Twice-daily insulin degludec/insulin aspart effectively improved morning and evening glucose levels and quality of life in patients previously treated with premixed insulin: an observational study
- PMID: 30127860
- PMCID: PMC6097398
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-018-0366-x
Twice-daily insulin degludec/insulin aspart effectively improved morning and evening glucose levels and quality of life in patients previously treated with premixed insulin: an observational study
Abstract
Background: Previous studies comparing insulin degludec/insulin aspart (IDegAsp) with premixed insulin twice daily among insulin users with type 2 diabetes have not thoroughly investigated differences in the glucose variability and psychological evaluations related to insulin regimen changes. We investigated changes in the daily and day-to-day glucose variability and quality of life (QOL) related to insulin use in patients with type 2 diabetes during a switch from premixed insulin preparations comprising either human insulin (BHI30) or insulin aspart (BIAsp30) to IDegAsp twice daily.
Methods: In this prospective observational study, 22 subjects (BHI30:BIAsp30 = 12:10) self-measured their blood glucose levels every morning, and before and after all meals each week. Premixed insulin was administered for the first 2 months, followed by IDegAsp for the next 2 months. Efficacy measures were evaluated during the last month or last day of both phases.
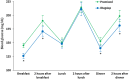
Results: The mean blood glucose levels (175.5 vs. 163.0 mg/dL; P = 0.004) and the M-values (53.9 vs. 27.6; P = 0.049) were significantly lower in the IDegAsp phase. However, no differences in the standard deviations of morning fasting glucose levels were observed between phases (premixed vs. IDegAsp, 20.0 vs. 19.3 mg/dL; P = 0.343). Compared to the premixed phase, the before-breakfast (145.3 vs. 126.0 mg/dL; P < 0.001), after-breakfast (190.3 vs. 170.7 mg/dL; P = 0.001), before-dinner (153.0 vs. 140.1 mg/dL; P = 0.007), and after-dinner glucose levels (198.7 vs. 181.4 mg/dL; P = 0.018) were lower in the IDegAsp phase. However, the before-lunch (150.8 vs. 148.2 mg/dL; P = 0.329) and after-lunch glucose levels (214.7 vs. 211.4 mg/dL; P = 0.308) did not significantly differ between phases. Regarding QOL, the total and therapy-related feeling Insulin Therapy Related-QOL (ITR-QOL) questionnaire scores favored IDegAsp, as did the ITR-QOL at Night questionnaire subscale score of glycemic control before breakfast.
Conclusions: Although the day-to-day variability of morning fasting glucose levels did not change, switching to IDegAsp improved daily glucose level variability, the morning and evening glucose control and QOL among patients treated with premixed insulin.Trial registration University Hospital Medical Information Network Clinical Trials Registry, UMIN000021939. Prospectively registered 18 April 2016.
Keywords: Glucose variability; Insulin degludec/insulin aspart; Quality of life; Type 2 diabetes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficacy and Safety of Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart Compared with a Conventional Premixed Insulin or Basal Insulin: A Meta-Analysis.Metabolites. 2021 Sep 18;11(9):639. doi: 10.3390/metabo11090639. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 34564455 Free PMC article.
-
Glycaemic outcomes in hospital with IDegAsp versus BIAsp30 premixed insulins.Intern Med J. 2024 Aug;54(8):1329-1336. doi: 10.1111/imj.16391. Epub 2024 Apr 5. Intern Med J. 2024. PMID: 38578058
-
Switching from Premixed Insulin to Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Implications of a Real-World Study on Insulin Degludec Dosing.Diabetes Ther. 2024 Dec;15(12):2515-2523. doi: 10.1007/s13300-024-01663-x. Epub 2024 Oct 26. Diabetes Ther. 2024. PMID: 39460908 Free PMC article.
-
The Clinical Role of Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart in Type 2 Diabetes: An Empirical Perspective from Experience in Australia.J Clin Med. 2020 Apr 11;9(4):1091. doi: 10.3390/jcm9041091. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32290465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart in the Management of Diabetes Mellitus: Expert Panel Recommendations on Appropriate Practice Patterns.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Mar 12;12:616514. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.616514. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33776914 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic Characteristics of Frail Older People with Diabetes Mellitus-A Systematic Search for Phenotypes.Metabolites. 2023 May 29;13(6):705. doi: 10.3390/metabo13060705. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37367862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intensification of Insulin Treatment With Insulin Degludec/Aspart in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A 2-Year Real-World Experience.Front Clin Diabetes Healthc. 2022 Jul 26;3:783277. doi: 10.3389/fcdhc.2022.783277. eCollection 2022. Front Clin Diabetes Healthc. 2022. PMID: 36992737 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Impact of Frailty Changes Diabetes Trajectory.Metabolites. 2023 Feb 16;13(2):295. doi: 10.3390/metabo13020295. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 36837914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart Compared with a Conventional Premixed Insulin or Basal Insulin: A Meta-Analysis.Metabolites. 2021 Sep 18;11(9):639. doi: 10.3390/metabo11090639. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 34564455 Free PMC article.
-
A Real-World, Prospective, Non-interventional Study of Adults with T2D Switching to IDegAsp from Glargine U100 or U300 in Japan.Diabetes Ther. 2021 Sep;12(9):2405-2421. doi: 10.1007/s13300-021-01117-8. Epub 2021 Jul 25. Diabetes Ther. 2021. PMID: 34304385 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient-centered approach: update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:140–149. doi: 10.2337/dc14-2441. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Freemantle N, Balkau B, Danchin N, Wang E, Marre M, Vespasiani G, et al. Factors influencing initial choice of insulin therapy in a large international non-interventional study of people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14:901–909. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2012.01613.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous


