061443. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33809981 Free PMC article.
-
SOCS2 is a potential prognostic marker that suppresses the viability of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Oncol Lett. 2021 May;21(5):399. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12660. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33777222 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Paulino AC, Okcu MF. Rhabdomyosarcoma. Current Problems in Cancer 2008; 32:7–34. - PubMed
-
- Parham DM, Ellison DA. Rhabdomyosarcomas in adults and children: an update. Archives of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine 2006; 130:1454–65. - PubMed
-
- Scrable HJ, Witte DP, Lampkin BC, Cavenee WK. Chromosomal localization of the human rhabdomyosarcoma locus by mitotic recombination mapping. Nature 1987; 329:645–7. - PubMed
-
- Breneman JC, Lyden E, Pappo AS, Link MP, Anderson JR, Parham DM, et al. Prognostic factors and clinical outcomes in children and adolescents with metastatic rhabdomyosarcoma--a report from the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study IV. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2003; 21:78–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous


